Abstract
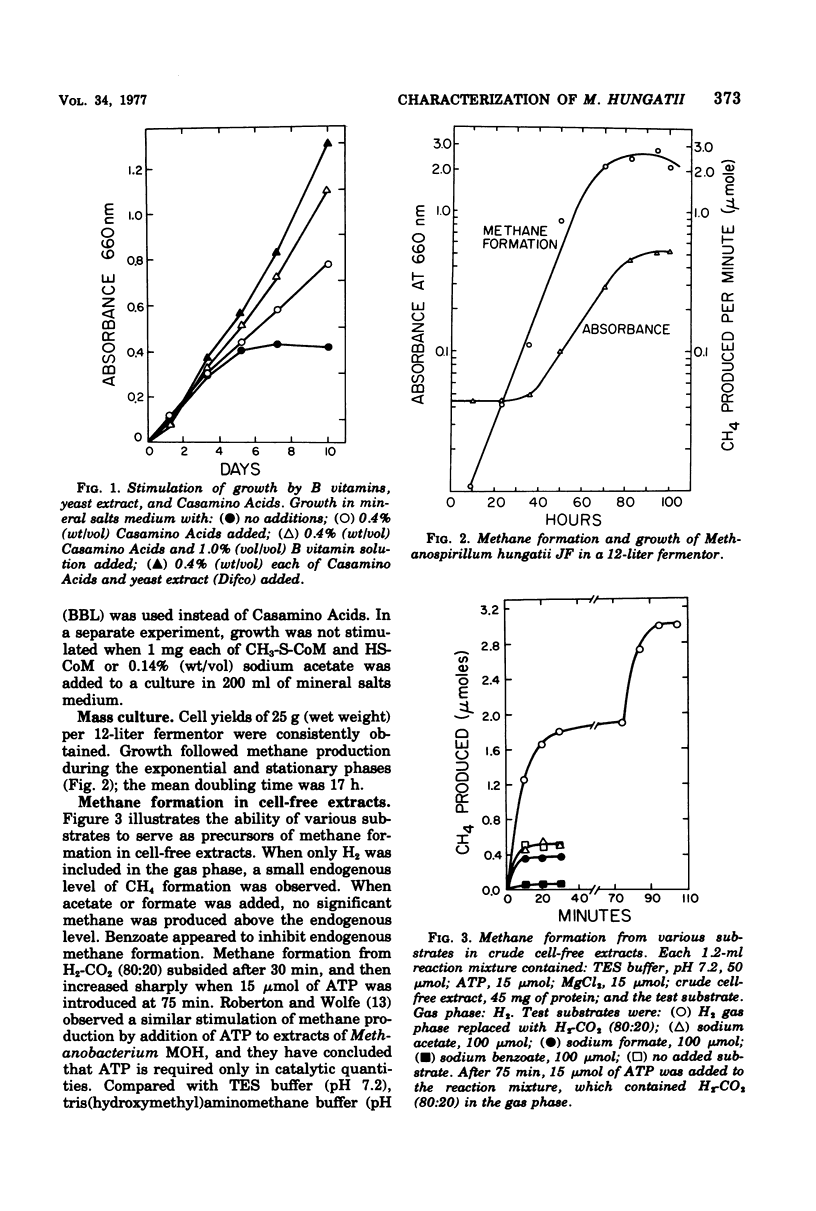
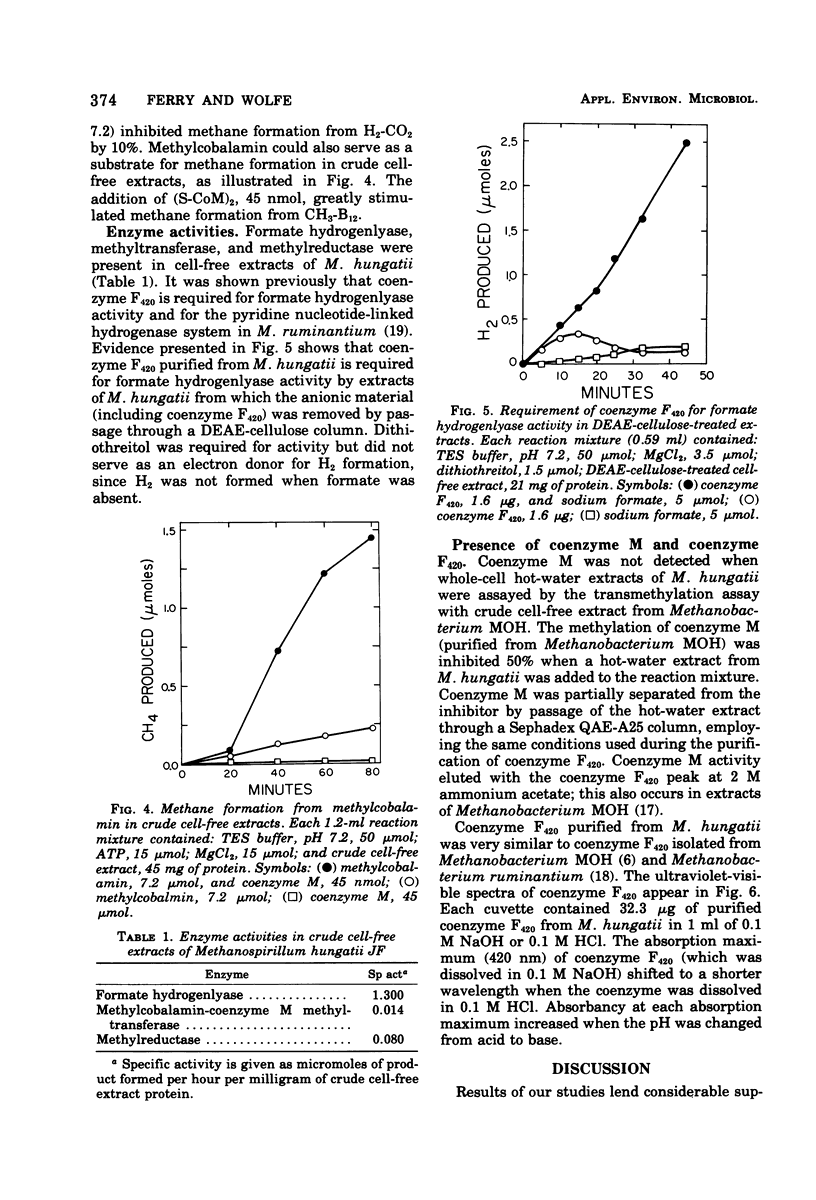
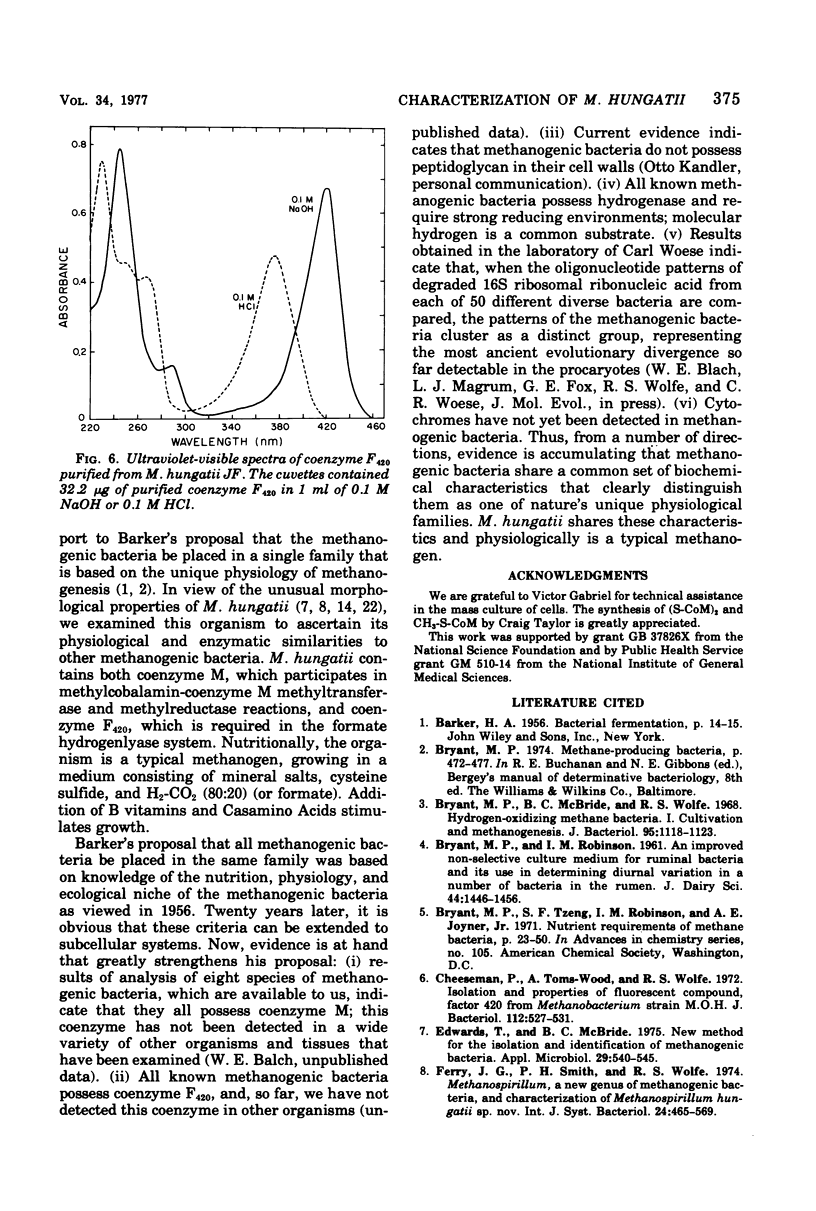
To ascertain its physiological similarity to other methanogenic bacteria, Methanospirillum hungatii, the type species of the genus, was characterized nutritionally and biochemically. Good growth occurred in a medium consisting of mineral salts, cysteine sulfide reducing buffer, and an H2-CO2 (80:20) atmosphere. Addition of amino acids and B vitamins stimulated growth. Cell-free extracts contained methylcobalamin-coenzyme M methyltransferase, methylreductase, and formate hydrogenlyase. Cells contained coenzyme M and coenzyme F420. Coenzyme F420 was required for formate hydrogenlyase activity. Coenzyme F420 purified from M. hungatii had identical properties to that purified from species of Methanobacterium. The physiological basis of the family Methanobacteriaceae is strengthened by these findings.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bryant M. P., McBride B. C., Wolfe R. S. Hydrogen-oxidizing methane bacteria. I. Cultivation and methanogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1118–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1118-1123.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheeseman P., Toms-Wood A., Wolfe R. S. Isolation and properties of a fluorescent compound, factor 420 , from Methanobacterium strain M.o.H. J Bacteriol. 1972 Oct;112(1):527–531. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.1.527-531.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards T., McBride B. C. New method for the isolation and identification of methanogenic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Apr;29(4):540–545. doi: 10.1128/am.29.4.540-545.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MYLROIE R. L., HUNGATE R. E. Experiments on the methane bacteria in sludge. Can J Microbiol. 1954 Aug;1(1):55–64. doi: 10.1139/m55-008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paynter M. J., Hungate R. E. Characterization of Methanobacterium mobilis, sp. n., isolated from the bovine rumen. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1943–1951. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1943-1951.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson A. M., Wolfe R. S. ATP requirement for methanogenesis in cell extracts of methanobacterium strain M.o.H. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Dec 30;192(3):420–429. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(69)90391-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN T. C., BARKER H. A. Studies on the methane fermentation. X. A new formate-decomposing bacterium, Methanococcus vannielii. J Bacteriol. 1951 Sep;62(3):269–280. doi: 10.1128/jb.62.3.269-280.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. D., Wolfe R. S. A simplified assay for coenzyme M (HSCH2CH2SO3). Resolution of methylcobalamin-coenzyme M methyltransferase and use of sodium borohydride. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4886–4890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. D., Wolfe R. S. Structure and methylation of coenzyme M(HSCH2CH2SO3). J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4879–4885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng S. F., Wolfe R. S., Bryant M. P. Factor 420-dependent pyridine nucleotide-linked hydrogenase system of Methanobacterium ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):184–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.184-191.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzing S. F., Bryant M. P., Wolfe R. S. Factor 420-dependent pyridine nucleotide-linked formate metabolism of Methanobacterium ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):192–196. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.192-196.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN E. A., WOLIN M. J., WOLFE R. S. FORMATION OF METHANE BY BACTERIAL EXTRACTS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2882–2886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Bowen V. G. Fine structure of Methanospirillum hungatii. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):373–380. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.373-380.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicus sp. n., an anaerobic, autotrophic, extreme thermophile. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):707–715. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.707-713.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


