Abstract
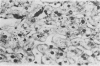
Hepatic injury in association with naproxen therapy is described and documented by liver biopsy in one patient. Histological findings were consistent with a drug-induced hepatitis, and cessation of therapy led to reversal of the clinical and biochemical changes. Circumstantial evidence is in favour of a hypersensitivity response to the drug rather than direct hepatotoxicity. Increased awareness of clinicians of this probably rare side effect of naproxen may help prompt identification of similar cases.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bass B. H. Letter: Jaundice associated with naproxen. Lancet. 1974 May 18;1(7864):998–998. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91315-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredell E. W., Strand L. J. Naproxen overdose. JAMA. 1977 Aug 29;238(9):938–938. doi: 10.1001/jama.238.9.938b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenger W., Morbach H. J. Klinische Untersuchung von Naproxen, vor allem mit Bezug auf seine Verträglichkeit. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1973;2:137–139. doi: 10.3109/03009747309097113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law I. P., Knight H. Jaundice associated with naproxen. N Engl J Med. 1976 Nov 18;295(21):1201–1201. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197611182952119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runkel R., Chaplin M. D., Sevelius H., Ortega E., Segre E. Pharmacokinetics of naproxen overdoses. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Sep;20(3):269–277. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976203269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]