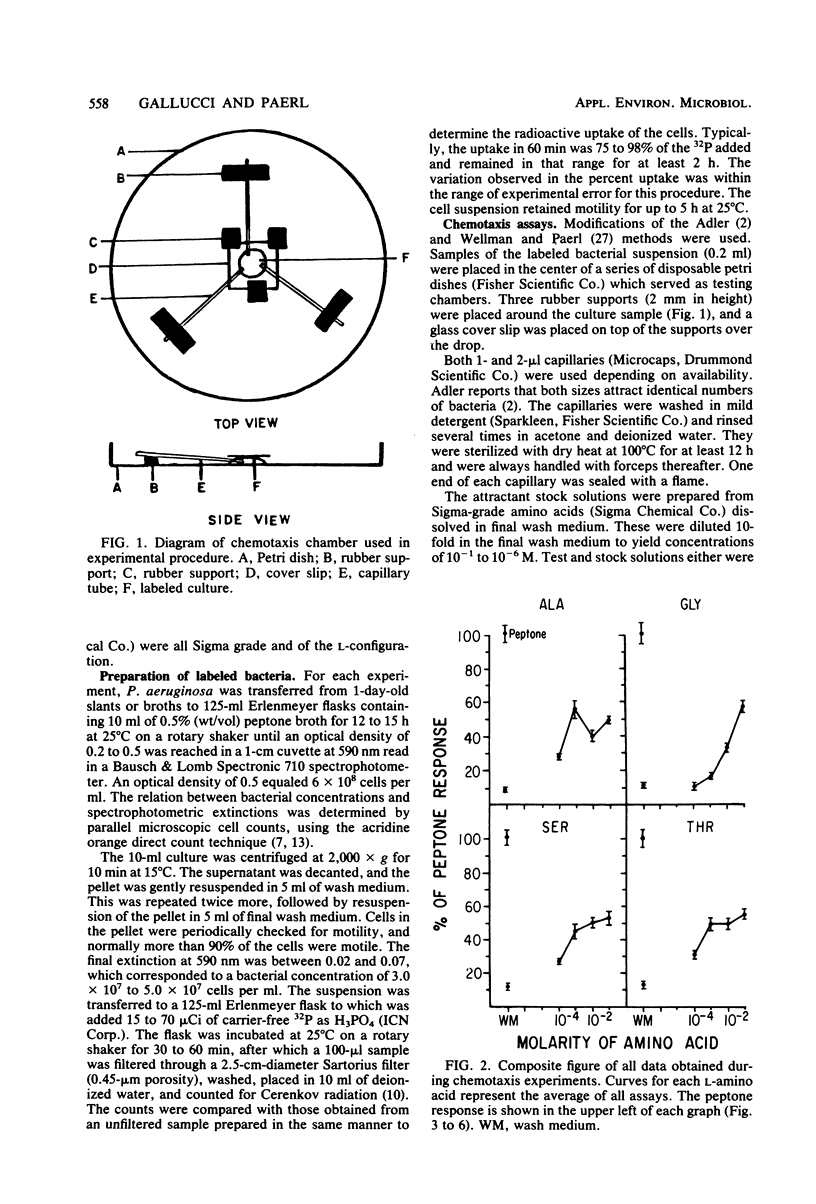
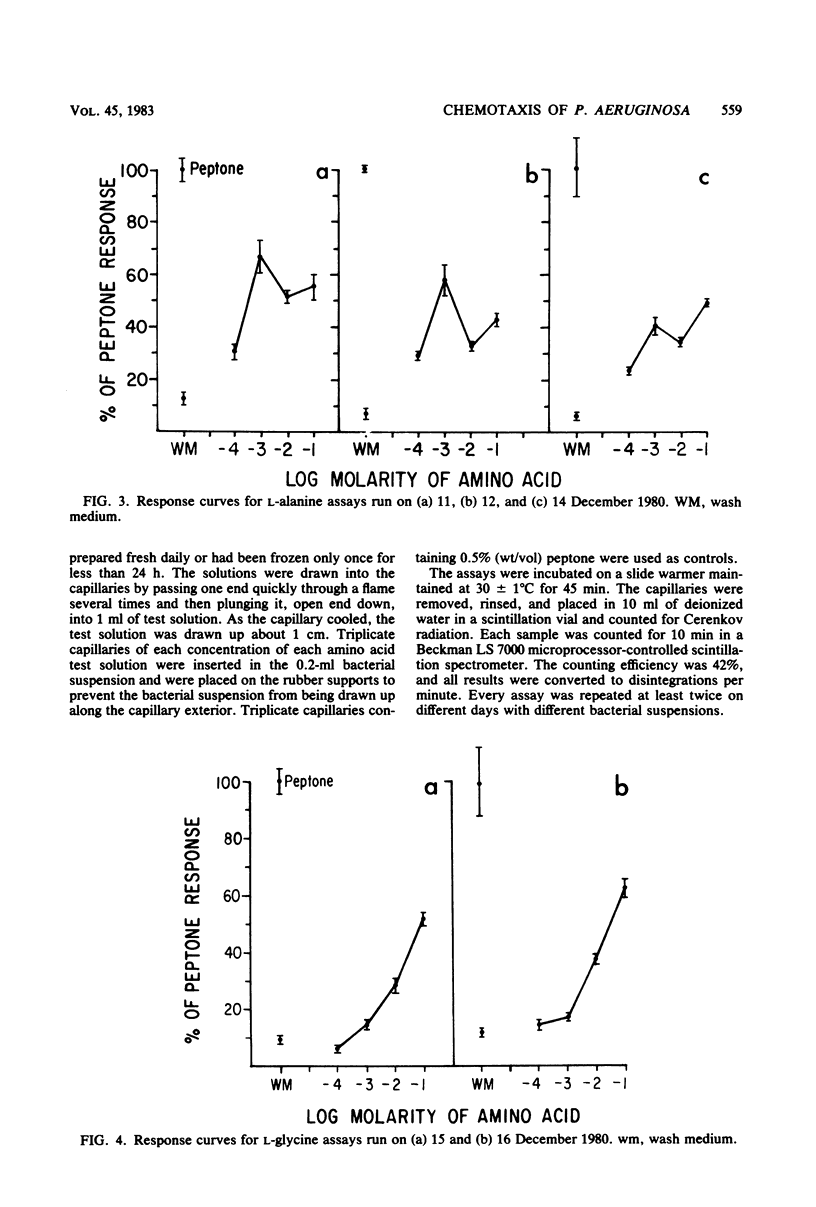
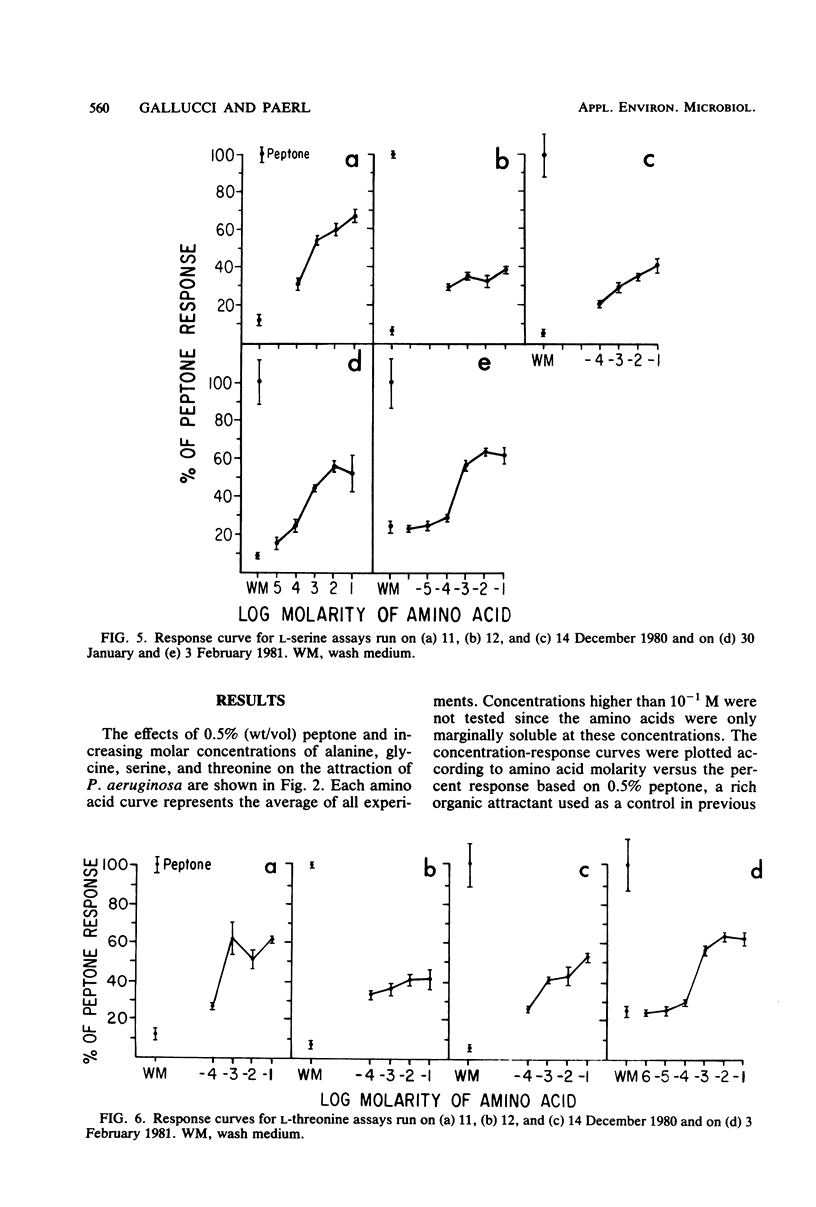
Abstract
Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Schroeter) Migula, a numerically significant bacterium found during N2-fixing blooms of the blue-green algae (cyanobacteria) Anabaena sp. in the Chowan River, North Carolina, was chemotactically attracted to amino acids when tested in a radioassay. The bacterium was labeled with 32Pi, and the disintegrations per minute determined by liquid scintillation counting were proportional to the number of cells accumulating in microcapillaries containing amino acids. Positive chemotaxis was observed toward all of the amino acids tested, although the degrees of response varied. Since many nitrogen-fixing blue-green algae secrete nitrogenous compounds, this attraction may be instrumental in establishing a symbiotic relationship between this bacterium and blue-green algae in freshwater.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. A method for measuring chemotaxis and use of the method to determine optimum conditions for chemotaxis by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):77–91. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J. Chemoreceptors in bacteria. Science. 1969 Dec 26;166(3913):1588–1597. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3913.1588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:341–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell D. E., Caldwell S. J. A Zoogloea sp. associated with blooms of Anabaena flos-aquae. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Aug;24(8):922–931. doi: 10.1139/m78-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOGG G. E. The production of extracellular nitrogenous substances by a blue-green alga. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1952 Apr 24;139(896):372–397. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1952.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbie J. E., Daley R. J., Jasper S. Use of nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1225–1228. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1225-1228.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEWART W. D. LIBERATION OF EXTRACELLULAR NITROGEN BY 2 NITROGEN-FIXING BLUE-GREEN ALGAE. Nature. 1963 Dec 7;200:1020–1021. doi: 10.1038/2001020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellman A. M., Paerl H. W. Rapid chemotaxis assay using radioactively labeled bacterial cells. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):216–221. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.216-221.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton B. A. Extracellular products of blue-green algae. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jul;40(1):1–11. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


