Abstract
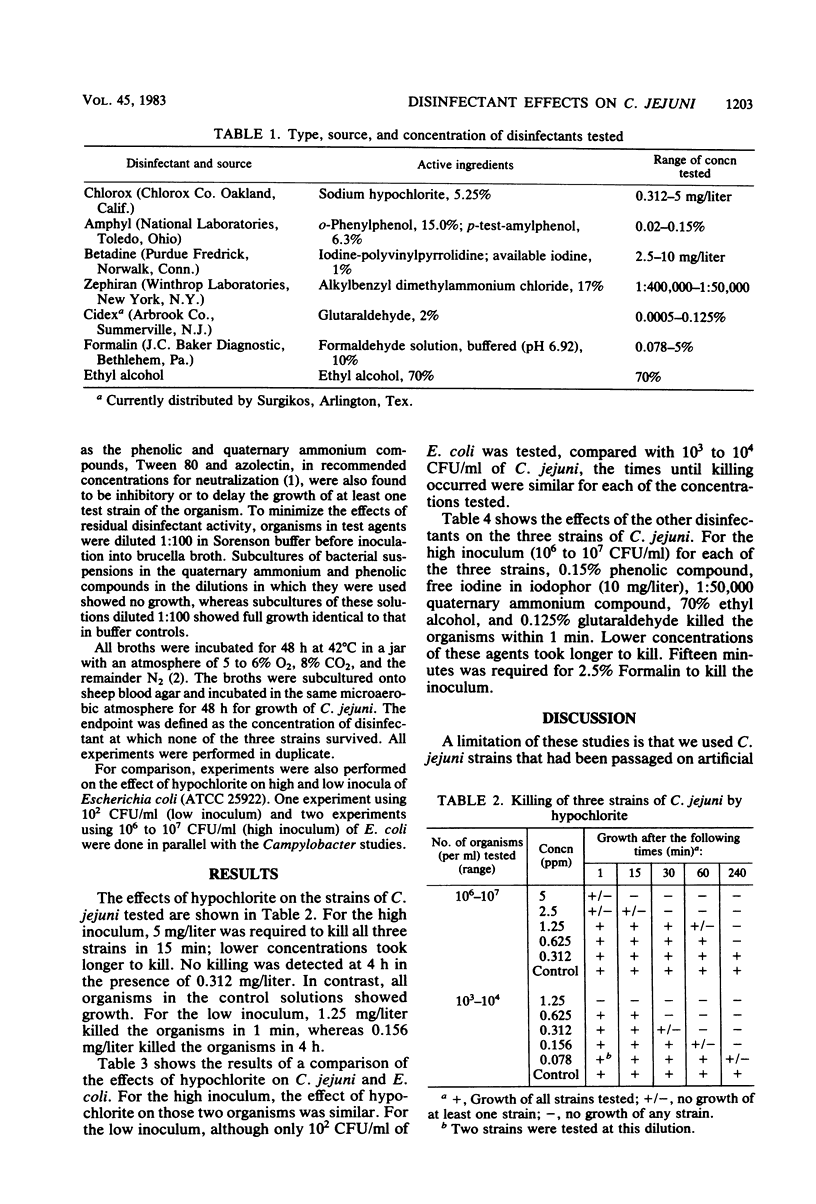
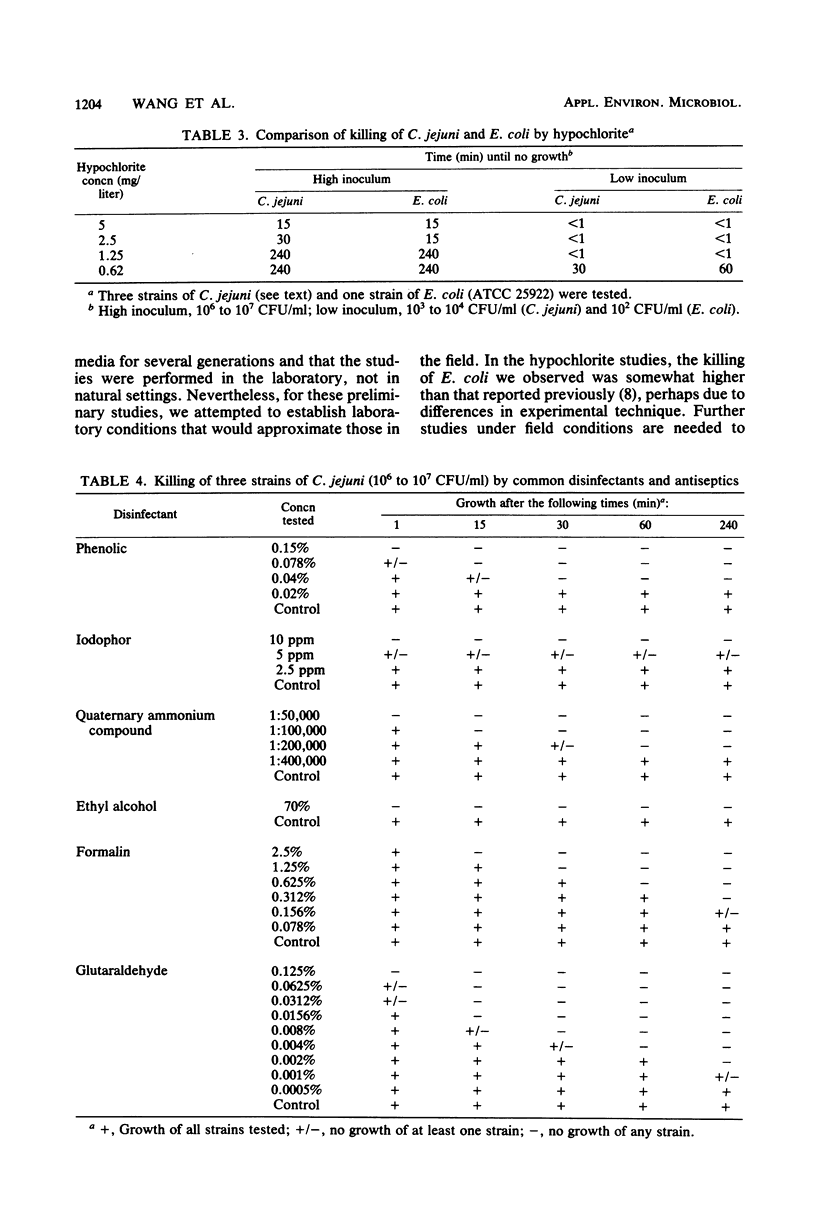
Because of the increasing recognition that Campylobacter jejuni is an important enteric pathogen of humans, we studied the effects of widely used disinfectants on the viability of this organism. At an inoculum size of 10(3) to 10(4) CFU/ml, 1.25 mg of hypochlorite per liter killed three strains within 1 min. At an inoculum size of 10(6) to 10(7) CFU/ml, 5 mg of hypochlorite per liter killed three strains within 15 min. Killing of similar concentrations of C. jejuni and Escherichia coli by hypochlorite was approximately the same. At the high inoculum, 0.15% phenolic compound, 10 mg of iodophor per liter, 1:50,000 quaternary ammonium compound, 70% ethyl alcohol, and 0.125% glutaraldehyde killed all three strains within 1 min. These studies demonstrate that, under the conditions we tested (pH 7.0; 24 to 26 degrees C), the recommended standard concentrations of disinfecting agents are adequate to destroy C. jejuni.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J., Berkowitz I. D., LaForce F. M., Cravens J., Reller L. B., Wang W. L. Campylobacter enteritis: clinical and epidemiologic features. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Aug;91(2):179–185. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., LaForce F. M., Wilson N. A., Wang W. L. Reservoirs for human campylobacteriosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 May;141(5):665–669. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.5.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaser M. J., Reller L. B. Campylobacter enteritis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Dec 10;305(24):1444–1452. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198112103052404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skirrow M. B. Campylobacter enteritis: a "new" disease. Br Med J. 1977 Jul 2;2(6078):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6078.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. R., Weinstein W. M., Bryner J. H. Campylobacter fetus infection in human subjects: association with raw milk. Am J Med. 1979 May;66(5):779–783. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)91116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt R. L., Sours H. E., Barrett T., Feldman R. A., Dickinson R. J., Witherell L. Campylobacter enteritis associated with contaminated water. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Mar;96(3):292–296. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-3-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


