Abstract
The acetylene reduction assay for the measurement of N2 fixation in a water-saturated paddy soil is limited by the slow diffusion of acetylene and ethylene. In laboratory incubation tests, vigorous shaking after the assay period is needed to release ethylene into the gas within the assay vials. Shaking prior to the incubation is also effective for dissolving acetylene in the water-saturated soil. However, a water-saturated soil depth of less than 10 mm during incubation is recommended. In field assays, some amounts of ethylene remain in the water-saturated soil phase of the acetylene reduction assay chamber, but stirring the water-saturated soil before sampling reduces the amount of ethylene remaining in soil. Evidence of a downward movement of acetylene and an upward movement of ethylene through rice plants was obtained. Because of the rapid transfer of acetylene to rice plant roots, an in situ acetylene reduction assay covering a rice hill is likely to detect nitrogen fixation in the proximity of roots where acetylene is easily accessible. Acetylene introduction to the water-saturated soil phase prior to assay did not greatly increase the acetylene reduction rate. Carbon dioxide enrichment in the assay chamber did not enhance nitrogen fixation in a paddy including rice and algae during a 1-day cycle.
Full text
PDF
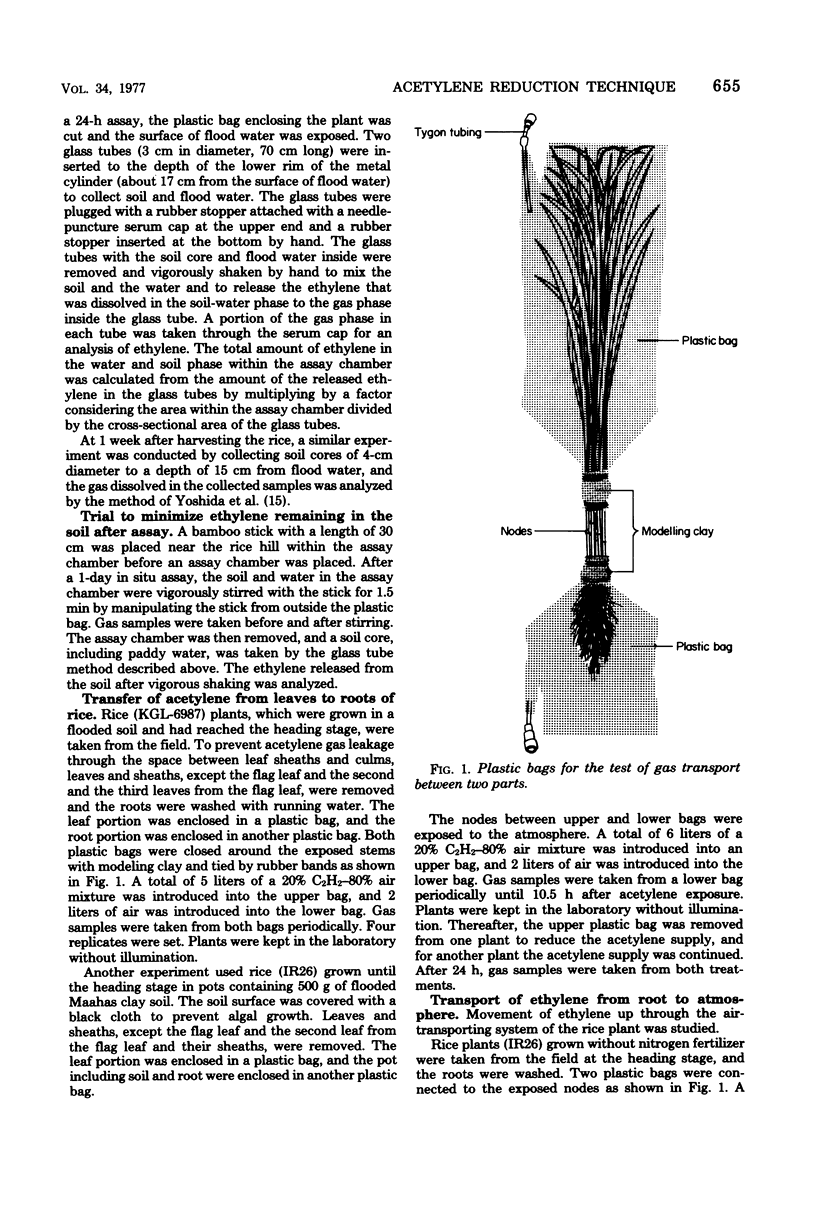
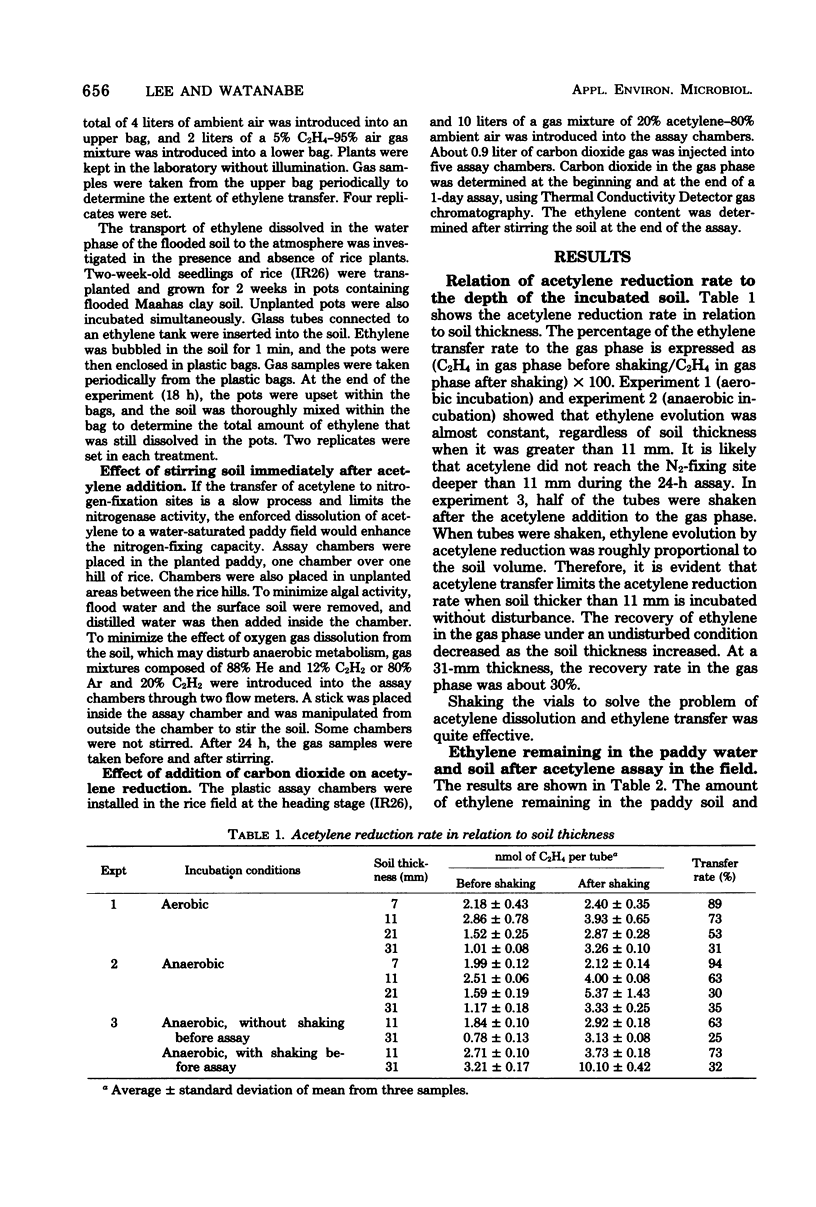
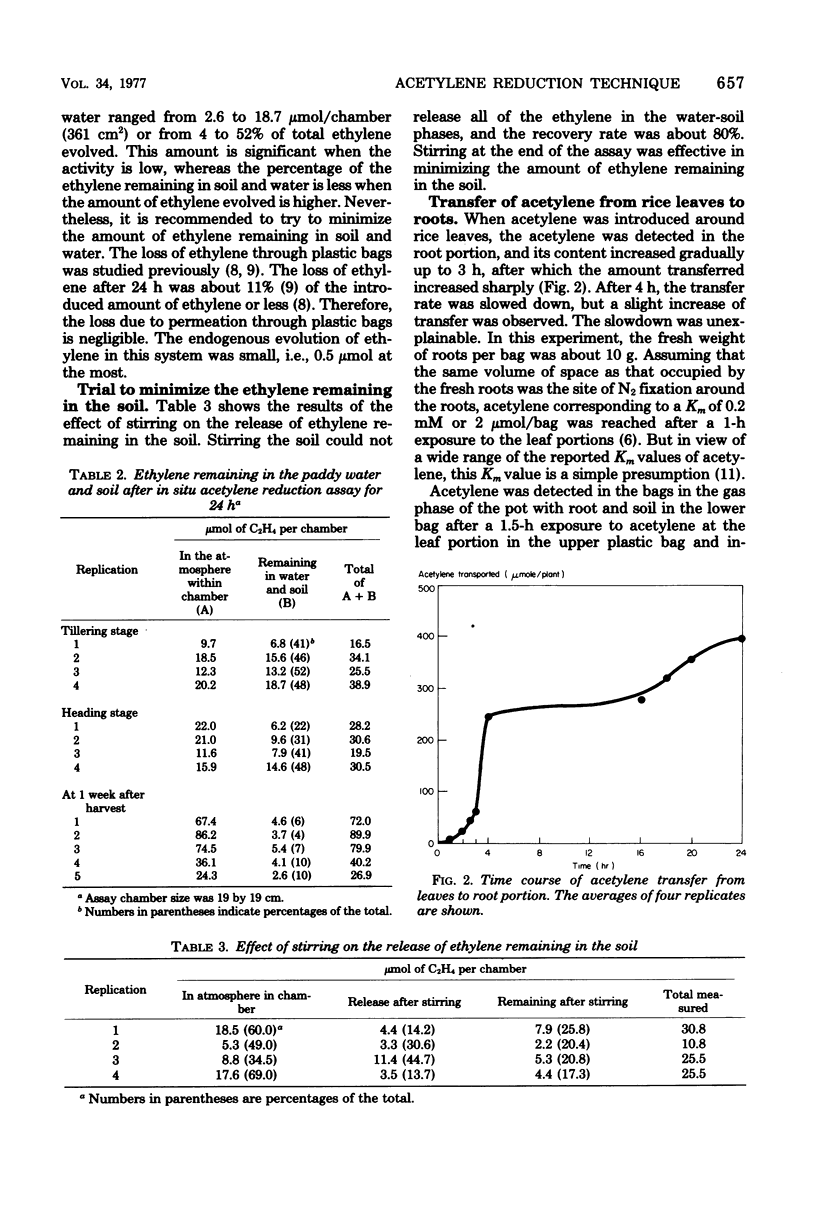
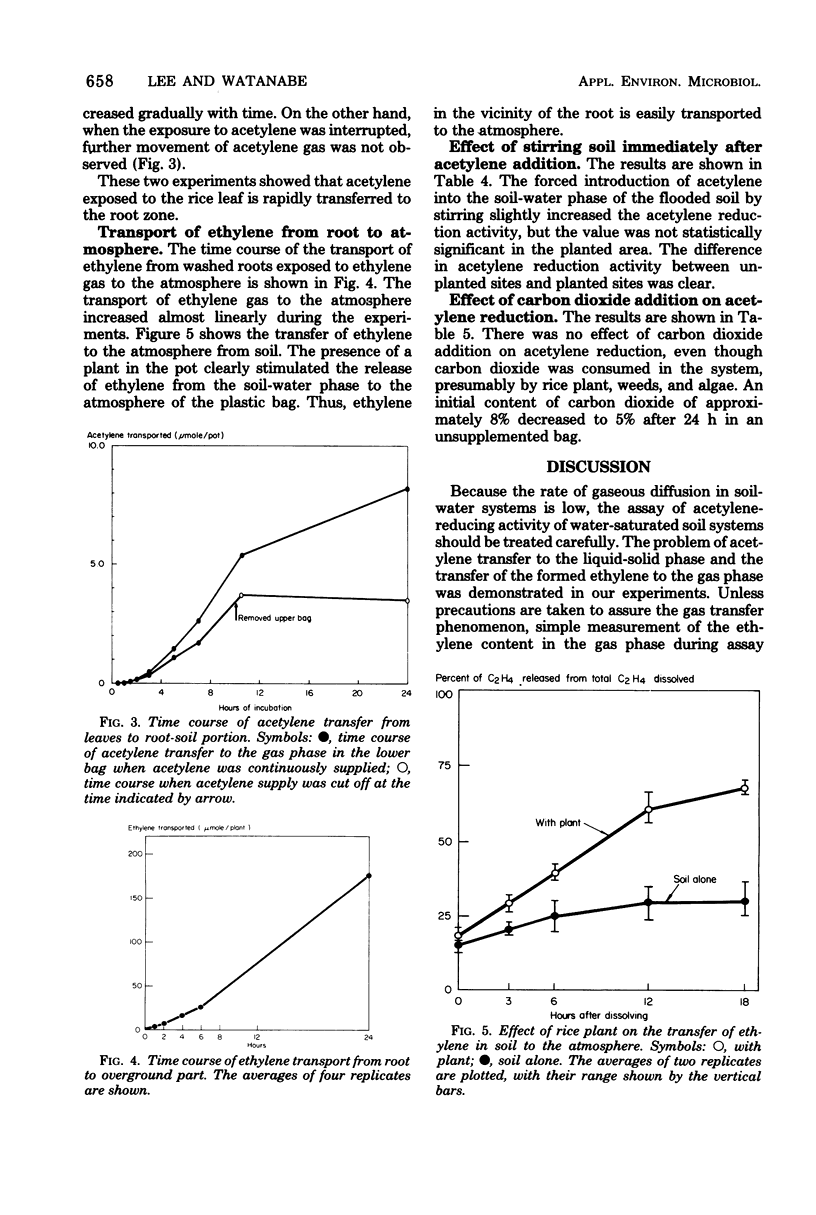

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Flett R. J., Hamilton R. D., Campbell N. E. Aquatic acetylene-reduction techniques: solutions to several problems. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jan;22(1):43–51. doi: 10.1139/m76-006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


