Abstract
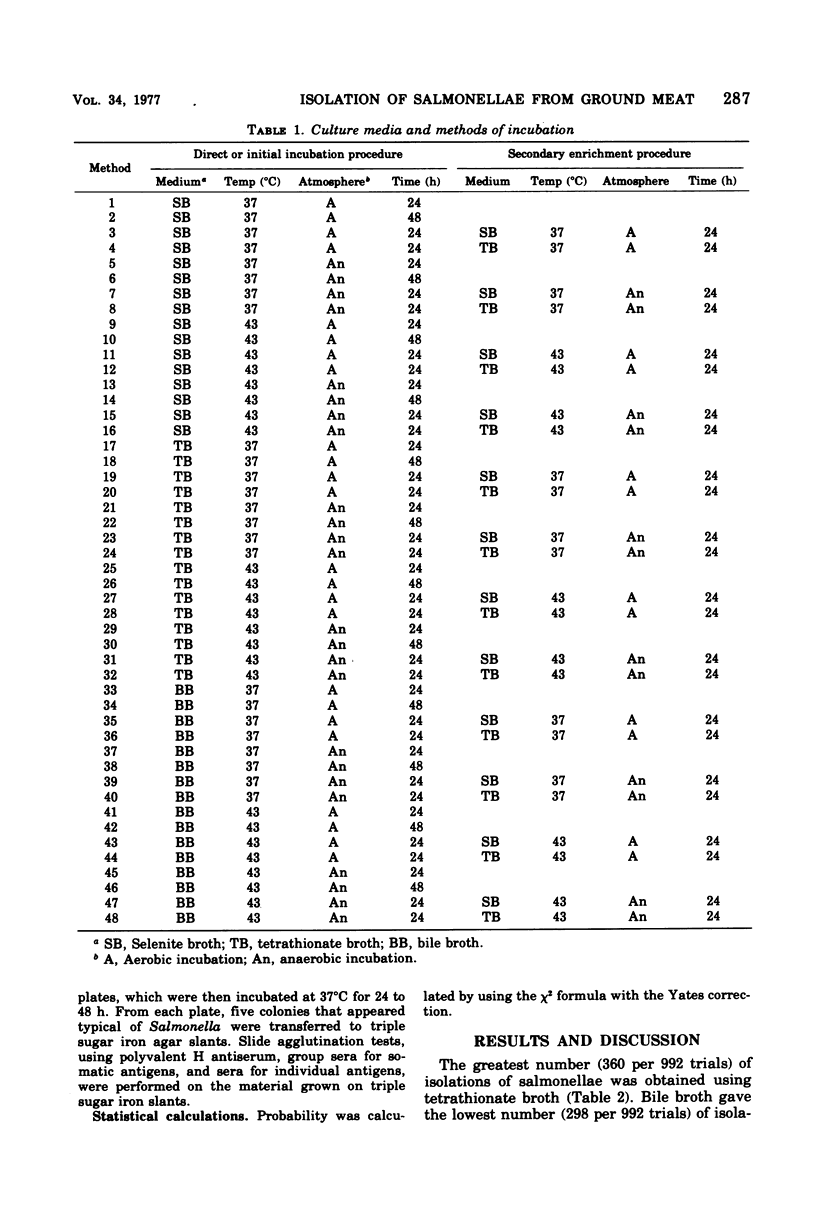
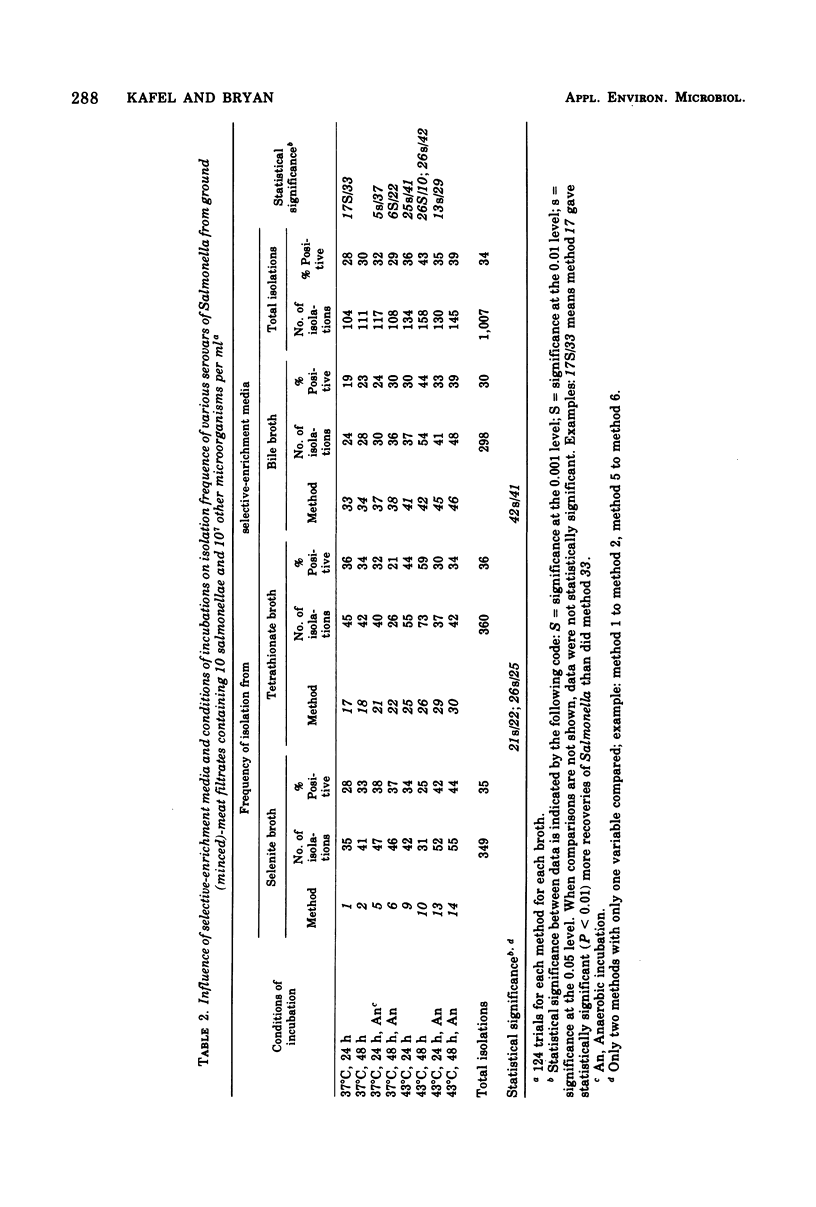
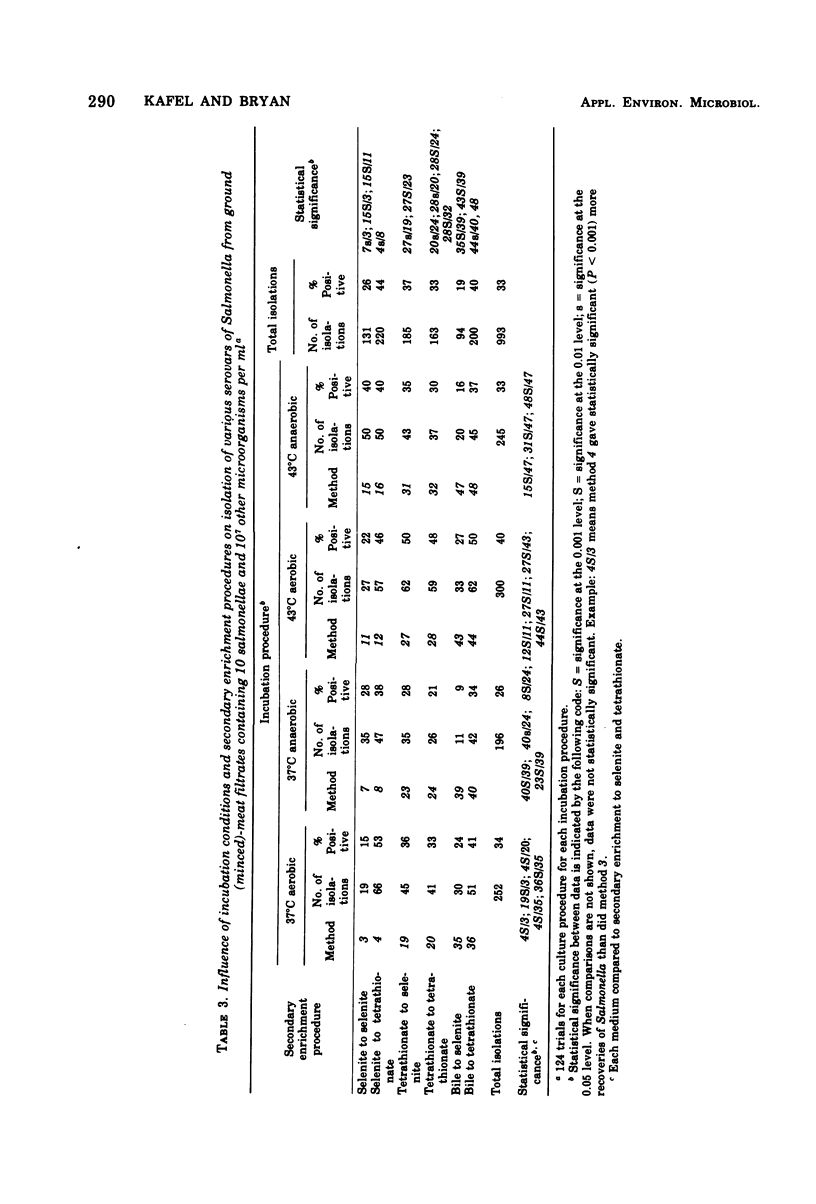
Forty-eight combinations of enrichment media, secondary enrichment, incubation times and temperatures, and atmospheres were examined for their efficacy in recovering different serovars of Salmonella that had been inoculated into ground-meat extract. Variations included three selective-enrichment media, two (37 and 43 degrees C) incubation temperatures, two (24 and 48 h) incubation times, two (aerobic and anaerobic) incubation atmospheres, and secondary enrichment to two of the selective-enrichment media. The ratio of Salmonella to other microorganisms was 10: greater than 1,000,000. One-hundred and twenty-four tests were conducted for each enrichment under each condition of incubation. None of the methods recovered Salmonella in more than 60% of the trials. Salmonella typhimurium was recovered most frequently of the serovars tested; S. abortusovis was recovered least frequently. There was considerable variation in the results obtained by the different methods, but there was a statistically significant advantage in the 43 degrees C incubation temperature. Secondary enrichment in tetrathionate broth showed a statistically significant advantage over secondary enrichment in selenite broth. Secondary enrichment into a different medium from the primary enrichment also was advantageous.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANWART G. J., AYRES J. C. Effect of various enrichment broths and selective agars upon the growth of several species of Salmonella. Appl Microbiol. 1953 Nov;1(6):296–301. doi: 10.1128/am.1.6.296-301.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson V. L., Snoeyenbos G. H., McKie B. A., Smyser C. F. A comparison of incubation time and temperature for the isolation of salmonella. Avian Dis. 1967 May;11(2):217–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON J. M. Rapid isolation of salmonellae from faeces. J Clin Pathol. 1961 Jul;14:397–399. doi: 10.1136/jcp.14.4.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edel W., Kampelmacher E. H. Comparative studies on Salmonella-isolation in eight European laboratories. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(3):487–491. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARVEY R. W., THOMSON S. Optimum temperature of incubation for isolation of Salmonellae. Mon Bull Minist Health Public Health Lab Serv. 1953 Jul;12:149–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBBS B. C. Techniques for the isolation of Salmonellae from eggs and egg-products. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1963 May;104:621–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMESON J. E. A discussion of the dynamics of Salmonella enrichment. J Hyg (Lond) 1962 Jun;60:193–207. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400039462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMESON J. E. A study of tetrathionate enrichment techniques, with particular reference to two new tetrathionate modifications used in isolating salmonellae from sewer swabs. J Hyg (Lond) 1961 Mar;59:1–13. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. K., Dunn C. G. Influence of incubation temperature and sodium heptadecyl sulfate (Tergitol No. 7) on the isolation of salmonellae from pork sausage. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):192–195. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.192-195.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORTH W. R., BARTRAM M. T. The efficiency of selenite broth of different compositions in the isolation of Salmonella. Appl Microbiol. 1953 May;1(3):130–134. doi: 10.1128/am.1.3.130-134.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORNE W. W., STOKES J. L. A modified selenite brilliant-green medium for the isolation of Salmonella from egg products. Appl Microbiol. 1955 Sep;3(5):295–299. doi: 10.1128/am.3.5.295-299.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H. W. The evaluation of culture media for the isolation of salmonellae from faeces. J Hyg (Lond) 1952 Mar;50(1):21–36. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400019409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOKES J. L., OSBORNE W. W. A selenite brilliant green medium for the isolation of Salmonella. Appl Microbiol. 1955 Jul;3(4):217–220. doi: 10.1128/am.3.4.217-220.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silliker J. H., Gabis D. A. ICMSF methods studies. V. The influence of selective enrichment media and incubation temperatures on the detection of salmonellae in raw frozen meats. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Jun;20(6):813–816. doi: 10.1139/m74-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spino D. F. Elevated-temperature technique for the isolation of Salmonella from streams. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Jul;14(4):591–596. doi: 10.1128/am.14.4.591-596.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMSON S. The numbers of pathogenic bacilli in faeces in intestinal diseases. J Hyg (Lond) 1955 Jun;53(2):217–224. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400000681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



