Abstract
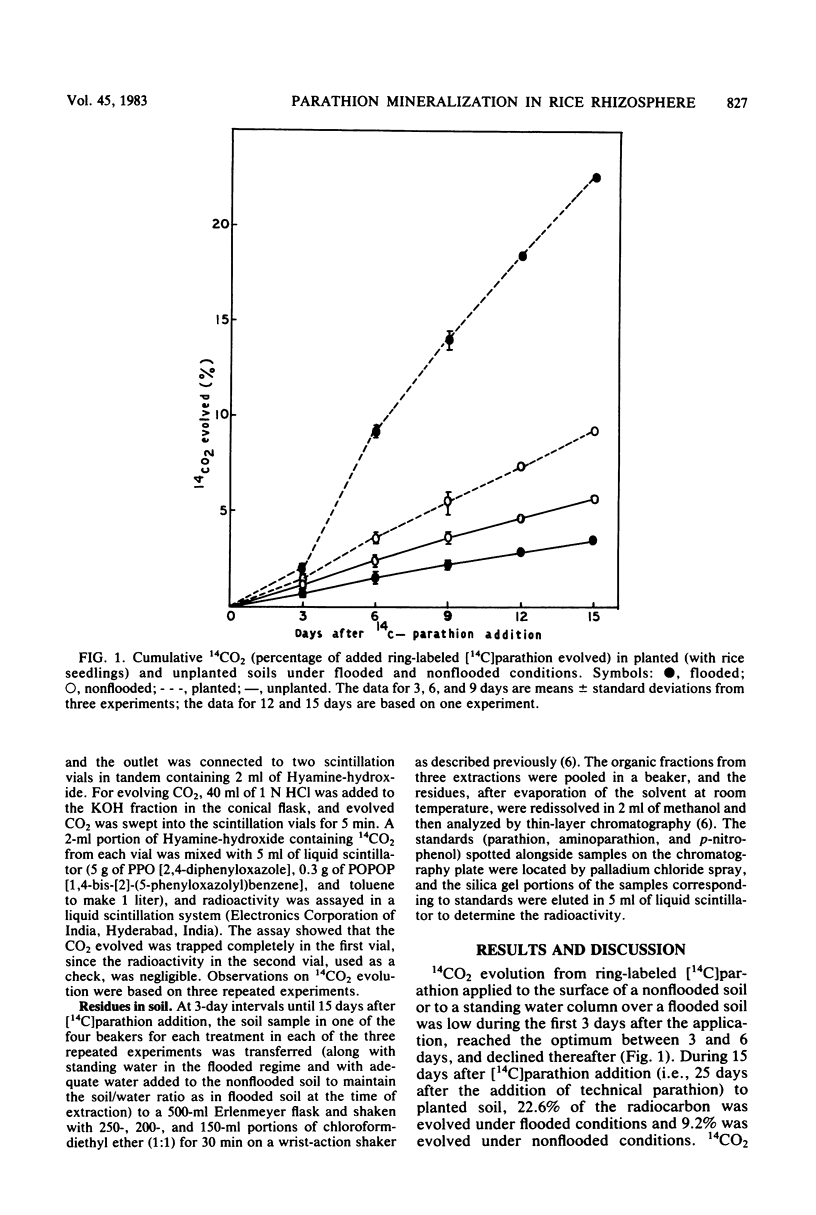
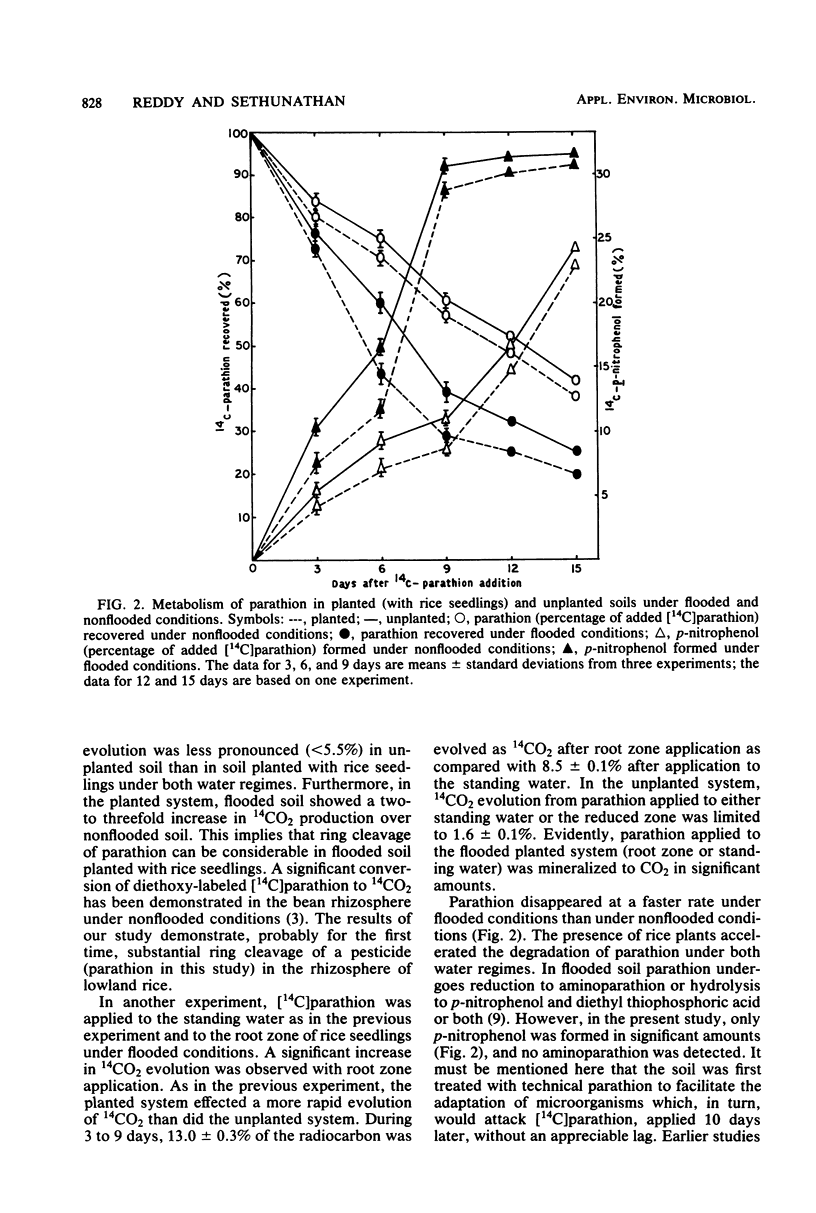
We studied 14CO2 evolution from ring-labeled [2,6-14C]parathion (O,O-diethyl-O-p-nitrophenyl phosphorothioate) in the rhizosphere of rice seedlings. The soil samples (nonflooded [60% water-holding capacity] and flooded) were treated first with technical parathion (20 μg/g) and then after 10 days with ring-labeled [14C]parathion. In unplanted soil, less than 5.5% of the 14C in the parathion was evolved as 14CO2 in 15 days under both flooded and nonflooded conditions. In soil planted with rice, 9.2% of the radiocarbon was evolved as 14CO2 under nonflooded conditions, and 22.6% was evolved under flooded conditions. These results suggest that soil planted with rice permits significant ring cleavage, especially under flooded conditions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gamble T. N., Betlach M. R., Tiedje J. M. Numerically dominant denitrifying bacteria from world soils. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):926–939. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.926-939.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. L. Analyse de différents groupes composant la microflore dénitrifiante des sols de rizière du Sénégal. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 May-Jun;128A(4):433–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu T. S., Bartha R. Accelerated mineralization of two organophosphate insecticides in the rhizosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.36-41.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna C., Sethunathan N. Stimulation of autotrophic ammonium oxidation in rice rhizosphere soil by the insecticide carbofuran. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):1–4. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.1-4.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethunathan N. Degradation of parathion in flooded acid soils. J Agric Food Chem. 1973 Jul-Aug;21(4):602–604. doi: 10.1021/jf60188a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethunathan N., Siddaramappa R., Rajaram K. P., Barik S., Wahid P. A. Parathion: residues in soil and water. Residue Rev. 1977;68:91–122. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4612-6355-5_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. J., Evans W. C. The metabolism of benzoate by Moraxella species through anaerobic nitrate respiration. Evidence for a reductive pathway. Biochem J. 1975 Apr;148(1):1–10. doi: 10.1042/bj1480001a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


