Abstract
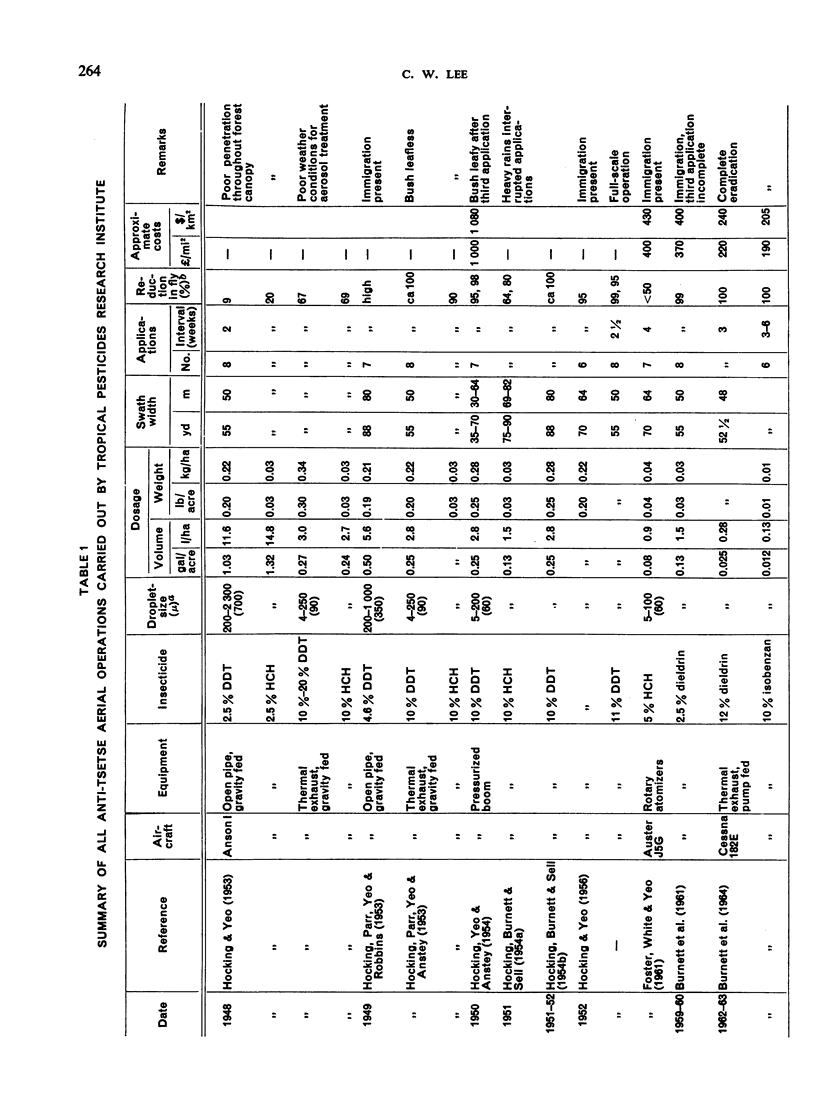
Since 1948, research has progressed in East Africa on the control of tsetse flies by aeria, applications of insecticides. Initial experiments proved that residual spray treatments were ineffective while repeated applications of coarse aerosols gave promising fly mortalities.
In recent years, with the development of more toxic insecticides used in conjunction with improved thermal exhaust equipment and modified rotary atomizers, sprays with fine aerosol characteristics have been produced at considerably reduced cost. Aerial applications of aerosols are confined to early morning and late afternoon when weather conditions are stable, but large areas can be treated during these short intervals, and the technique is efficient and economical. Control of tsetse flies has been good; where complete isolation of an area has been possible, eradication has been achieved.
It would be economically worth while to assess the possibility of increasing spray swath widths, and also to continue with research into the biological effectiveness of pyrethrum, primarily because of its absolute safety in use. There is a need for a simple method for the determination of tsetse fly populations in woodland and savanna habitats. Finally, it is recommended that the results of research to date should be brought more forcefully to the attention of government bodies and commercial airspray operators so that the techniques be more fully exploited.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNETT G. F. Effect of age and pregnancy on the tolerance of tsetse flies to insecticides. Nature. 1961 Oct 14;192:188–188. doi: 10.1038/192188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hocking K. S., Lee C. W., Beesley J. S., Matechi H. T. Aircraft applications of insecticides in East Africa. XVI.Airspray experiment with endosulfan against Glossina morsitans Westw., G. swynnertoni Aust. and G. pallidipes Aust. Bull Entomol Res. 1966 Aug;56(4):737–744. doi: 10.1017/s0007485300056728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


