Abstract
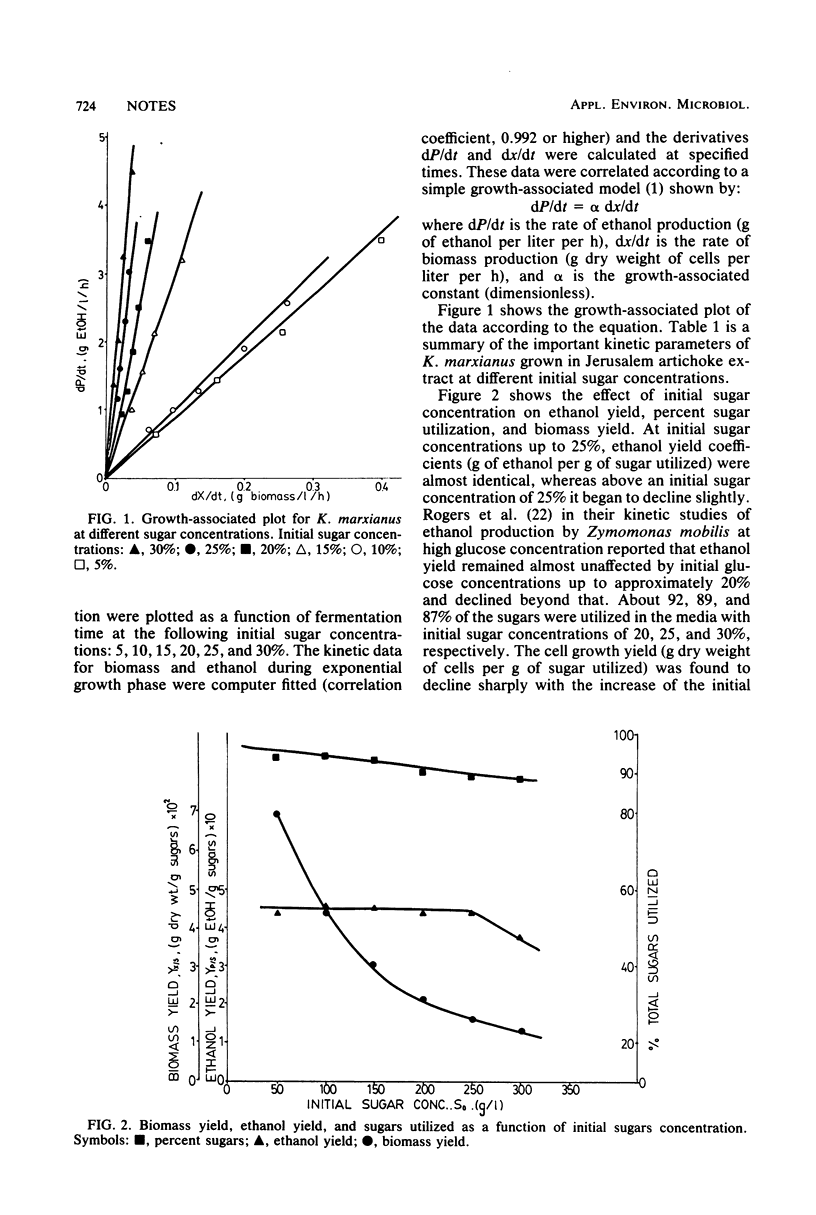
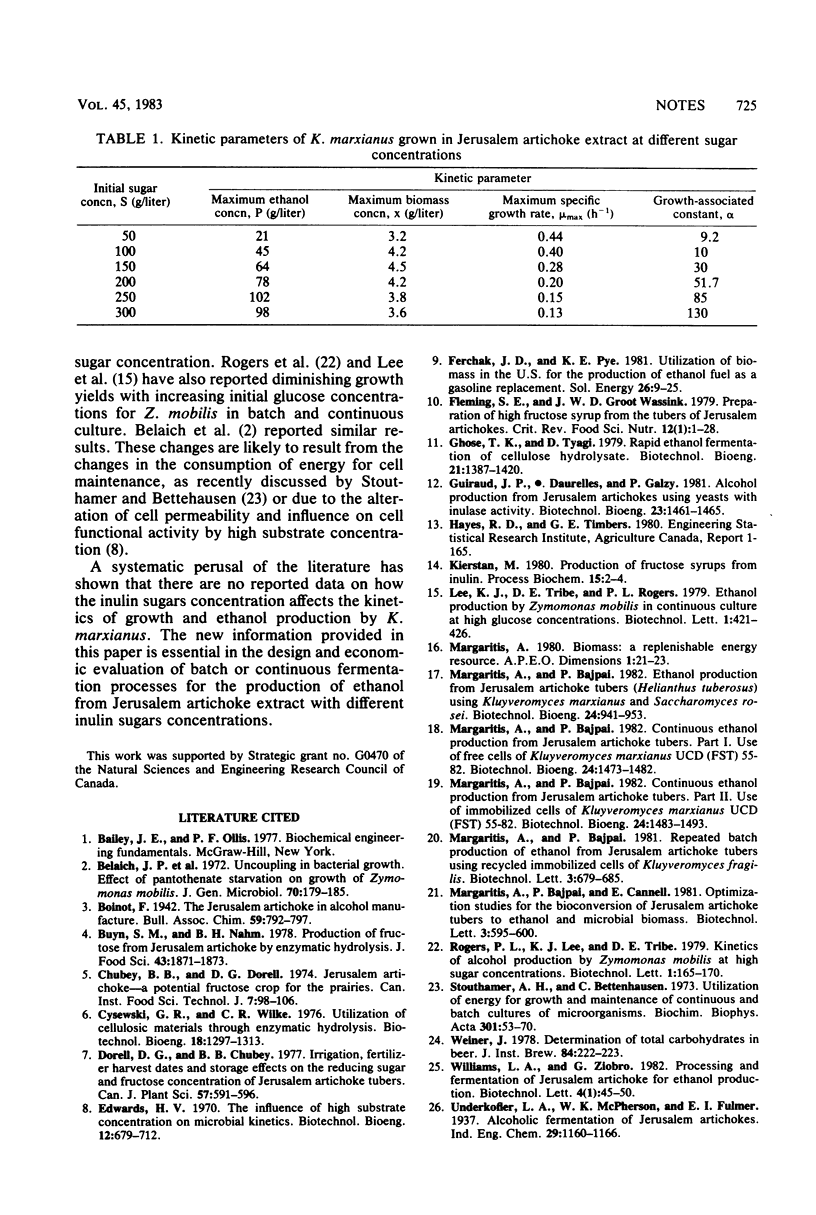
The effect of inulin sugars concentration on the growth and ethanol production by Kluyveromyces marxianus UCD (FST) 55-82 was studied. A maximum ethanol concentration of 102 g/liter was obtained from 250 g of sugars per liter initial concentration. The maximum specific growth rate varied from 0.44 h−1 at 50 g of sugar per liter to 0.13 h−1 at 300 g of sugar per liter, whereas the ethanol yield remained almost constant at 0.45 g of ethanol per g of sugars utilized.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cysewski G. R., Wilke C. R. Utilization of cellulosic materials through enzyamtic hydrolysis. I. Fermentation of hydrolysate to ethanol and single-cell protein. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1976 Sep;18(9):1297–1313. doi: 10.1002/bit.260180908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards V. H. The influence of high substrate concentrations on microbial kinetics. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1970 Sep;12(5):679–712. doi: 10.1002/bit.260120504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming S. E., GrootWassink J. W. Preparation of high-fructose syrup from the tubers of the Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L. CRC Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 1979 Nov;12(1):1–28. doi: 10.1080/10408397909527271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouthamer A. H., Bettenhaussen C. Utilization of energy for growth and maintenance in continuous and batch cultures of microorganisms. A reevaluation of the method for the determination of ATP production by measuring molar growth yields. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 12;301(1):53–70. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(73)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


