Abstract
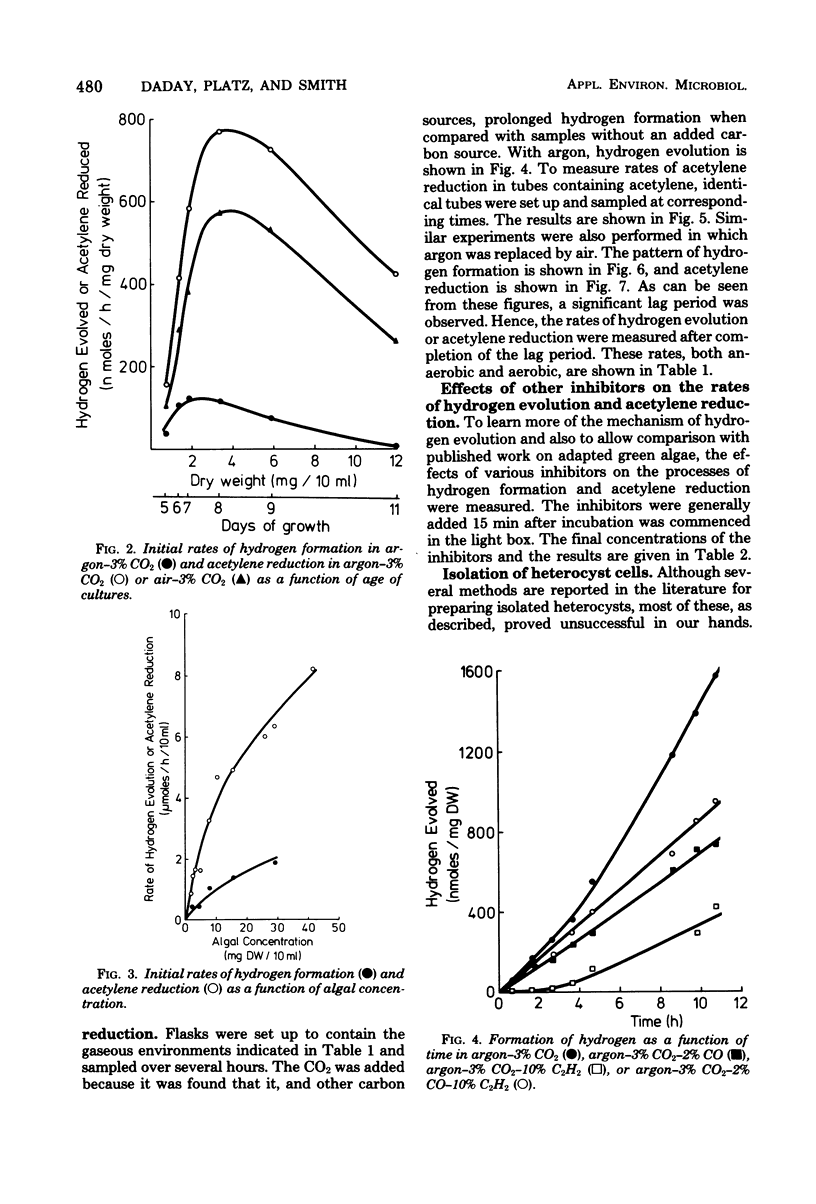
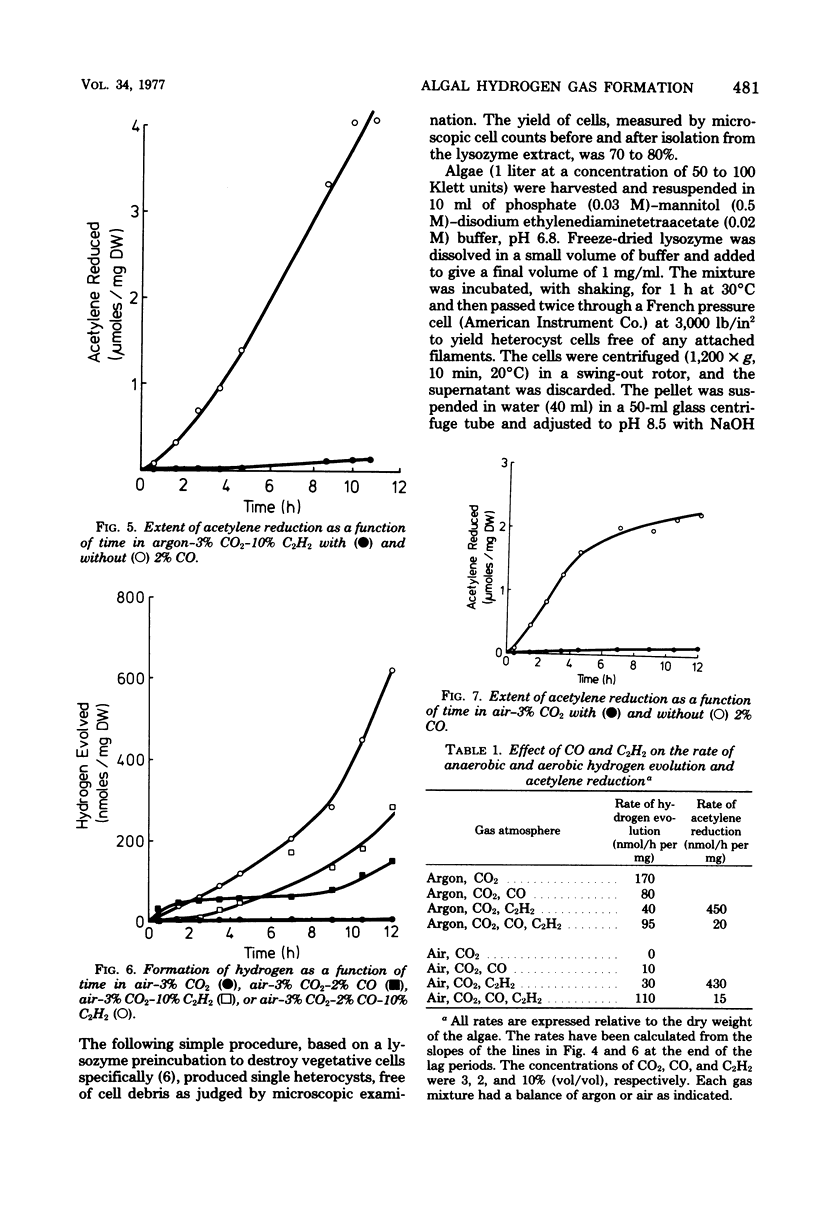
An investigation was made of certain factors involved in the formation of hydrogen gas, both in an anaerobic environment (argon) and in air, by the blue-green alga Anabaena cylindrica. The alga had not been previously adapted under hydrogen gas and hence the hydrogen evolution occurred entirely within the nitrogen-fixing heterocyst cells; organisms grown in a fixed nitrogen source, and which were therefore devoid of heterocysts, did not produce hydrogen under these conditions. Use of the inhibitor dichlorophenyl-dimethyl urea showed that hydrogen formation was directly dependent on photosystem I and only indirectly dependent on photosystem II, consistent with heterocysts being the site of hydrogen formation. The uncouplers carbonyl cyanide chlorophenyl hydrazone and dinitrophenol almost completely inhibited hydrogen formation, indicating that the process occurs almost entirely via the adenosine 5′-triphosphate-dependent nitrogenase. Salicylaldoxime also inhibited hydrogen formation, again illustrating the necessity of photophosphorylation. Whereas hydrogen formation could usually only be observed in anaerobic, dinitrogen-free environments, incubation in the presence of the dinitrogen-fixing inhibitor carbon monoxide plus the hydrogenase inhibitor acetylene resulted in significant formation of hydrogen even in air. Hydrogen formation was studied in batch cultures as a function of age of the cultures and also as a function of culture concentration, in both cases the cultures being harvested in logarithmic growth. Hydrogen evolution (and acetylene-reducing activity) exhibited a distinct maximum with respect to the age of the cultures. Finally, the levels of the protective enzyme, superoxide dismutase, were measured in heterocyst and vegetative cell fractions of the organism; the level was twice as high in heterocyst cells (2.3 units/mg of protein) as in vegetative cells (1.1 units/mg of protein). A simple procedure for isolating heterocyst cells is described.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen M. B., Arnon D. I. Studies on Nitrogen-Fixing Blue-Green Algae. I. Growth and Nitrogen Fixation by Anabaena Cylindrica Lemm. Plant Physiol. 1955 Jul;30(4):366–372. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.4.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benemann J. R., Weare N. M. Hydrogen Evolution by Nitrogen-Fixing Anabaena cylindrica Cultures. Science. 1974 Apr 12;184(4133):174–175. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4133.174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin M. Photosynthesis as a resource for energy and materials. Photochem Photobiol. 1976 Jun;23(6):425–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1976.tb07276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvin M. Solar energy by photosynthesis. Science. 1974 Apr 19;184(4134):375–381. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4134.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOGG G. E. The production of extracellular nitrogenous substances by a blue-green alga. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1952 Apr 24;139(896):372–397. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1952.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P., Walsby A. E. Metabolic activities of isolated heterocysts of the blue-green alga Anabaena cylindrica. Nature. 1966 Jan 1;209(5018):94–95. doi: 10.1038/209094a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lex M., Stewart W. D. Algal nitrogenase, reductant pools and photosystem I activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 22;292(2):436–443. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert K. R., Evans H. J. Hydrogen evolution: A major factor affecting the efficiency of nitrogen fixation in nodulated symbionts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1207–1211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith L. A., Hill S., Yates M. G. Inhibition by acetylene of conventional hydrogenase in nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Nature. 1976 Jul 15;262(5565):209–210. doi: 10.1038/262209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weare N. M., Benemann J. R. Nitrogen fixation by Anabaena cylindrica. II. Nitrogenase activity during induction and aging of batch cultures. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Oct 19;93(2):101–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



