Abstract
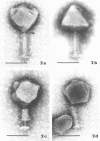
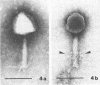
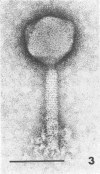
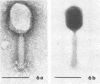
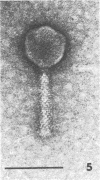
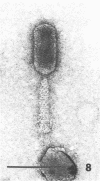
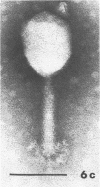
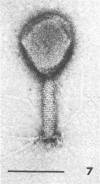
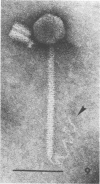
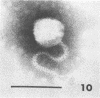
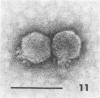
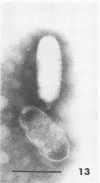
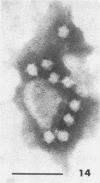
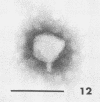
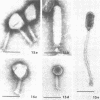
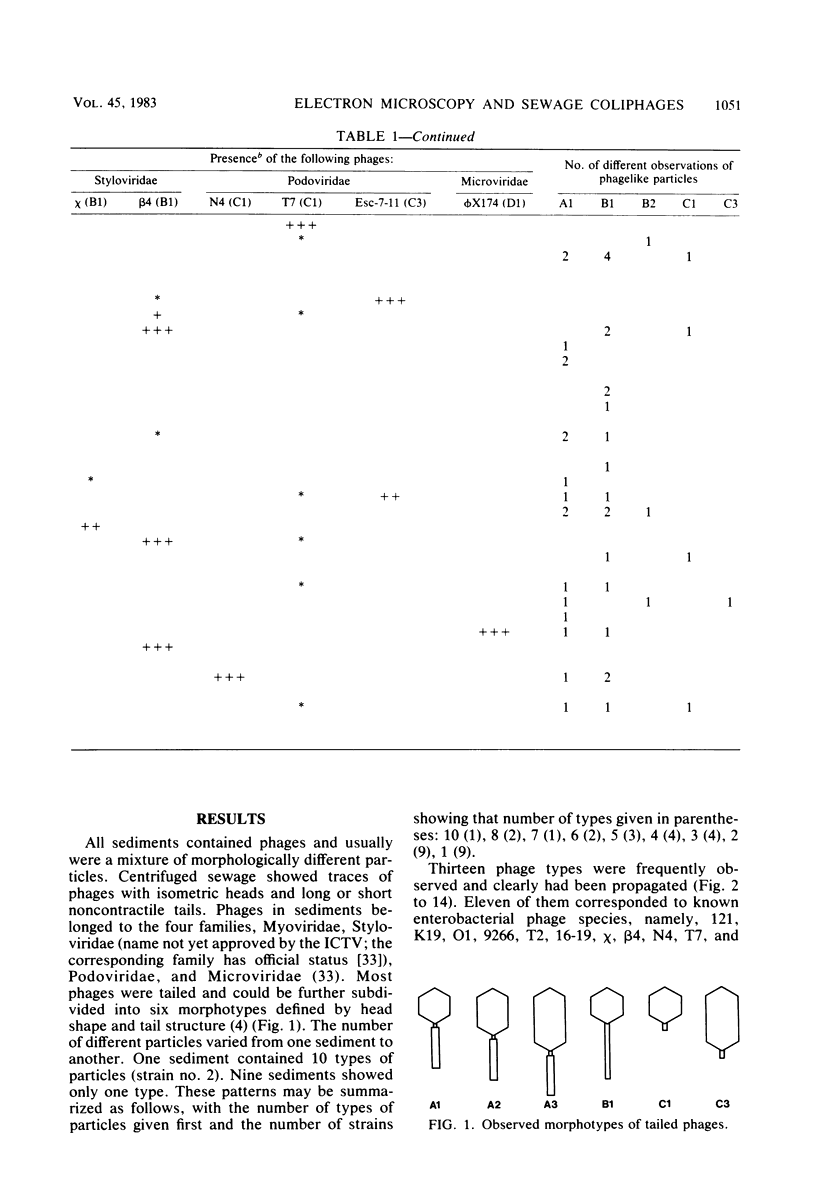
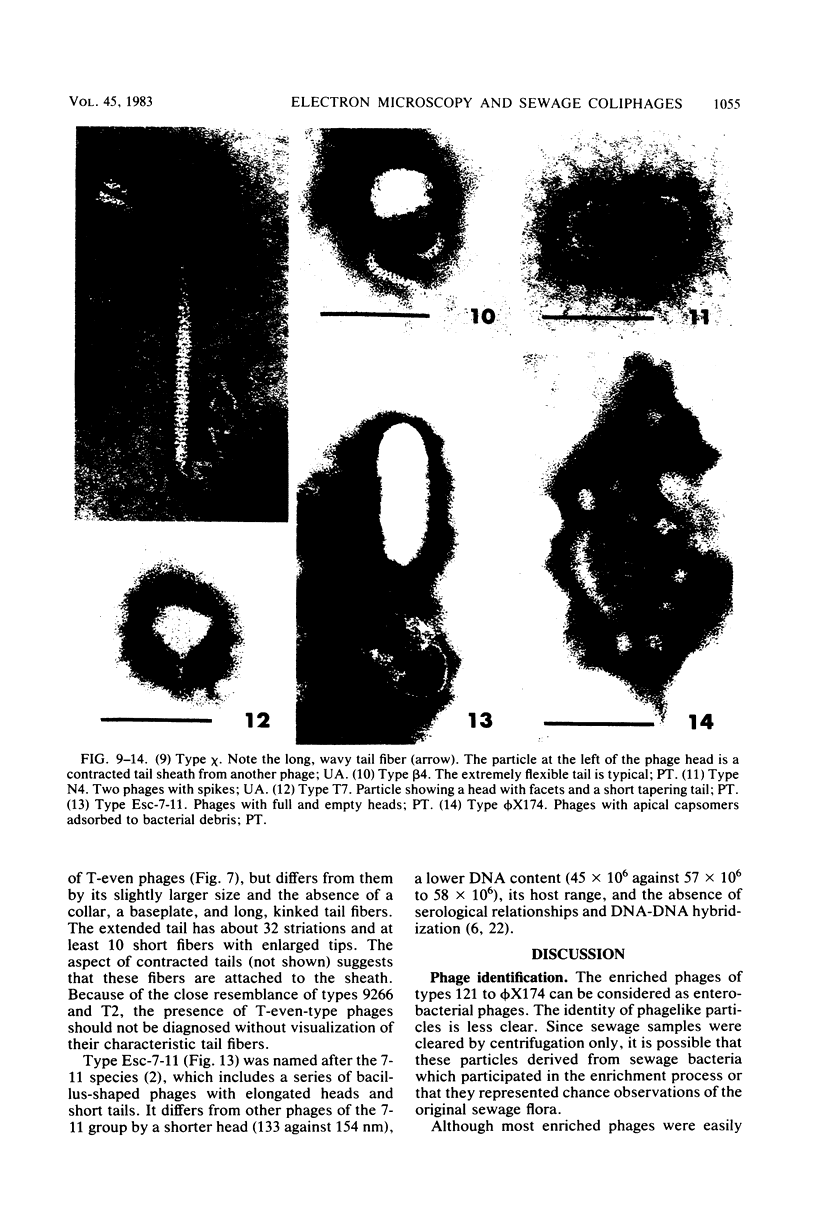
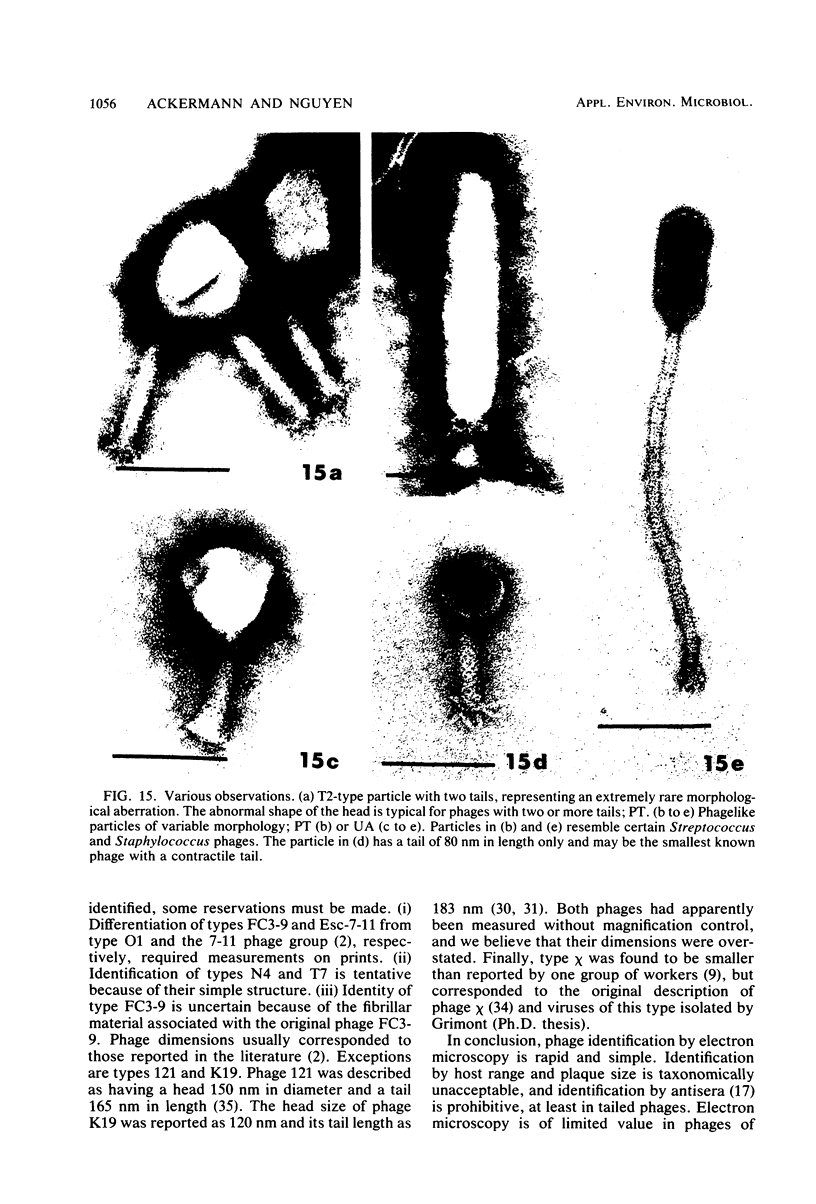
Sewage was enriched with 35 Escherichia coli strains, and sediments of enrichment cultures were studied in the electron microscope. They contained up to 10 varieties of morphologically different particles. T-even-type phages predominated in 14 samples. Thirteen phages were enriched, representing the families Myoviridae (seven), Styloviridae (two), Podoviridae (three), and Microviridae (one). Twelve of these corresponded to known enterobacterial phage species, namely, 121, K19, FC3-9, O1, 9266, T2, 16-19, kappa, beta 4, N4, T7, and phi X174. Cubic RNA phages and filamentous phages were not detected. Types 121 and 9266 have previously been observed only in Romania and South Africa. Identification by morphology is usually simple. Our investigative technique is qualitative and will not detect all phages present. Most enrichment strains are polyvalent, and electron microscopy is always required for phage identification. In a general way, electron microscopy seems to be the method of choice for investigation of phage geography and ecology.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann H. W., Eisenstark A. The present state of phage taxonomy. Intervirology. 1974;3(4):201–219. doi: 10.1159/000149758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann H. W., Jolicoeur P., Berthiaume L. Avantages et inconvénients de l'acétate d'uranyle en virologie comparée: étude de quatre bactériophages caudés. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Aug;20(8):1093–1099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann H. W. La classification des bactériophages des cocci Gram-positifs: Micrococcus, Staphylococcus et Streptococcus. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1975 Mar;23(3):247–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann H. W. La classification des phages caudés des entérobactéries. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1976 May;24(5):359–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann H. W., Petrow S., Kasatiya S. S. Unusual bacteriophages in Salmonella newport. J Virol. 1974 Mar;13(3):706–711. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.3.706-711.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appelbaum P. C., Hugo N., Coetzee J. N. A flagellar phage for the proteus-providence group. J Gen Virol. 1971 Oct;13(1):153–162. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-1-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthiaume L., Ackermann H. W. La classification des actinophages. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1977 Mar;25(3):195–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calberg-Bacq C. M., Siquet-Descans F., Kozma S., Gratia J. P. phi gamma: A coliphage coliphage related to, but distinct from the phi 80 virion. Intervirology. 1975;6(2):98–107. doi: 10.1159/000149461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammack K. A., Wade H. E. The sedimentation behaviour of ribonuclease-active and -inactive ribosomes from bacteria. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):671–680. doi: 10.1042/bj0960671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Classification and nomenclature of viruses. Fourth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Intervirology. 1982;17(1-3):1–199. doi: 10.1159/000149278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Klerk H. C., Prozesky O. W., Prinsloo H. E. The morphology of temperate bacteriophages of Serratia marcescens. S Afr Med J. 1967 May 6;41(18):469–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon E. K., Dhillon T. S., Lam Y. Y., Tsang A. H. Temperate coliphages: classification and correlation with habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 May;39(5):1046–1053. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.5.1046-1053.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhillon T. S., Chan Y. S., Sun S. M., Chau W. S. Distribution of coliphages in Hong Kong sewage. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):187–191. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.187-191.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewert D. L., Paynter M. J. Enumeration of bacteriophages and host bacteria in sewage and the activated-sludge treatment process. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Mar;39(3):576–583. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.3.576-583.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewert D. L., Paynter M. J. Technique for determining total bacterial virus counts in complex aqueous systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):253–260. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.253-260.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuse K., Ando A., Osawa S., Watanabe I. Distribution of ribonucleic acid coliphages in raw sewage from treatment plants in Japan. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1139–1143. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1139-1143.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison A., Gibbins L. N. The isolation and characterization of a temperate phage, Y46/(E2), from Erwinia herbicola Y40. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jul;21(7):937–944. doi: 10.1139/m75-138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilton M. C., Stotzky G. Use of coliphages as indicators of water pollution. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jun;19(6):747–751. doi: 10.1139/m73-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kott Y. Estimation of low numbers of Escherichia coli bacteriophage by use of the most probable number method. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):141–144. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.141-144.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzywy T., Przondo-Hessek A., Slopek S. Morphology of bacteriophages of Klebsiella bacilli. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1972;20(1):85–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzywy T. Ultrastructure of Shigella and Klebsiella bacteriophages. Bacteriophages with contractile tails. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1972;20(5):621–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luftig R. An accurate measurement of the catalase crystal period and its use as an internal marker for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Sep;20(1):91–102. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL E. W. A phage, phi chi, which attacks motile bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jun;25:253–290. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Năcesco N., Constantinesco S. P., Petrovici A. Aspects électrono-optiques du phage convertisseu Proteus vulgaris 121. Arch Roum Pathol Exp Microbiol. 1969 Dec;28(4):838–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S., Furuse K., Choi M. S., Ando A., Sakurai T., Watanabe I. Distribution of ribonucleic acid coliphages in Korea. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):909–911. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.909-911.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S., Furuse K., Watanabe I. Distribution of ribonucleic acid coliphages in animals. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):164–168. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.164-168.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrow S., Kasatiya S. S., Pelletier J., Ackermann H. W., Peloquin J. A phage typing scheme for Salmonella newport. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1974 May-Jun;125(4):433–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primrose S. B., Day M. Rapid concentration of bacteriophages from aquatic habitats. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;42(3):417–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prozesky O. W., De Klerk H. C., Coetzee J. N. The morphology of Proteus bacteriophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Oct;41(1):29–36. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-1-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxelin M. L., Nurmiaho E. L., Korhola M. P., Sundman V. Partial characterization of a new C3-type capsule-dissolving phage of Streptococcus cremoris. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Oct;25(10):1182–1187. doi: 10.1139/m79-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrella F., Morita R. Y. Evidence by electron micrographs for a high incidence of bacteriophage particles in the waters of Yaquina Bay, oregon: ecological and taxonomical implications. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Apr;37(4):774–778. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.4.774-778.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]