Abstract
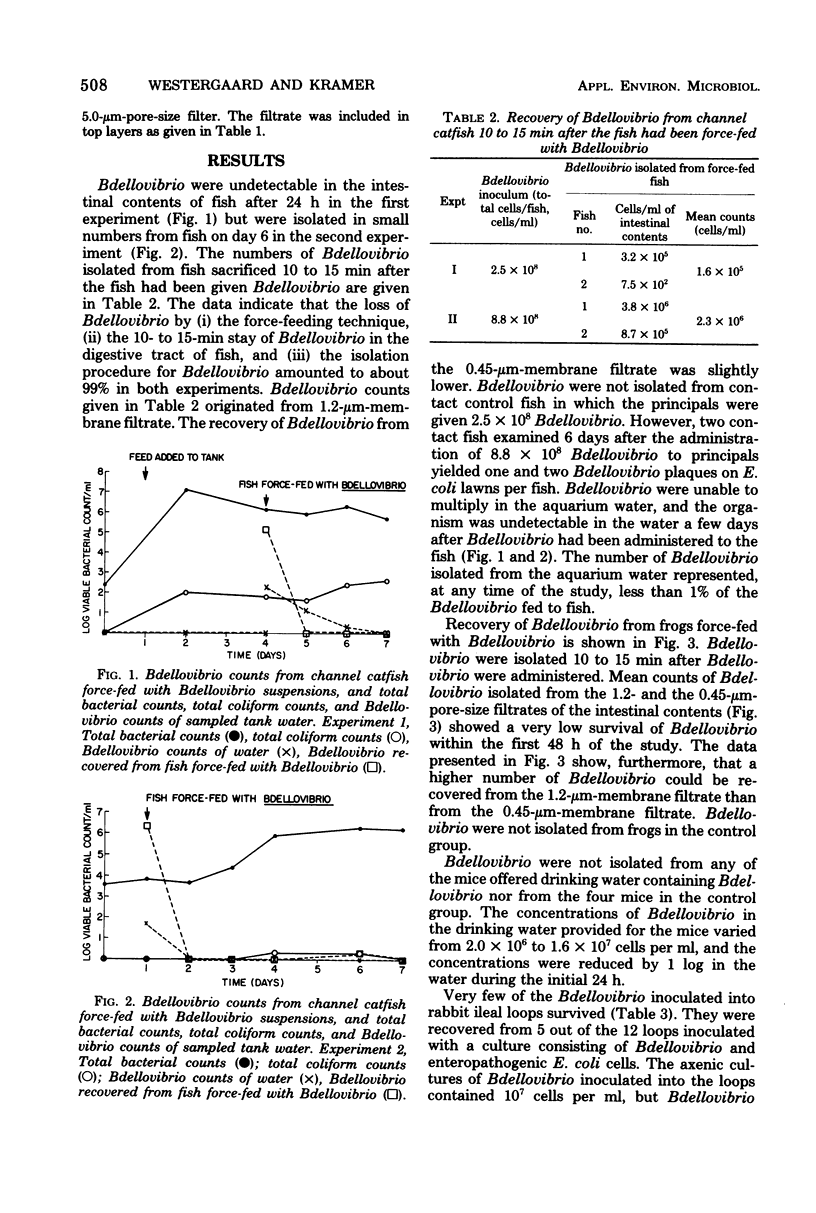
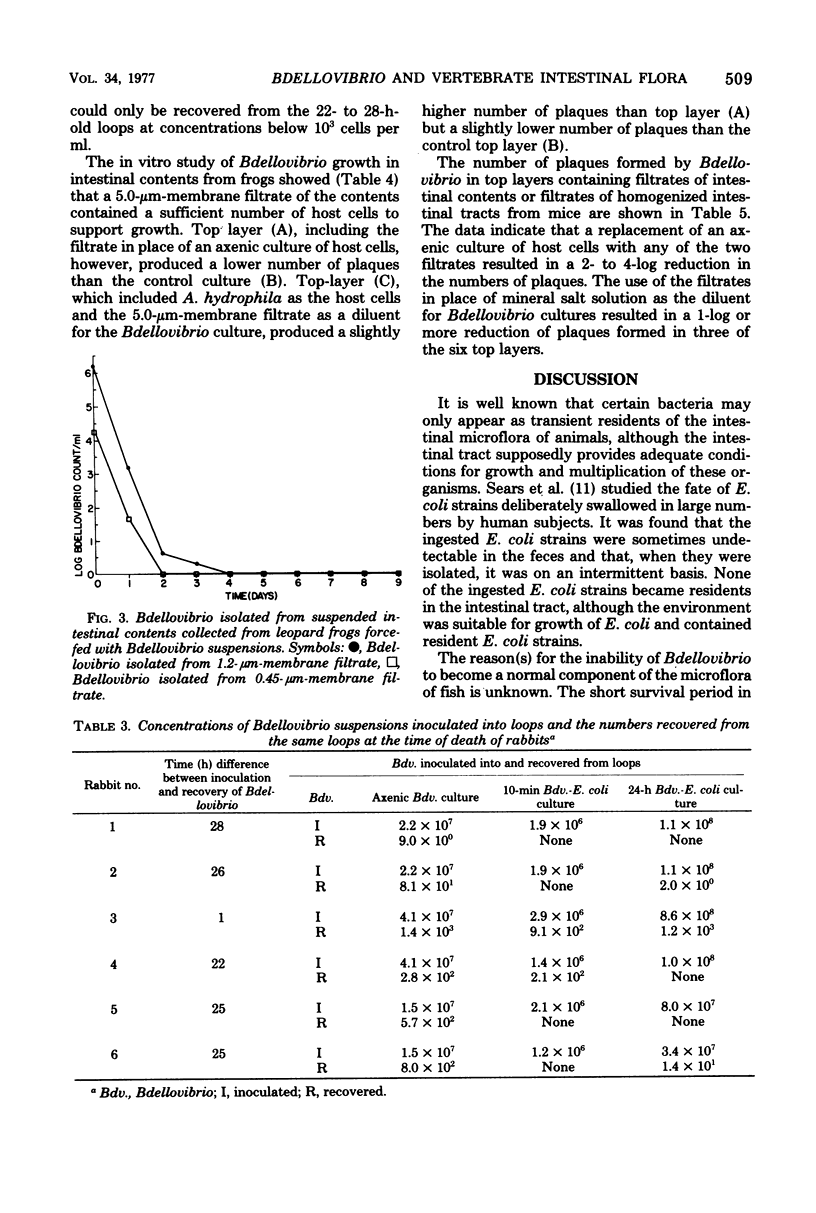
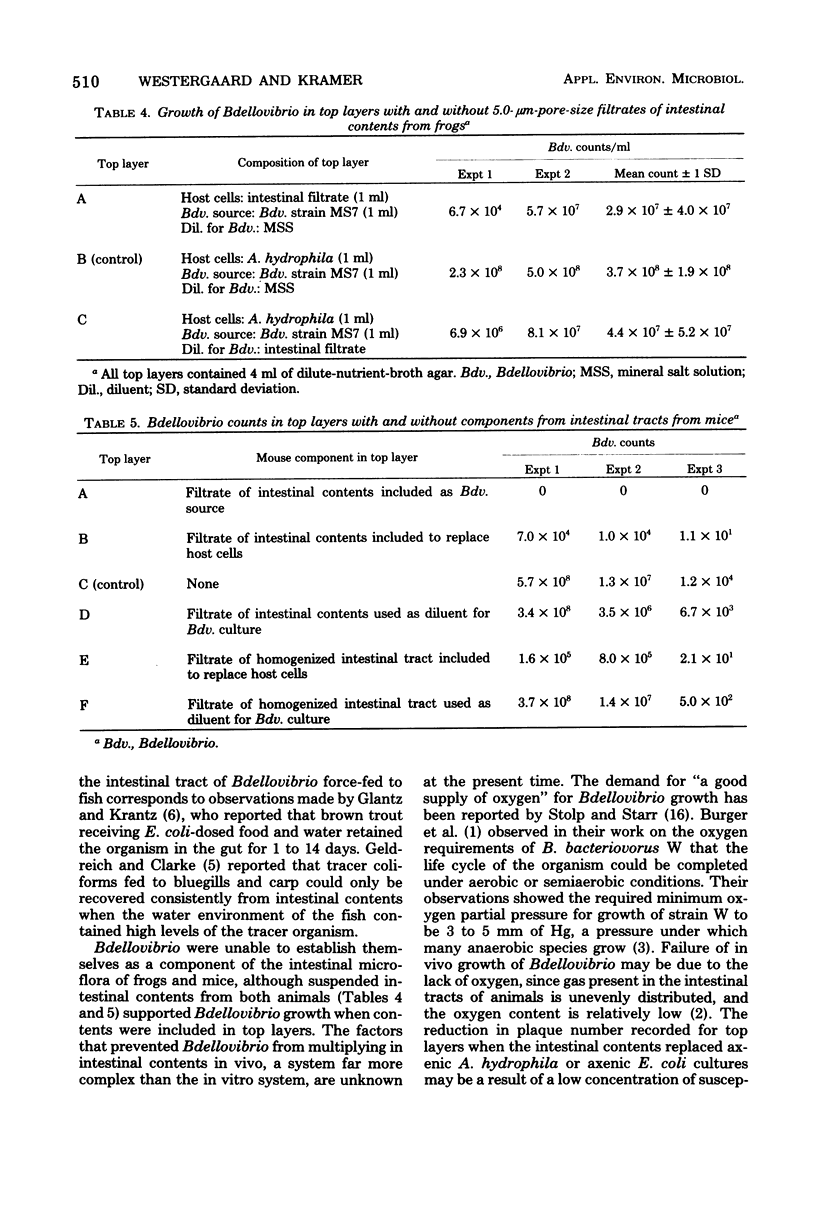
Bdellovibrio strain MS7 force-fed to fish and frogs via an intragastric tube did not become an integral component of the intestinal microflora. Strain MS7 fed to mice in drinking water was not recovered from the intestinal tract of mice. However, in vitro, the organism multiplied in intestinal contents of frogs and mice. Bdellovibrio inoculated into rabbit ileal loops was greatly reduced in number within 24 h. It was concluded that strains MS7 could be considered nonpathogenic to animals, at least when introduced into the digestive tract, and that it is not feasible at the present time to lyse pathogenic, gram-negative bacteria in the alimentary tract with Bdellovibrio.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burger A., Drews G., Ladwig R. Wirtskreis und Infektionscyclus eines neu isolierten Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus-Stammes. Arch Mikrobiol. 1968 May 8;61(3):261–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLANTZ P. J., KRANTZ G. E. ESCHERICHIA COLI SEROTYPES ISOLATED FROM FISH AND THEIR ENVIRONMENT. Health Lab Sci. 1965 Jan;2:54–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geldreich E. E., Clarke N. A. Bacterial pollution indicators in the intestinal tract of freshwater fish. Appl Microbiol. 1966 May;14(3):429–437. doi: 10.1128/am.14.3.429-437.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaura Y. K., Sharma V. K., Singh I. P., Sakazaki R., Rohde R. Snakes as reservoirs of Arizona and Salmonella. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1972 Apr;219(4):506–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Rittenberg S. C. Kinetics of deoxyribonucleic acid destruction and synthesis during growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus strain 109D on pseudomonas putida and escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Sep;111(3):664–673. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.3.664-673.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura M. Alteration of Shigella pathogenicity by other bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1441–1451. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS H. J., BROWNLEE I., UCHIYAMA J. K. Persistence of individual strains of Escherichia coli in the intestinal tract of man. J Bacteriol. 1950 Feb;59(2):293–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.59.2.293-301.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOLP H., STARR M. P. BDELLOVIBRIO BACTERIOVORUS GEN. ET SP. N., A PREDATORY, ECTOPARASITIC, AND BACTERIOLYTIC MICROORGANISM. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1963;29:217–248. doi: 10.1007/BF02046064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidler R. J., Starr M. P. Factors affecting the intracellular parasitic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus developing within Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):912–923. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.912-923.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr M. P., Huang J. C. Physiology of the bdellovibrios. Adv Microb Physiol. 1972;8:215–261. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starr M. P., Huang J. C. Physiology of the bdellovibrios. Adv Microb Physiol. 1972;8:215–261. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verklova Z. S. Izuchenie virulentnosti, toksichnosti, immunogennosti razlichnykh shtammov Bdellovibrio bakteriovorus. Gig Sanit. 1973 Mar;38(3):10–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


