Abstract
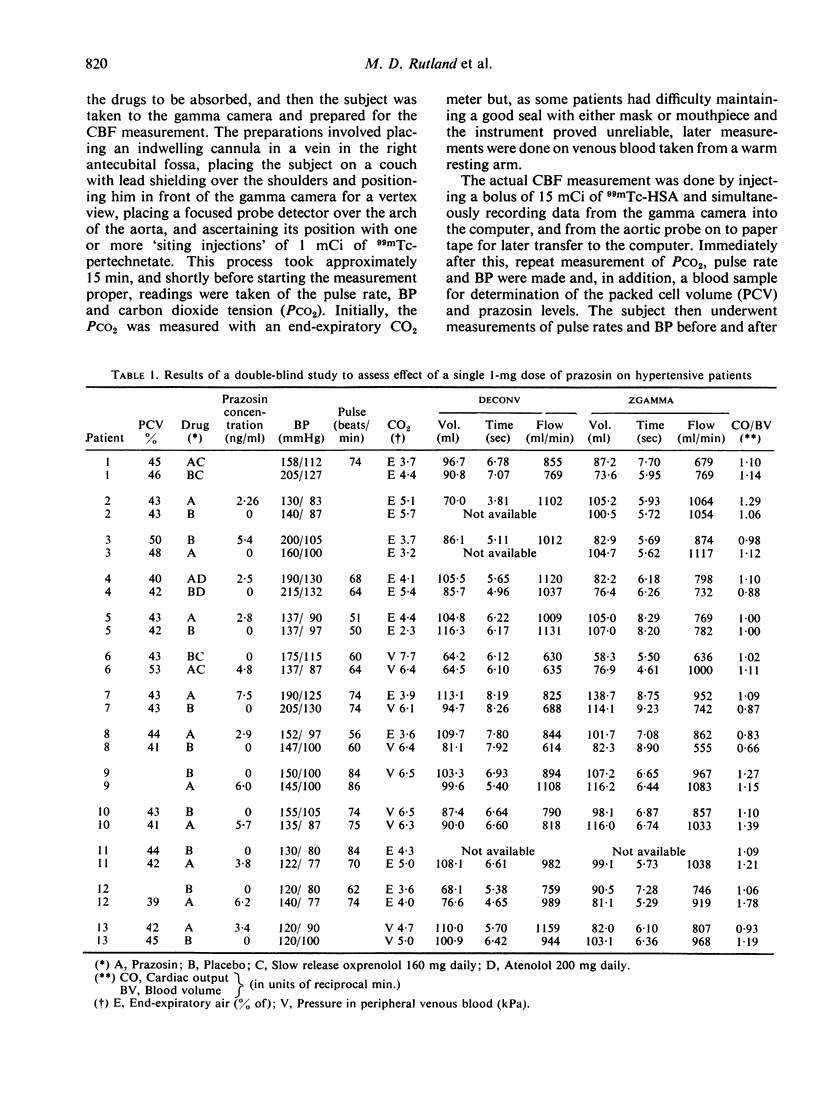
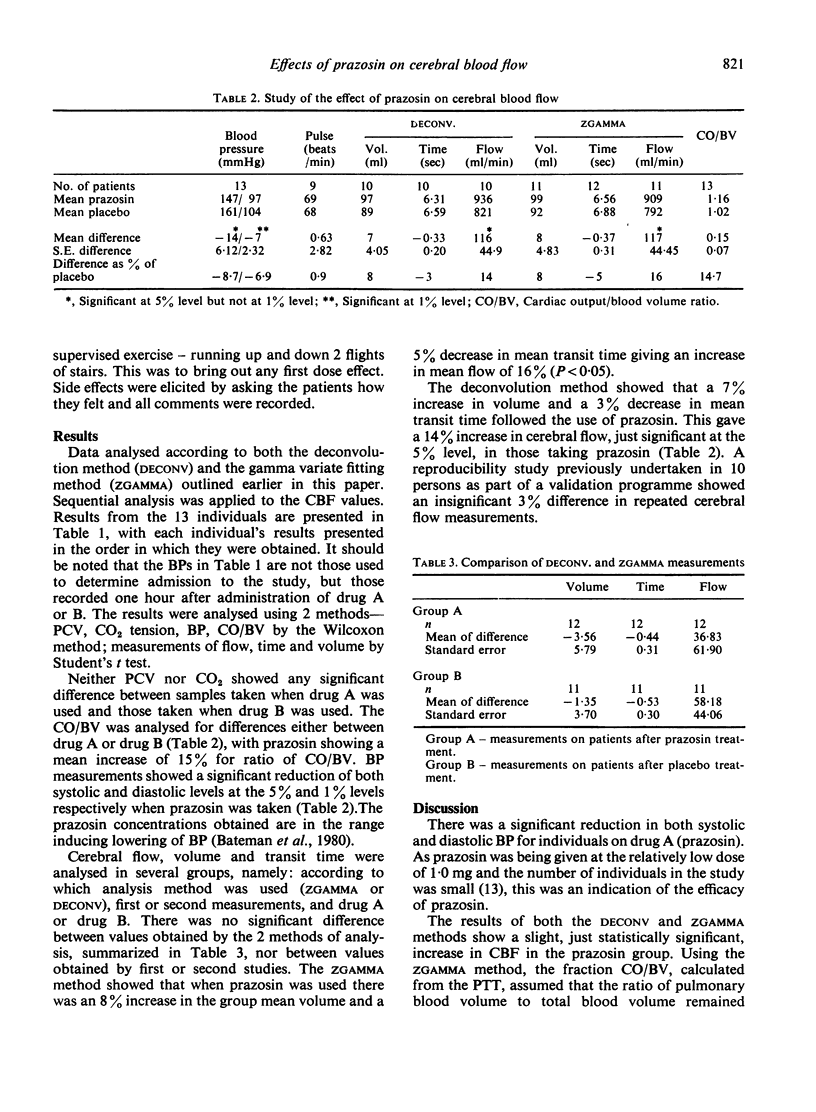
It was considered that the first dose reaction occurring with prazosin may have been due either to hypotension or to a specific reduction in cerebral blood flow. The development of a quantitative non-invasion nuclear medicine technique for cerebral flow has now made it possible to investigate the effects of prazosin on cerebral blood flow in hypertensive patients. This double-blind study showed a significant decrease in BP and a small just significant increase in cerebral blood flow following a single 1-mg dose of prazosin, when compared with a placebo. From these results, it is unlikely that the first dose reactions which occurred with prazosin were due to a specific reduction in cerebral blood flow.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bendall M. J., Baloch K. H., Wilson P. R. Side effects due to treatment of hypertension with prazosin. Br Med J. 1975 Jun 28;2(5973):727–728. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5973.727-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIUNTINI C., LEWIS M. L., LUIS A. S., HARVEY R. M. A STUDY OF THE PULMONARY BLOOD VOLUME IN MAN BY QUANTITATIVE RADIOCARDIOGRAPHY. J Clin Invest. 1963 Oct;42:1589–1605. doi: 10.1172/JCI104844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabriel R., Meek D., Ghosh B. C. Letter: Collapse after prazosin hydrochloride. Lancet. 1975 May 10;1(7915):1095–1095. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91873-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. M., Thornell I. R., Gain J. M., Bagnoli C., Oates H. F., Stokes G. S. Prazosin: the first-dose phenomenon. Br Med J. 1976 Nov 27;2(6047):1293–1294. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6047.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson G. E., Pacifico A. D., Frank F. M. Studies of cardiopulmonary blood volume. Measurement of total cardiopulmonary blood volume in normal human subjects at rest and during exercise. Circulation. 1966 Mar;33(3):347–356. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.33.3.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B. W., Rikner G., Wolgast M. On the theory of an intravenous isotope method for cerebral blood flow measurements. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1977 May;37(3):195–200. doi: 10.3109/00365517709091482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


