Abstract
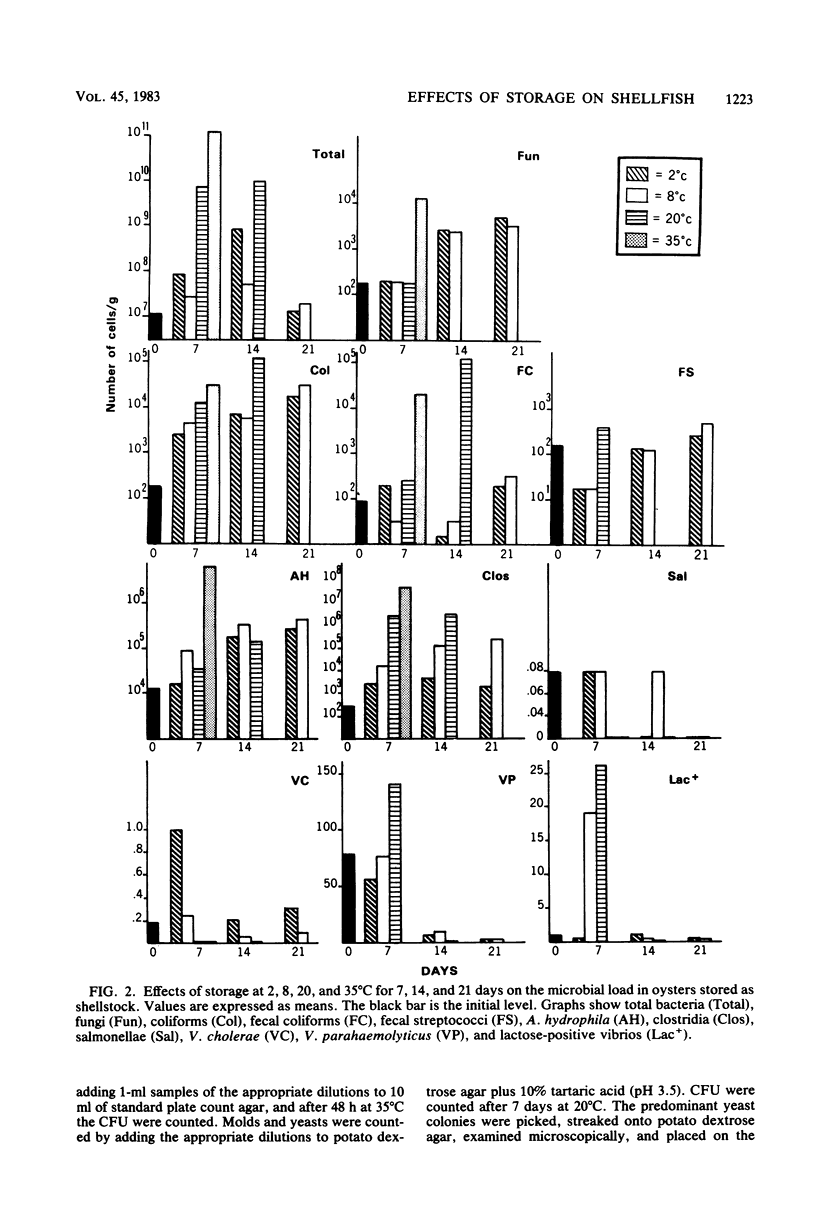
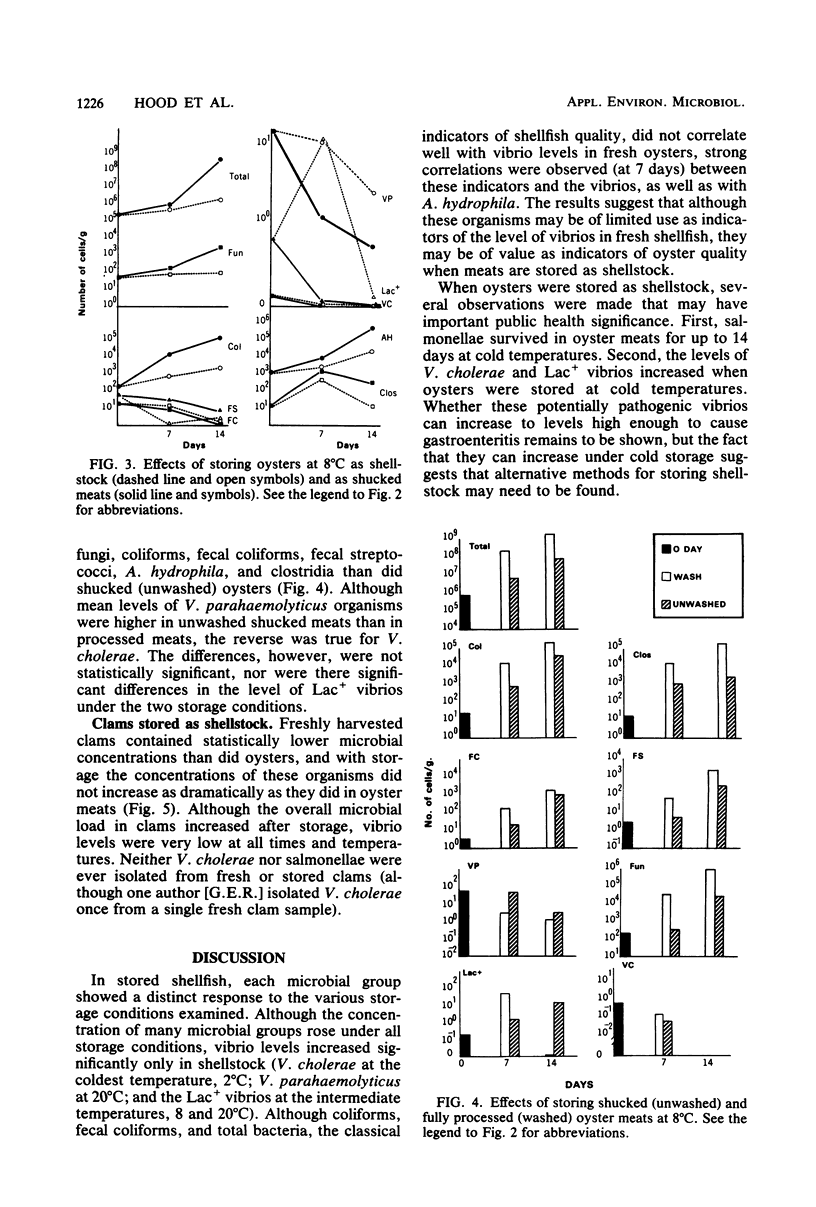
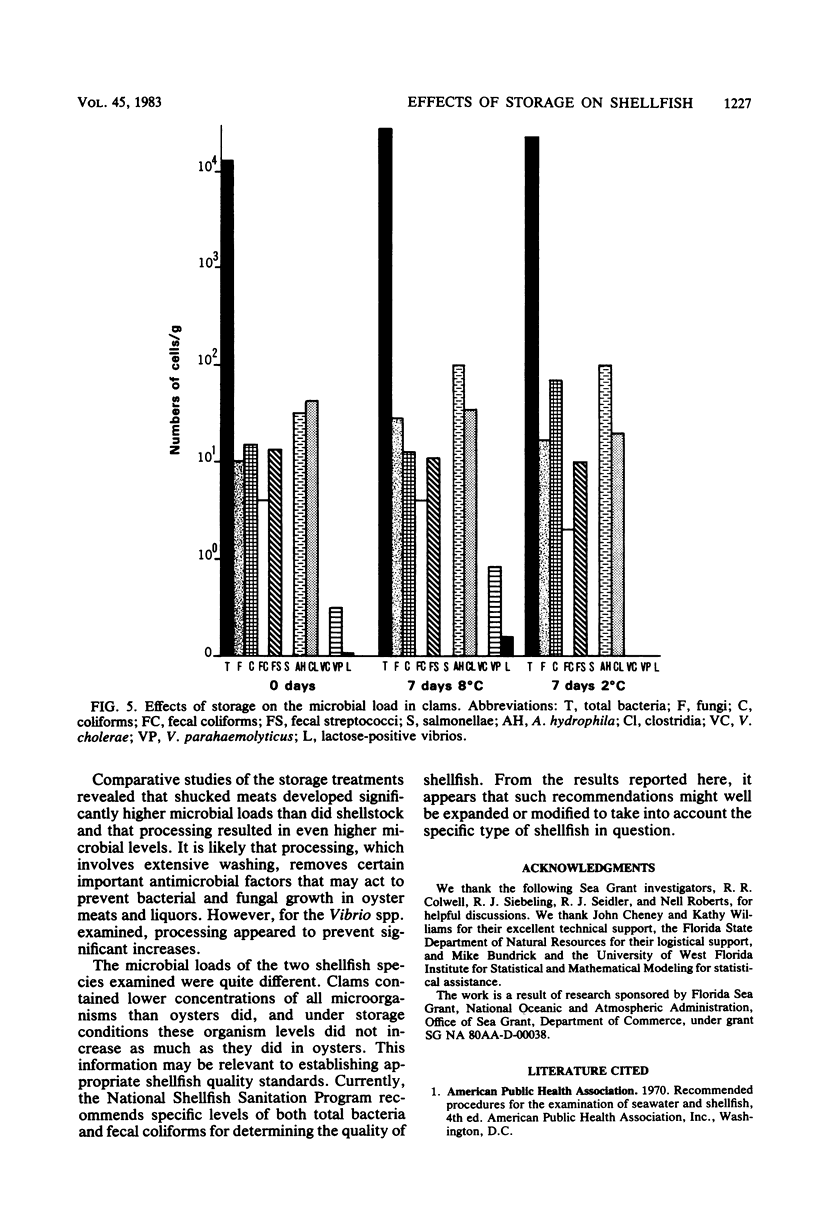
The effects of storage on the microbial load in two commercially important species of shellfish were examined. Oysters (Crassostrea virginica) were stored as shellstock, shucked meats, and fully processed meats at four temperatures for up to 21 days, and clams (Mercenaria campechiensis) were stored only as shellstock. The concentrations of most microbiological groups of organisms increased with the duration and temperature of storage in both shellfish species, although the increases were significantly lower in claims. Concentrations of Vibrio cholerae rose by approximately 1 log in oysters stored as shellstock after 7 days at 2 degrees C, and Lac+ vibrios increased 2 logs at 8 degrees C. Total counts of bacteria, fungi, coliforms, fecal streptococci, Aeromonas hydrophila, and clostridia were significantly higher in shucked oysters than in those stored as shellstock. Fecal coliforms were statistically the same, but V. cholerae, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and the Lac+ vibrios were higher in oysters stored as shellstock. The concentrations of all microbial groups were higher in fully processed oysters than in shucked meats, with the exception of the vibrios, which showed no significant difference among the treatments. The results showed that although traditional methods of storing shellfish resulted in an overall increase in the microbial load, vibrio levels increased only in oysters stored as shellstock. Although fecal coliform and total bacterial counts did not correlate with those for vibrios in fresh oysters, strong correlations were observed in oysters stored for 7 days, suggesting that these indicators may be useful in monitoring oyster quality when meats are stored for a limited time as shellstock.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake P. A., Allegra D. T., Snyder J. D., Barrett T. J., McFarland L., Caraway C. T., Feeley J. C., Craig J. P., Lee J. V., Puhr N. D. Cholera--a possible endemic focus in the United States. N Engl J Med. 1980 Feb 7;302(6):305–309. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198002073020601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulanger Y., Lallier R., Cousineau G. Isolation of enterotoxigenic Aeromonas from fish. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Sep;23(9):1161–1164. doi: 10.1139/m77-174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLWELL R. R., LISTON J. Microbiology of shellfish. Bacteriological study of the natural flora of Pacific oysters (Crassostrea gigas). Appl Microbiol. 1960 Mar;8:104–109. doi: 10.1128/am.8.2.104-109.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee B. D., Neogy K. N. Studies on Aeromonas and Plesiomonas species isolated from cases of choleraic diarrhoea. Indian J Med Res. 1972 Apr;60(4):520–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell R. R., Seidler R. J., Kaper J., Joseph S. W., Garges S., Lockman H., Maneval D., Bradford H., Roberts N., Remmers E. Occurrence of Vibrio cholerae serotype O1 in Maryland and Louisiana estuaries. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):555–558. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.555-558.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschild A. H., Hilsheimer R. Evaluation and modifications of media for enumeration of Clostridium perfringens. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):78–82. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.78-82.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood M. A., Ness G. E., Rodrick G. E. Isolation of Vibrio cholerae serotype O1 from the eastern oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):559–560. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.559-560.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Sayler G. S., Baldini M. M., Colwell R. R. Ambient-temperature primary nonselective enrichment for isolation of Salmonella spp. from an estuarine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):829–835. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.829-835.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J., Seidler R. J., Lockman H., Colwell R. R. Medium for the presumptive identification of Aeromonas hydrophila and Enterobacteriaceae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):1023–1026. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.1023-1026.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivier G., Lallier R., Larivière S. A toxigenic profile of Aeromonas hydrophila and Aeromonas sobria isolated from fish. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Mar;27(3):330–333. doi: 10.1139/m81-050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shotts E. B., Jr, Rimler R. Medium for the isolation of Aeromonas hydrophila. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):550–553. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.550-553.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Son N. T., Fleet G. H. Behavior of pathogenic bacteria in the oyster, Crassostrea commercialis, during depuration, re-laying, and storage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Dec;40(6):994–1002. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.6.994-1002.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman J. B., DeWitt W. E., Thompson J., Muchnick C. N., Portnoy B. L., Feeley J. C., Gangarosa E. J. A case of cholera in Texas, 1973. Am J Epidemiol. 1974 Dec;100(6):487–498. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


