Abstract
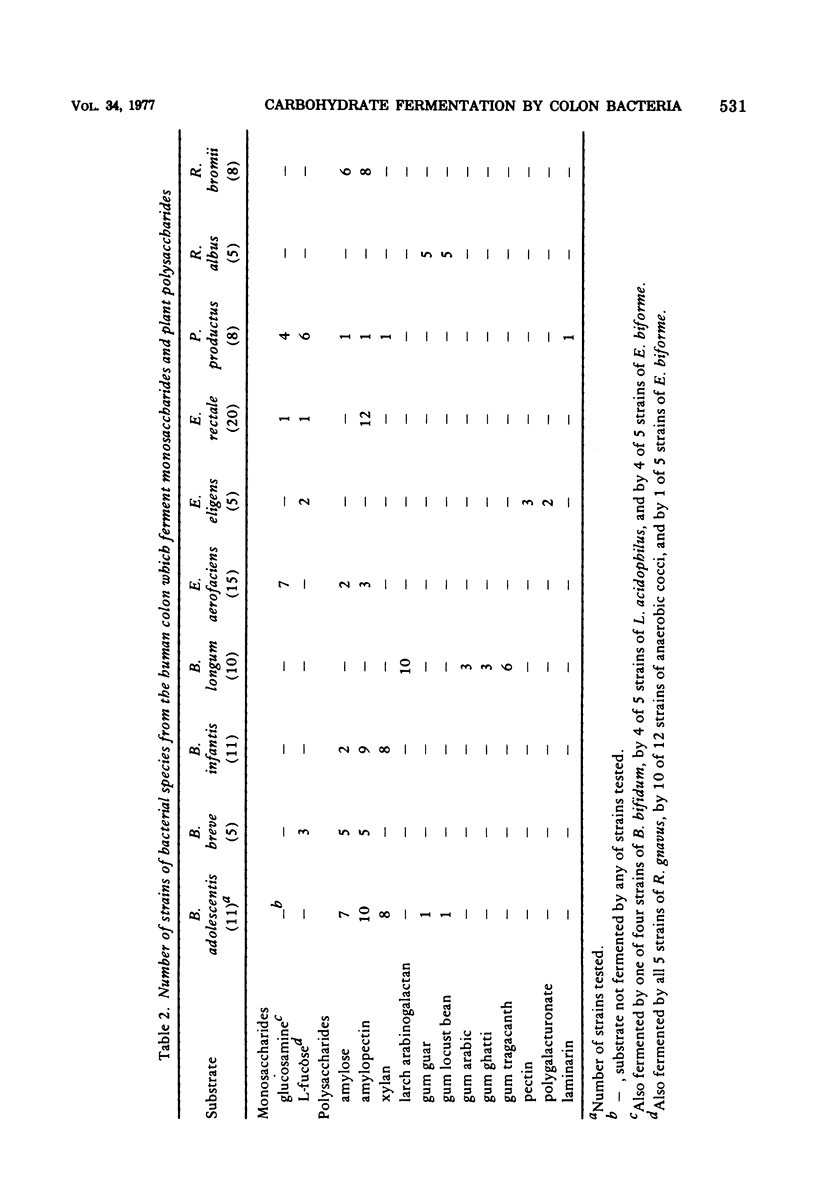
A total of 154 strains from 22 species of Bifidobacterium, Peptostreptococcus, Lactobacillus, Ruminococcus, Coprococcus, Eubacterium, and Fusobacterium, which are present in high concentrations in the human colon, were surveyed for their ability to ferment 21 different complex carbohydrates. Plant polysaccharides, including amylose, amylopectin, pectin, polygalacturonate, xylan, laminarin, guar gum, locust bean gum, gum ghatti, gum arabic, and gum tragacanth, were fermented by some strains from Bifidobacterium, Peptostreptococcus, Ruminococcus, and Eubacterium species. Porcine gastric mucin, which was fermented by some strains of Ruminococcus torques and Bifidobacterium bifidum, was the only mucin utilized by any of the strains tested.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N., BOUMA C., CHU H. Bacteroides ruminicola n. sp. and Succinimonas amylolytica; the new genus and species; species of succinic acid-producing anaerobic bacteria of the bovine rumen. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jul;76(1):15–23. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.1.15-23.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betian H. G., Linehan B. A., Bryant M. P., Holdeman L. V. Isolation of a cellulotytic Bacteroides sp. from human feces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):1009–1010. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.1009-1010.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P. Nutritional features and ecology of predominant anaerobic bacteria of the intestinal tract. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Nov;27(11):1313–1319. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.11.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEHORITY B. A. DEGRADATION AND UTILIZATION OF ISOLATED HEMICELLULOSE BY PURE CULTURES OF CELLULOLYTIC RUMEN BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1515–1520. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1515-1520.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker R. F., Richards G. N. Hemicellulases: their occurrence, purification, properties, and mode of action. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem. 1976;32:277–352. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2318(08)60339-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradel C. M., Dehority B. A. Fermentation of isolated pectin and pectin from intact forages by pure cultures of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Feb;23(2):332–340. doi: 10.1128/am.23.2.332-340.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoskins L. C., Boulding E. T. Degradation of blood group antigens in human colon ecosystems. I. In vitro production of ABH blood group-degrading enzymes by enteric bacteria. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):63–73. doi: 10.1172/JCI108270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabbal I., Kells D. I., Forstner G., Forstner J. Human intestinal goblet cell mucin. Can J Biochem. 1976 Aug;54(8):707–716. doi: 10.1139/o76-102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V. Human fecal flora: the normal flora of 20 Japanese-Hawaiians. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):961–979. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.961-979.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Palmer J. K., Wilkins T. D. Laminarinase (beta-glucanase) activity in Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1118–1124. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1118-1124.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salyers A. A., Vercellotti J. R., West S. E., Wilkins T. D. Fermentation of mucin and plant polysaccharides by strains of Bacteroides from the human colon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):319–322. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.319-322.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannock G. W. Characteristics of Bacteroides isolates from the cecum of conventional mice. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):745–750. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.745-750.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Walker C. B. Development of a micromethod for identification of anaerobic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Nov;30(5):825–830. doi: 10.1128/am.30.5.825-830.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins T. D., Walker C. B., Moore W. E. Micromethod for identification of anaerobic bacteria: design and operation of apparatus. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Nov;30(5):831–837. doi: 10.1128/am.30.5.831-837.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


