Abstract
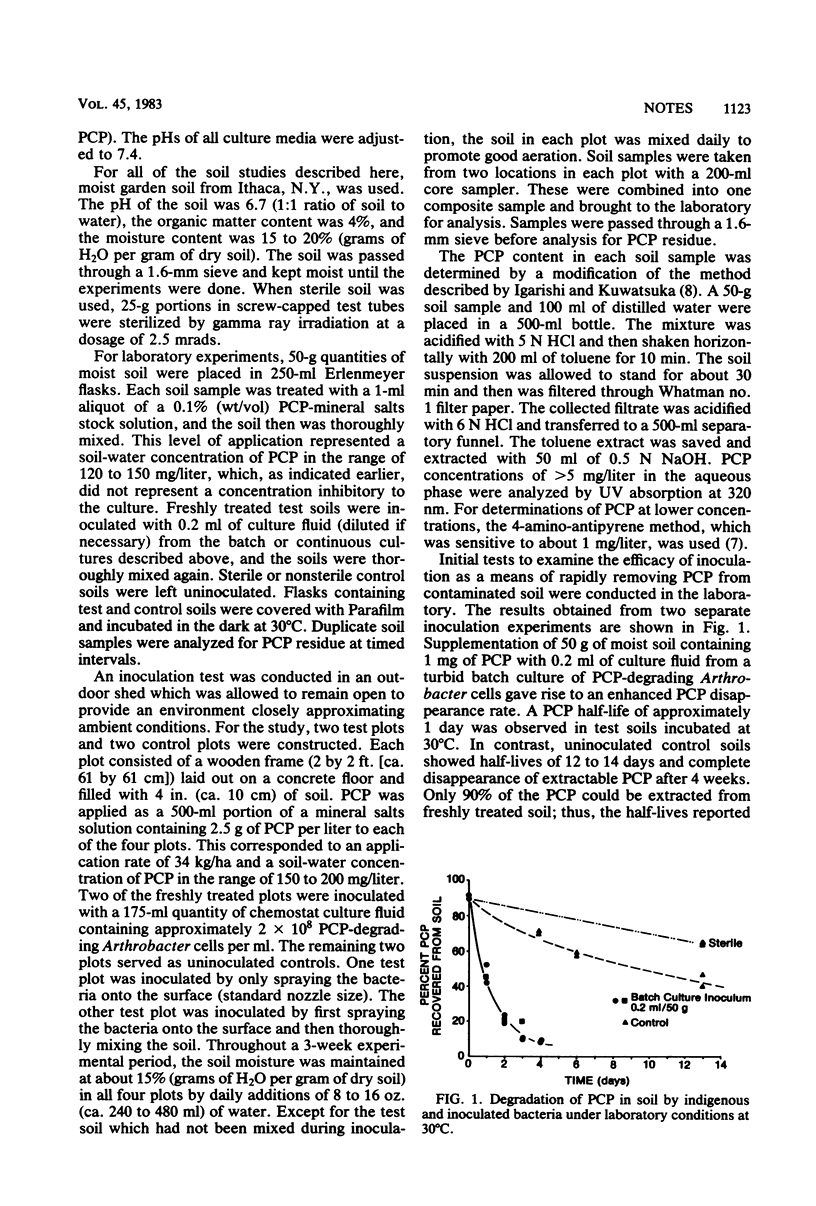
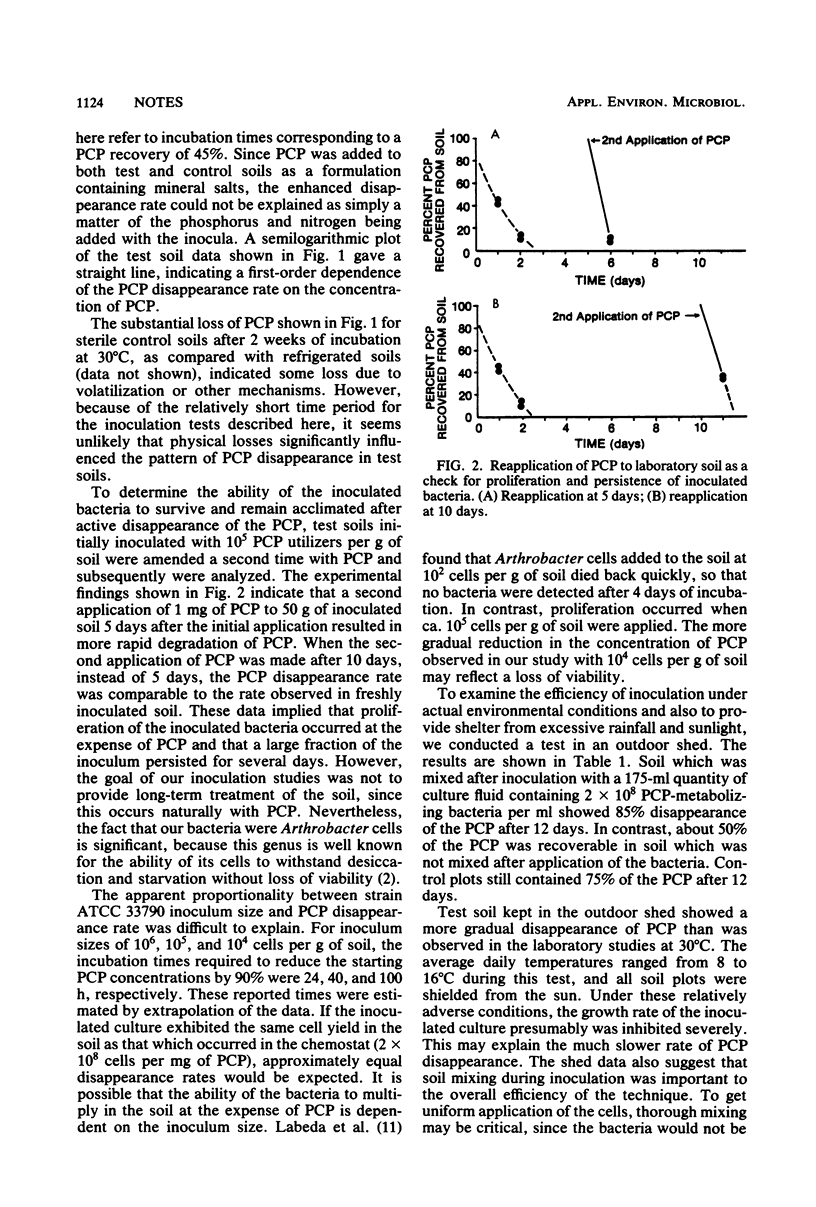
Direct inoculation of bacteria capable of degrading pentachlorophenol (PCP) into PCP-contaminated soil was investigated as a prophylactic measure to reduce the hazards of runoffs when spills occur or when wooden poles freshly treated with PCP-containing preservatives are located near streams and lakes. In laboratory tests at 30°C, the direct addition of 106 PCP-utilizing Arthrobacter cells per g of dry soil reduced the half-life of the pesticide from 2 weeks to <1 day. Soil inoculation also was shown to be an effective way to increase the PCP disappearance rate in a test conducted in an outdoor shed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chatterjee D. K., Kilbane J. J., Chakrabarty A. M. Biodegradation of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid in soil by a pure culture of Pseudomonas cepacia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Aug;44(2):514–516. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.2.514-516.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu J. P., Kirsch E. J. Metabolism of pentachlorophenol by an axenic bacterial culture. Appl Microbiol. 1972 May;23(5):1033–1035. doi: 10.1128/am.23.5.1033-1035.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daughton C. G., Hsieh D. P. Accelerated parathion degradation in soil by inoculation with parathion-utilizing bacteria. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1977 Jul;18(1):48–56. doi: 10.1007/BF01686304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeda D. P., Liu K. C., Casida L. E., Jr Colonization of soil by Arthrobacter and Pseudomonas under varying conditions of water and nutrient availability as studied by plate counts and transmission electron microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Apr;31(4):551–561. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.4.551-561.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond R. L., Hudson J. O., Jamison V. W. Oil degradation in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Apr;31(4):522–535. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.4.522-535.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanlake G. J., Finn R. K. Isolation and characterization of a pentachlorophenol-degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1421–1427. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1421-1427.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


