Abstract
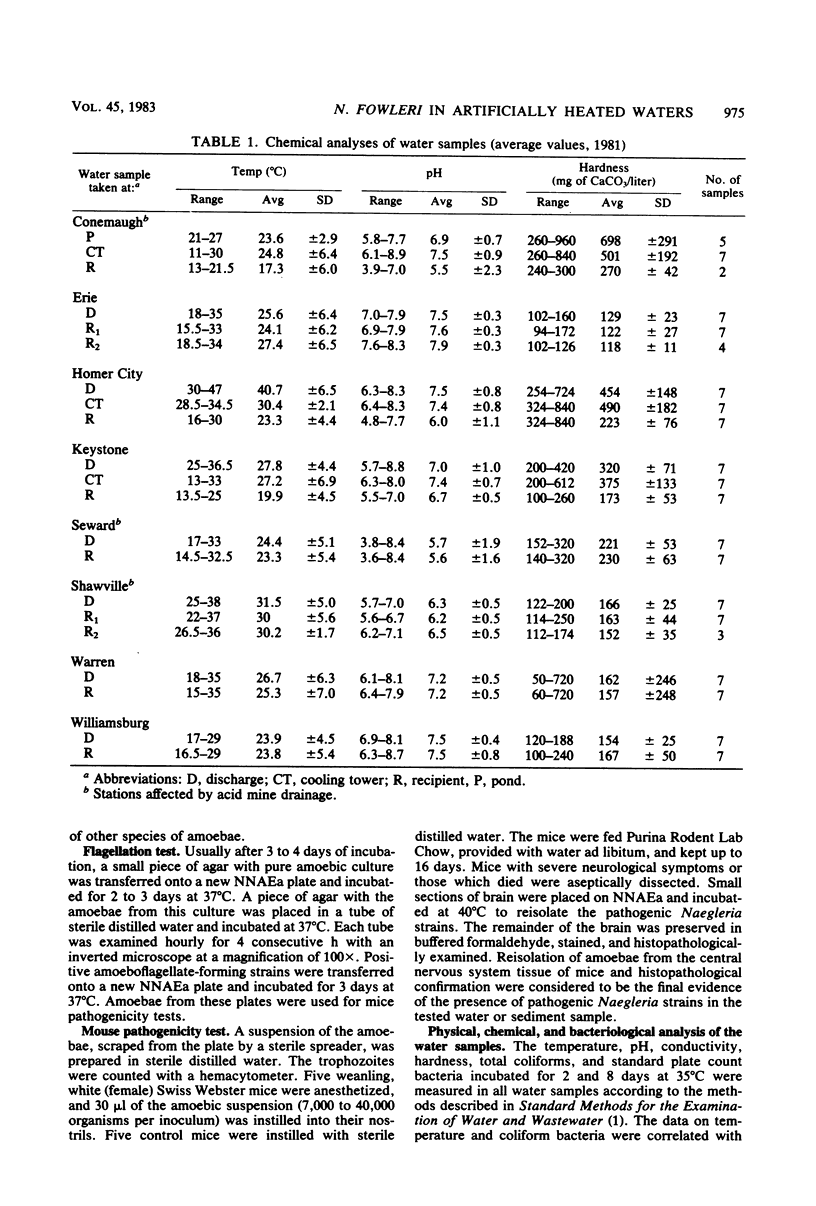
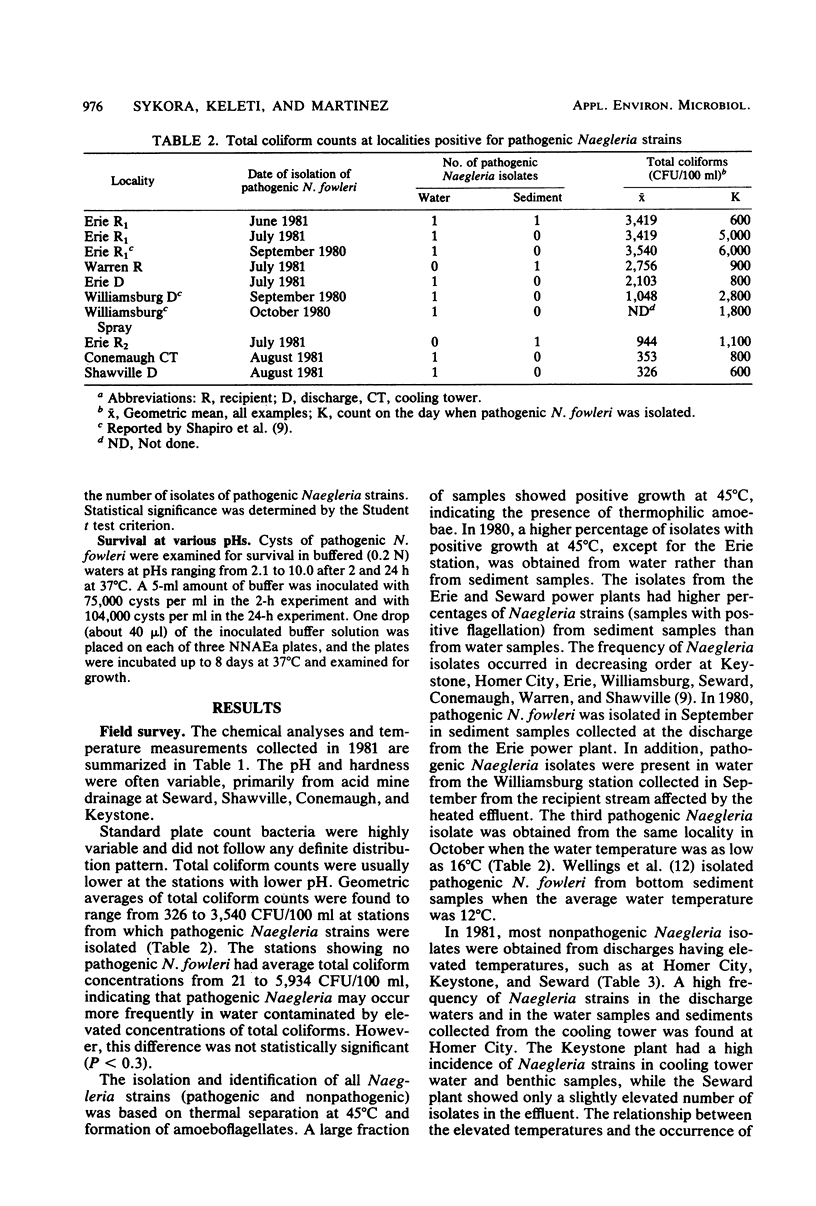
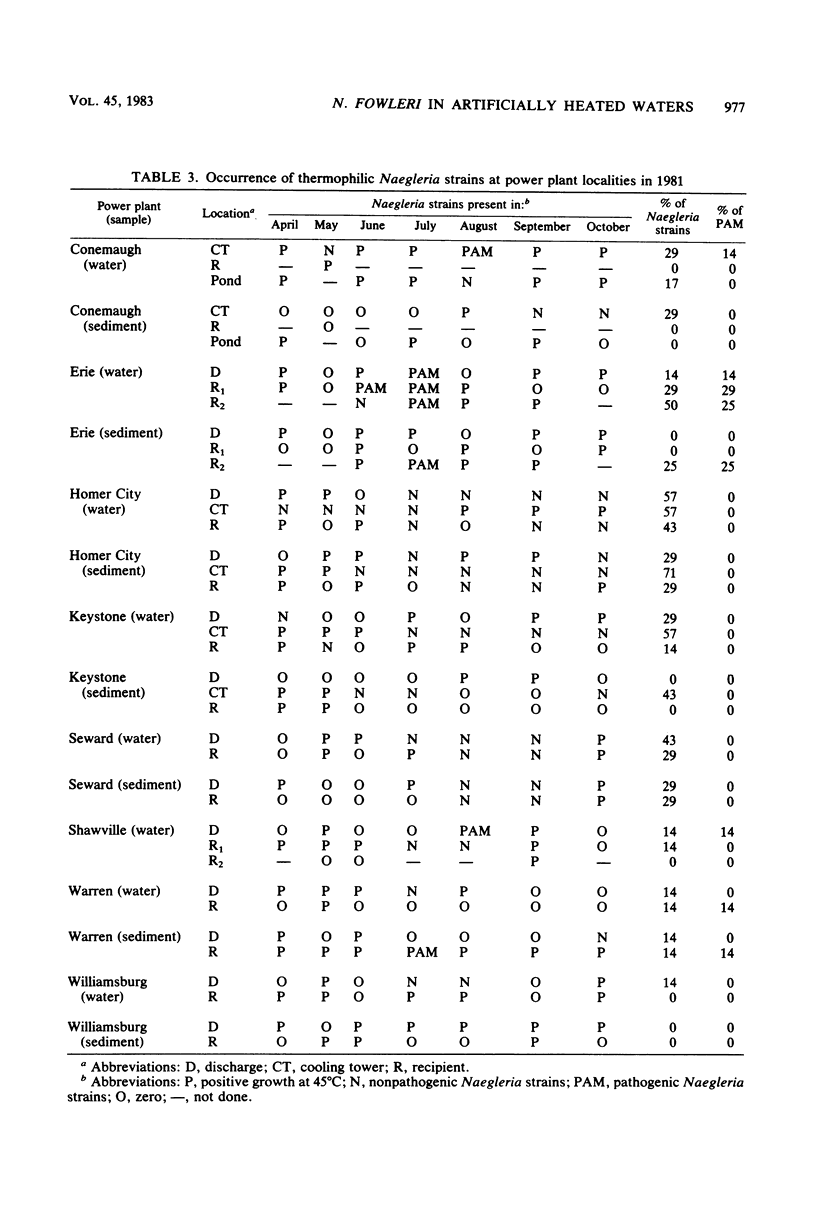
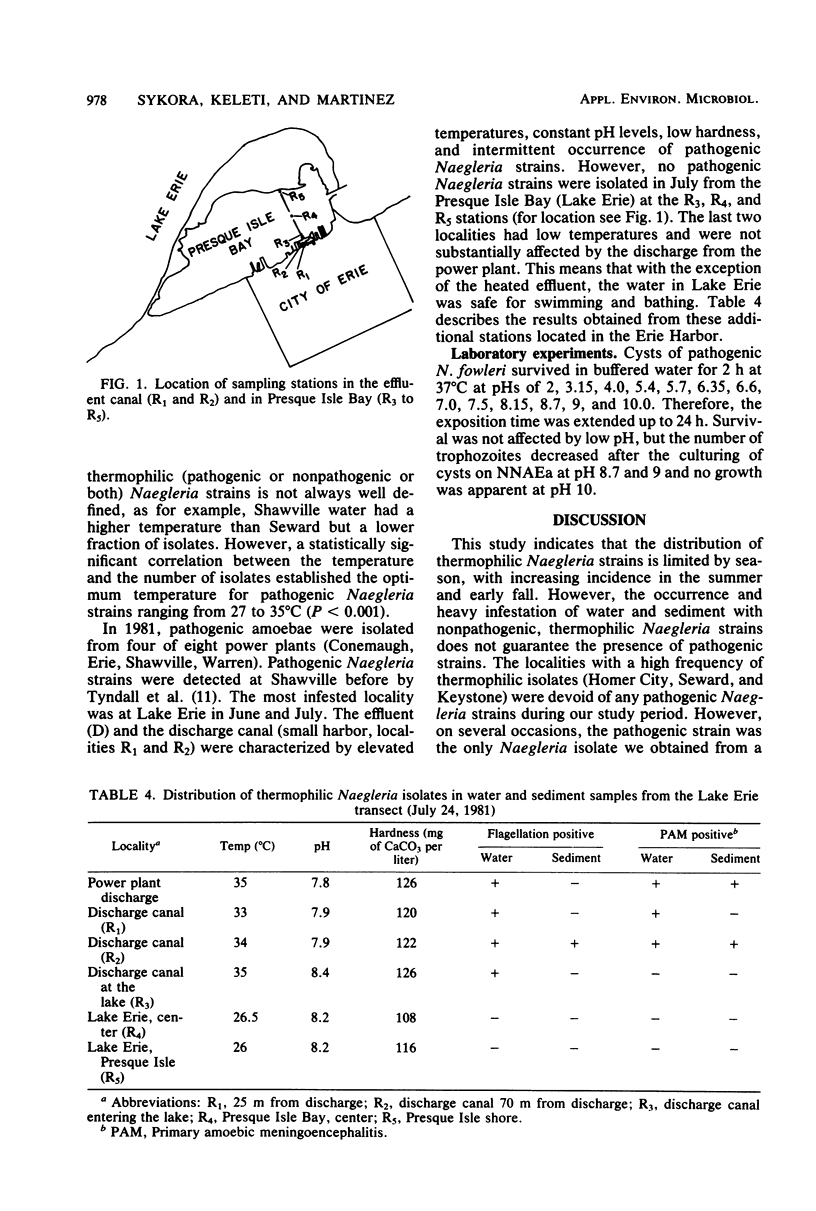
The occurrence of pathogenic Naegleria fowleri in thermal discharges, recipient waters, and cooling towers of eight power plants located in western Pennsylvania was investigated for 2 years in conjunction with several environmental measurements. Pathogenic N. fowleri was detected in one cooling tower and in the discharge, receiving waters, or both of five of eight localities. The occurrence of this organism was related to elevated temperatures, but no significant correlation was found for other biological and chemical parameters. Laboratory experiments on the effect of pH on pathogenic N. fowleri documented 100% survival at a range from 2.1 to 8.15. Higher pH reduced or killed the amoebae. No case of human primary amoebic meningoencephalitis occurred during the study.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Jonckheere J. F. Isoenzyme patterns of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Naegleria spp. using agarose isoelectric focusing. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Mar-Apr;133(2):319–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J., Van Dijck P., Van de Voorde H. The effect of thermal pollution on the distribution of Naegleria fowleri. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Aug;75(1):7–13. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400047021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler M., Carter R. F. Acute pyogenic meningitis probably due to Acanthamoeba sp.: a preliminary report. Br Med J. 1965 Sep 25;2(5464):740–742. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5464.734-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. R., Tyndall R. L., Coutant C. C., Willaert E. Isolation of the etiological agent of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis from artifically heated waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Dec;34(6):701–705. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.6.701-705.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


