Abstract
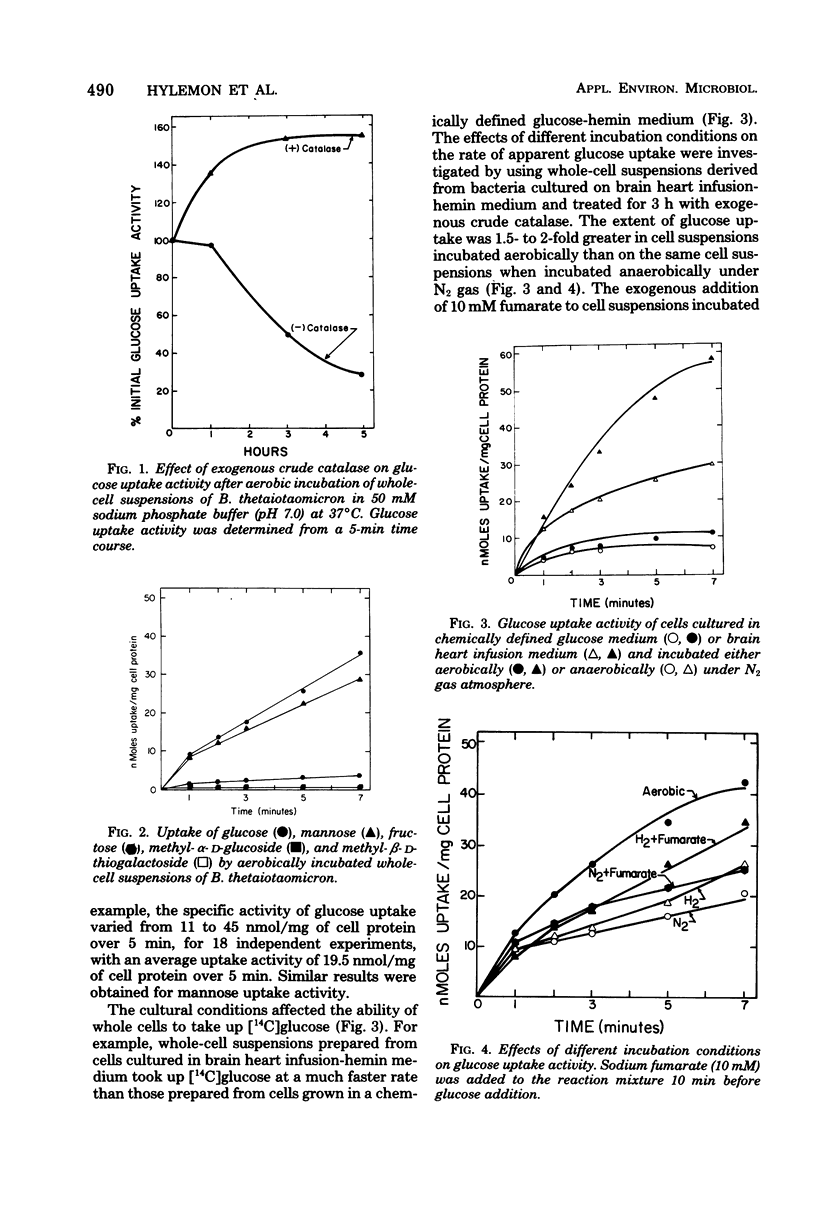
Glucose uptake by whole-cell suspensions of the obligate anaerobe Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron was two- to fourfold higher under aerobic conditions than during incubation under atmospheres of N2 or H2 gas. The O2-stimulated uptake activity was lost rapidly (>70% in 5 h) when cell suspensions were incubated aerobically, but this loss was prevented by the addition of crude catalase. Catalase had no apparent effect on cell viability during these incubations. Glucose uptake activity was strongly inhibited by a 10-fold excess of mannose or galactose but not by methyl-α-d-glucoside, fructose, or lactose. Both glucose and mannose were rapidly incorporated into polyglucose after uptake. The O2-stimulated glucose uptake was not inhibited by cyanide, azide, 2,4-dinitrophenol, or 2-N-heptyl-4-hydroxyquinoline-N-oxide. However, p-chloromercuribenzoate, menadione, and sodium fluoride inhibited uptake by 88, 67, and 55%, respectively. All attempts to detect phosphoenolpyruvate-phosphotransferase activity for glucose, methyl-α-d-glucoside, and 2-deoxyglucose were negative. The bacteria contained hexokinase activity and a complete glycolytic Embden-Meyerhof pathway.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheng K. J., Hironaka R., Roberts D. W., Costerton J. W. Cytoplasmic glycogen inclusions in cells of anaerobic gram-negative rumen bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Dec;19(12):1501–1506. doi: 10.1139/m73-244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gachelin G. A new assay of the phosphotransferase system in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Feb 21;34(4):382–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90392-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdeman L. V., Good I. J., Moore W. E. Human fecal flora: variation in bacterial composition within individuals and a possible effect of emotional stress. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):359–375. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.359-375.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett M. R., Mountfort D. O., Turner K. W., Roberton A. M. Metabolism and growth yields in Bacteroides ruminicola strain b14. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Aug;32(2):274–283. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.2.274-283.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Krieg N. R., Phibbs P. V., Jr Transport and catabolism of D-fructose by Spirillum itersomii. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):144–150. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.144-150.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Phibbs P. V., Jr Evidence against the presence of cyclic AMP and related enzymes in selected strains of Bacteroides fragilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 9;60(1):88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Phibbs P. V., Jr Independent regulation of hexose catabolizing enzymes and glucose transport activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1041–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90813-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. The role of the phosphoenolpyruvate-phosphotransferase system in the transport of sugars by isolated membrane preparations of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jul 10;243(13):3711–3724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundig W., Kundig F. D., Anderson B., Roseman S. Restoration of active transport of glycosides in Escherichia coli by a component of a phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3243–3246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macy J., Probst I., Gottschalk G. Evidence for cytochrome involvement in fumarate reduction and adenosine 5'-triphosphate synthesis by Bacteroides fragilis grown in the presence of hemin. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):436–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.436-442.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V. Human fecal flora: the normal flora of 20 Japanese-Hawaiians. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):961–979. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.961-979.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phibbs P. V., Jr, Eagon R. G. Transport and phosphorylation of glucose, fructose, and mannitol by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Jun;138(2):470–482. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90371-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preiss J., Lammel C., Greenberg E. Biosynthesis of bacterial glycogen. Kinetic studies of a glucose-1-P adenylyltransferase (EC 2.7.7.27) from a glycogen-excess mutant of Escherichia coli B. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 May;174(1):105–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90329-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Eberhard S. J., Dingle S. L., McDowell T. D. Distribution of the phosphoenolpyruvate: glucose phosphotransferase system in bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):808–813. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.808-813.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Vercellotti J. R., West S. E., Wilkins T. D. Fermentation of mucin and plant polysaccharides by strains of Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):319–322. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.319-322.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoni R. D., Levinthal M., Kundig F. D., Kundig W., Anderson B., Hartman P. E., Roseman S. Genetic evidence for the role of a bacterial phosphotransferase system in sugar transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1963–1970. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


