Abstract
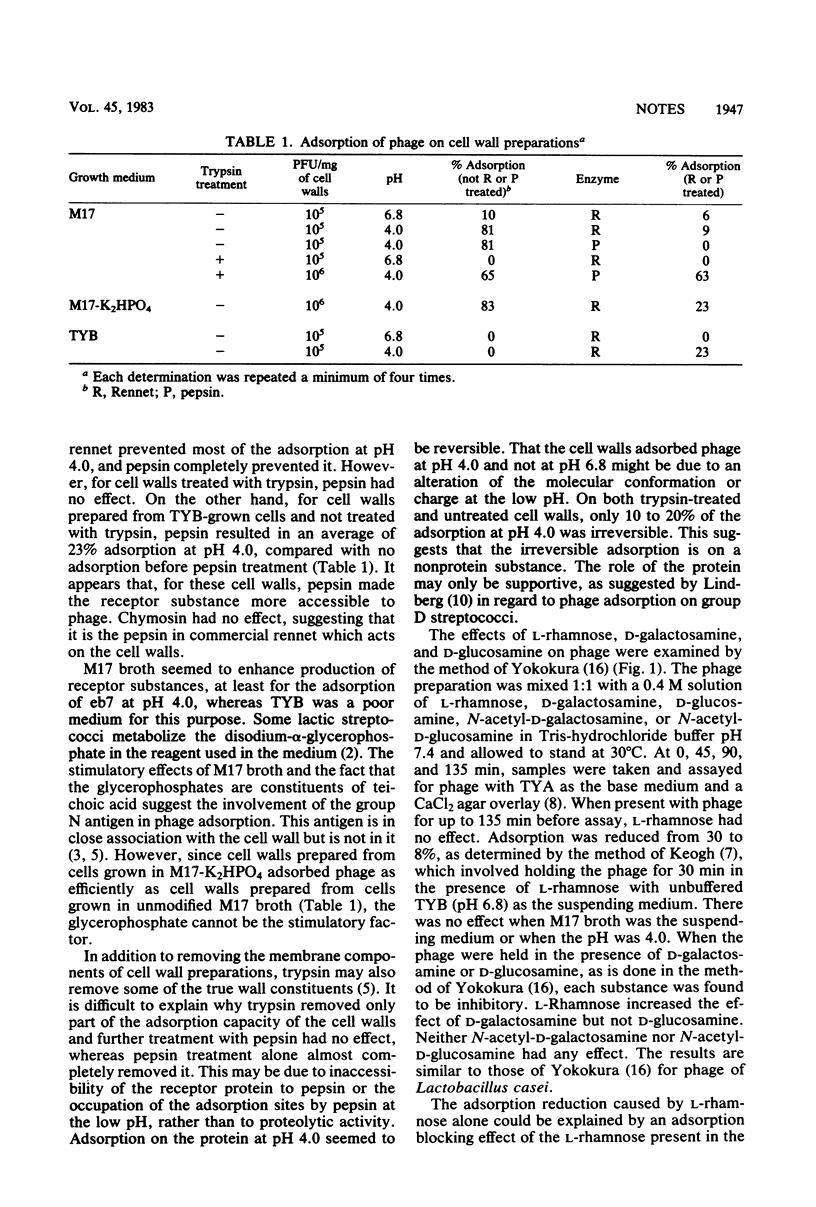
When M17 broth was used as growth medium before preparation of cell walls, adsorption of phage eb7 on Streptococcus cremoris EB7 at pH 4.0 was stimulated. When preparation included treatment with trypsin, absorption of phage was 65%. Without trypsin treatment, absorption was 81%. Only 10 to 20% of the adsorption was irreversible. Treatment with pepsin or commercial rennet but not pure chymosin prevented adsorption on non-trypsin-treated cell walls. d-Galactosamine treatment of phage eb7 had an inactivating effect which was enhanced by l-rhamnose.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CUMMINS C. S., HARRIS H. The chemical composition of the cell wall in some gram-positive bacteria and its possible value as a taxonomic character. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Jul;14(3):583–600. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-3-583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. A critical review of the use of glycerophosphates in microbiological media. Lab Pract. 1971 May;20(5):414–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIOTT S. D. TEICHOIC ACID AND THE GROUP ANTIGEN OF LACTIC STREPTOCOCCI (GROUP N). Nature. 1963 Dec 21;200:1184–1185. doi: 10.1038/2001184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott S. D., Hayward J., Liu T. Y. The presence of a group A variant-like antigen in streptococci of other groups with special reference to group N. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):479–493. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh B. P. Appraisal of media and methods for assay of bacteriophages of lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Oct;40(4):798–802. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.4.798-802.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh B. P., Pettingill G. Long-term storage of bacteriophages of lactic streptococci. Appl Microbiol. 1966 May;14(3):421–424. doi: 10.1128/am.14.3.421-424.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh B. P. Survival and activity of frozen starter cultures for cheese manufacture. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Jun;19(6):928–931. doi: 10.1128/am.19.6.928-931.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A. Bacteriophage receptors. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1973;27:205–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.27.100173.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. D. Isolation and properties of a phage receptor substance from the plasma membrane of Streptococcus lactis ML 3. J Gen Virol. 1971 Oct;13(1):59–71. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. D., Reiter B. The adsorption of phage to group N streptococci. The specificity of adsorption and the location of phage receptor substances in cell-wall and plasma-membrane fractions. J Gen Virol. 1968 Jul;3(1):103–119. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-3-1-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaver A. K., Brock T. D. Purification and properties of a bacteriophage receptor material from Streptococcus faecium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 29;121(2):298–314. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokokura T. Phage receptor material in Lactobacillus casei. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 May;100(1):139–145. doi: 10.1099/00221287-100-1-139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



