Abstract
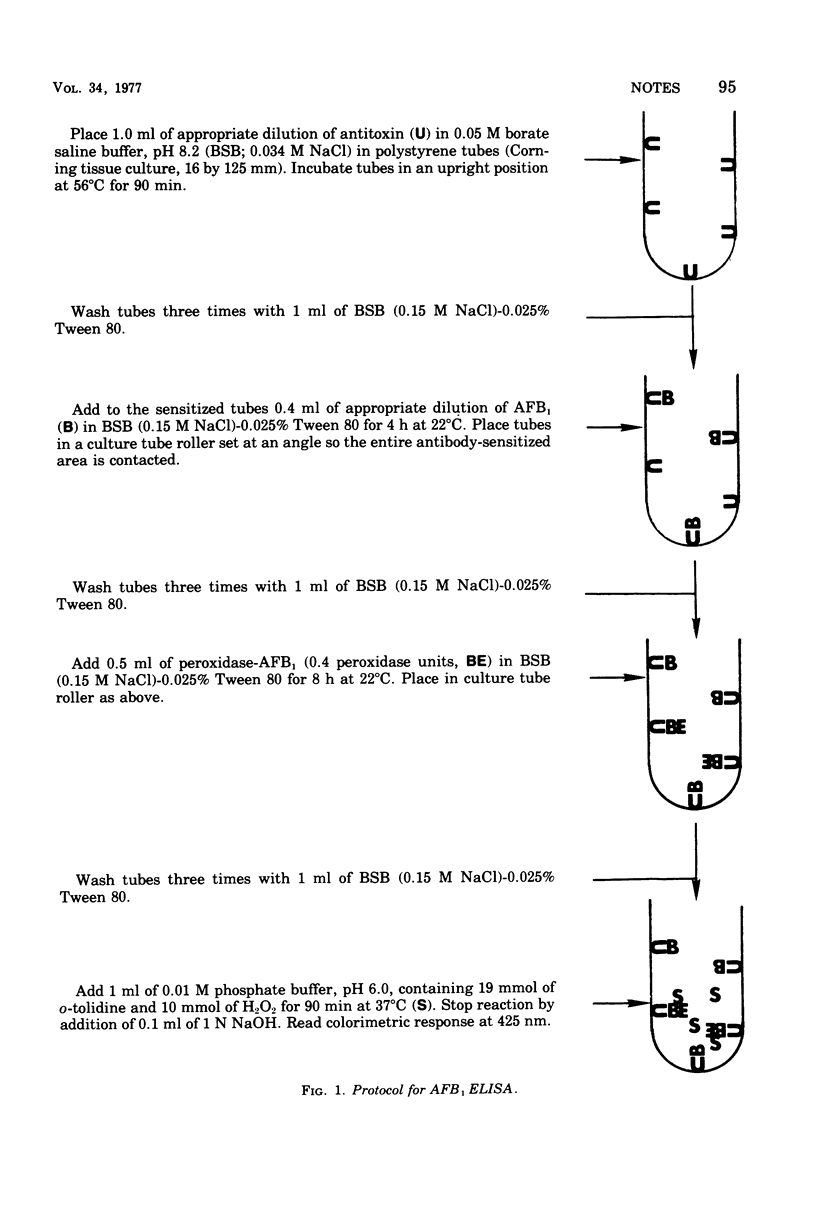
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent analysis (ELISA) permitted the detection of less than 10 pg of aflatoxin B1 per ml. The antitoxin was most specific for aflatoxins B1 and B2alpha, and least specific for aflatoxin G1.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brewster T. C., Grant D. W. Excretion of aflatoxin by frogs after implantation with Aspergillus flavus. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jan;125(1):66–68. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.1.66. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Jonsson K., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. II. Quantitative assay of protein antigen, immunoglobulin G, by means of enzyme-labelled antigen and antibody-coated tubes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90132-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



