Abstract
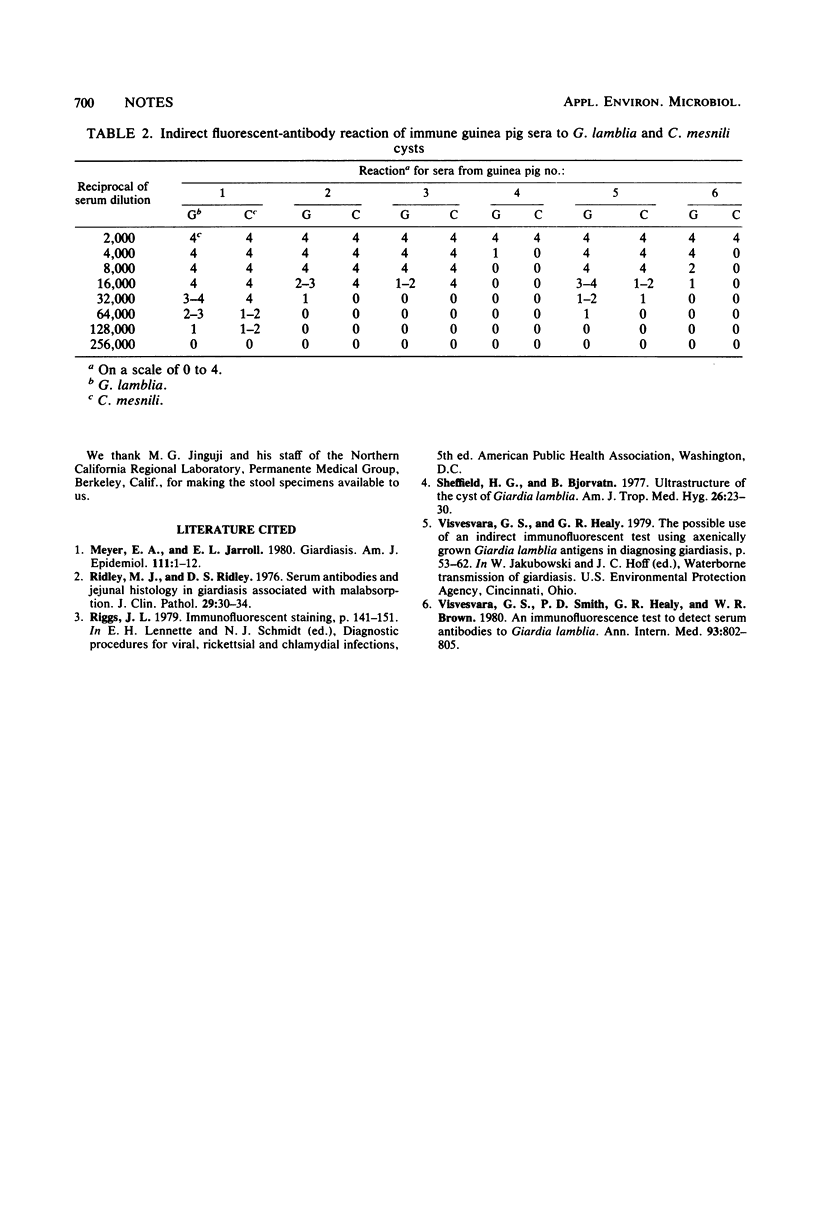
High-titer immune sera to cysts of Giardia lamblia, produced in guinea pigs, were labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate. The resulting conjugates were used to detect G. lamblia in stool specimens by fluorescence microscopy. The sera also reacted with cysts of Chilomastix mesnili, but the two organisms could be differentiated by their size.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Meyer E. A., Jarroll E. L. Giardiasis. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Jan;111(1):1–12. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley M. J., Ridley D. S. Serum antibodies and jejunal histology in giardiasis associated with malabsorption. J Clin Pathol. 1976 Jan;29(1):30–34. doi: 10.1136/jcp.29.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield H. G., Bjorvat B. Ultrastructure of the cyst of Giardia lamblia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Jan;26(1):23–30. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Smith P. D., Healy G. R., Brown W. R. An immunofluorescence test to detect serum antibodies to Giardia lamblia. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Dec;93(6):802–805. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-93-6-802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




