Abstract
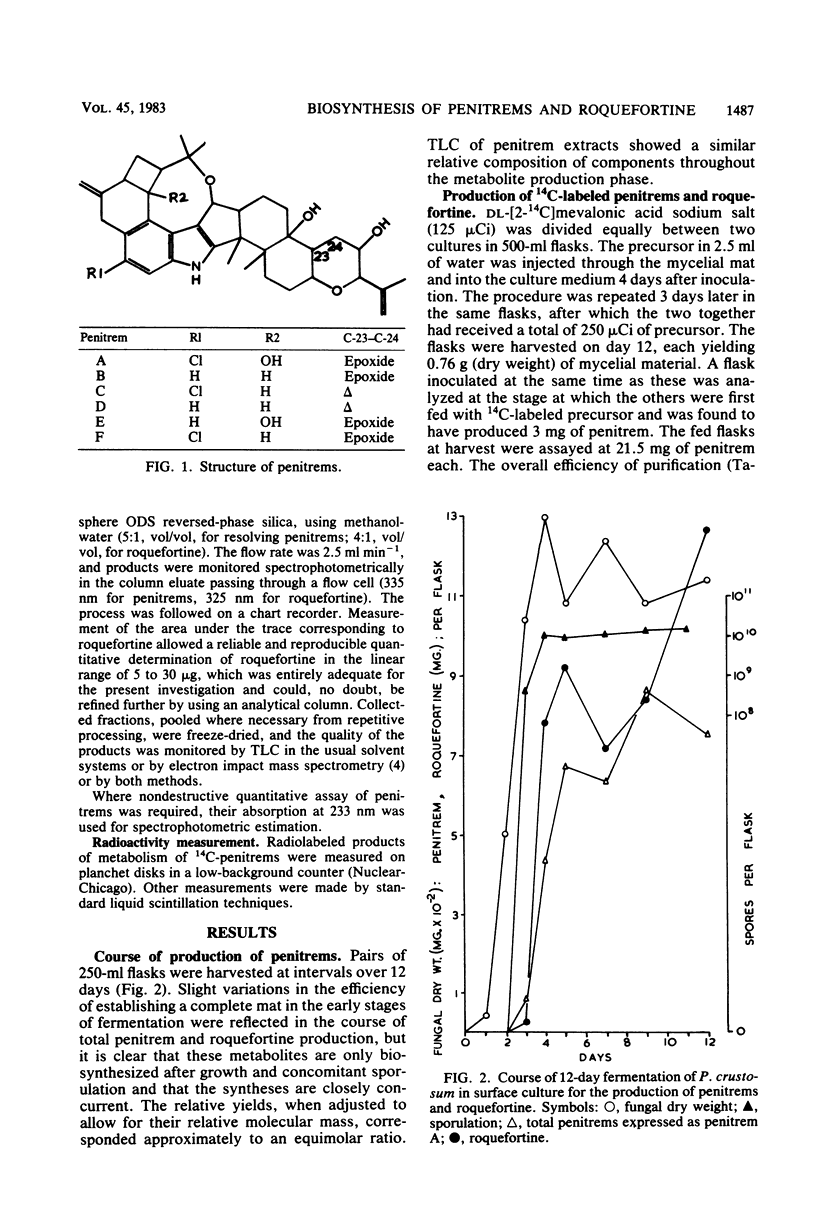
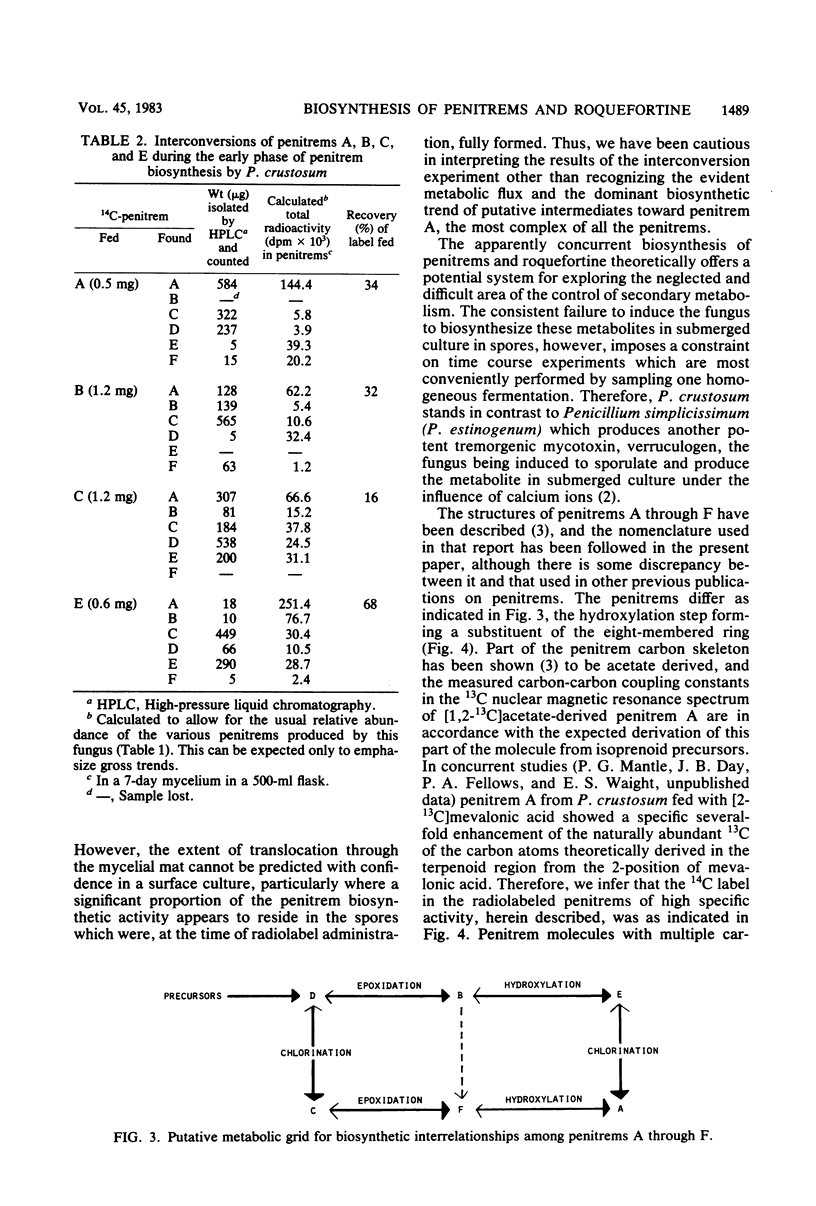
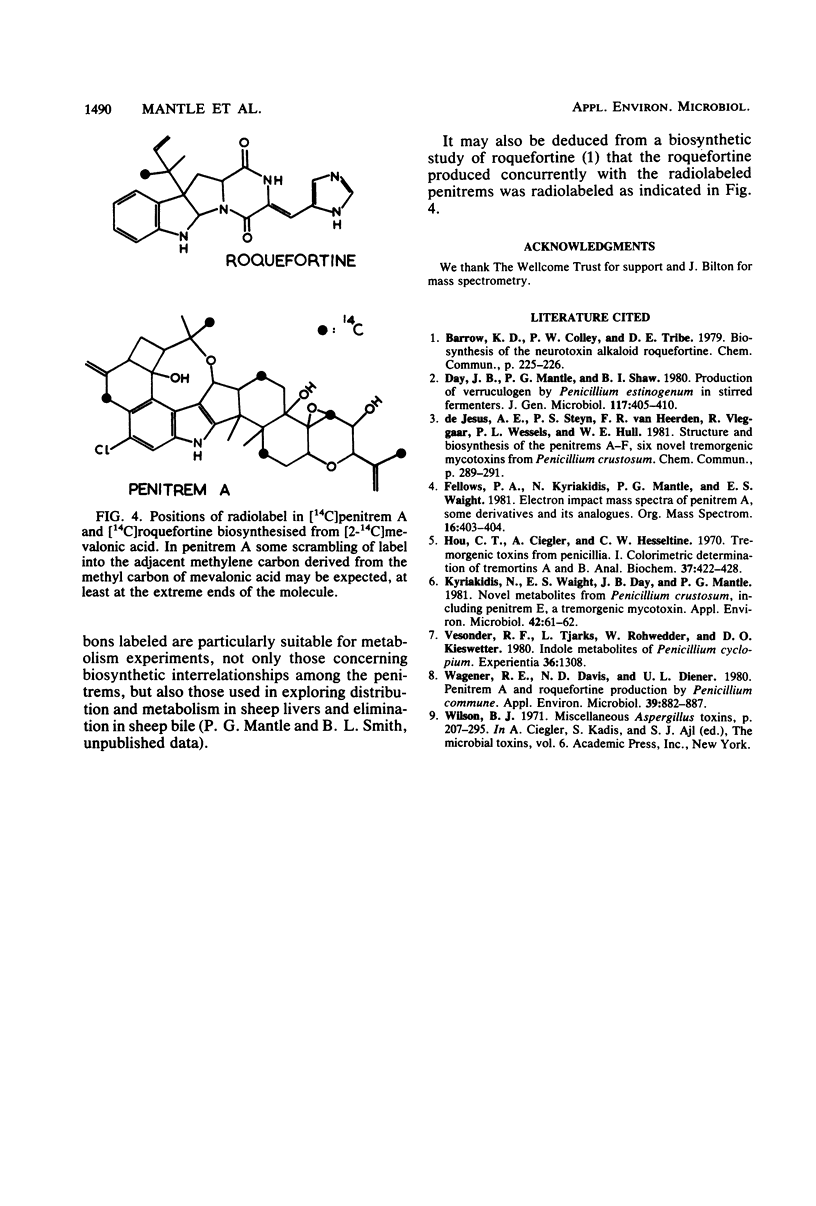
Roquefortine and the penitrems were biosynthesised concurrently at an approximately equimolar rate by Penicillium crustosum after growth and sporulation. [14C]mevalonic acid was incorporated (15% efficiency) into the isoprenoid regions of the penitrem and roquefortine molecules to an extent consistent with their 6:1 molar ratio of isoprenoid components. [14C]penitrem A (specific activity, 3.4 X 10(2) mu Ci mmol-1) and 14C-penitrems B, C, and E readministered to young cultures were metabolically interconverted, indicating considerable metabolic flux, though generally directed towards penitrem A as the end product and suggesting a metabolic grid for the penitrem metabolites. Addition of bromide to the medium preferentially favored the production of bromo-analogs rather than the usual chloropenitrems.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Day J. B., Mantle P. G., Shaw B. I. Production of verruculogen by Penicillium estinogenum in stirred fermenters. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Apr;117(2):405–410. doi: 10.1099/00221287-117-2-405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou C. T., Ciegler A., Hesseltine C. W. Tremorgenic toxins from Penicillia. I. Colorimetric determination of tremortins A and B. Anal Biochem. 1970 Oct;37(2):422–428. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakidis N., Waight E. S., Day J. B., Mantle P. G. Novel metabolites from Penicillium crustosum, including penitrem E, a tremorgenic mycotoxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):61–62. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.61-62.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagener R. E., Davis N. D., Diener U. L. Penitrem A and Roquefortine Production by Penicillium commune. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Apr;39(4):882–887. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.4.882-887.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



