Abstract
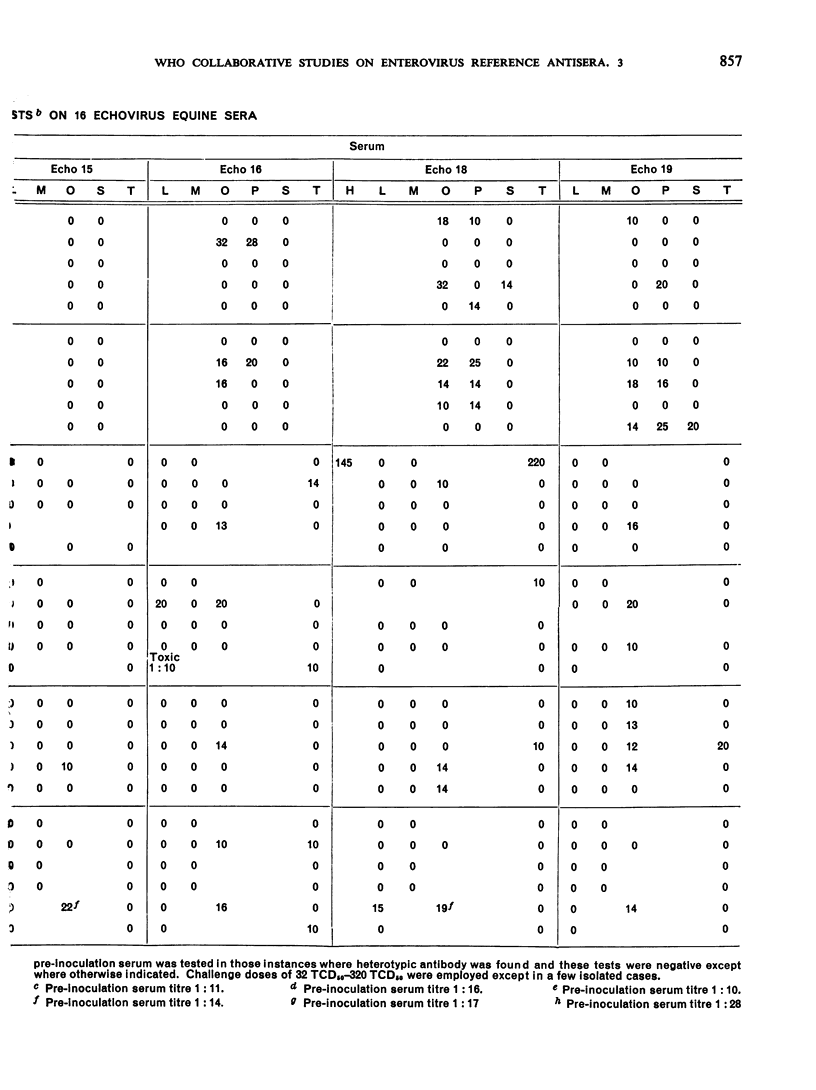
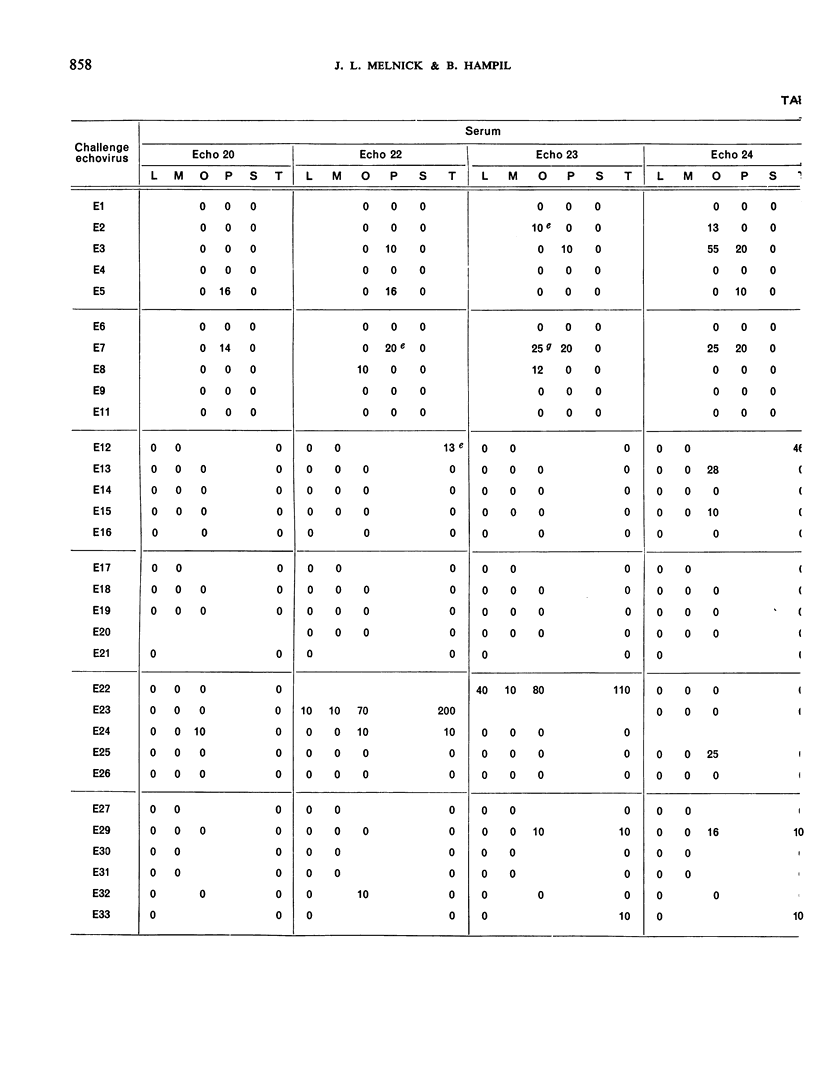
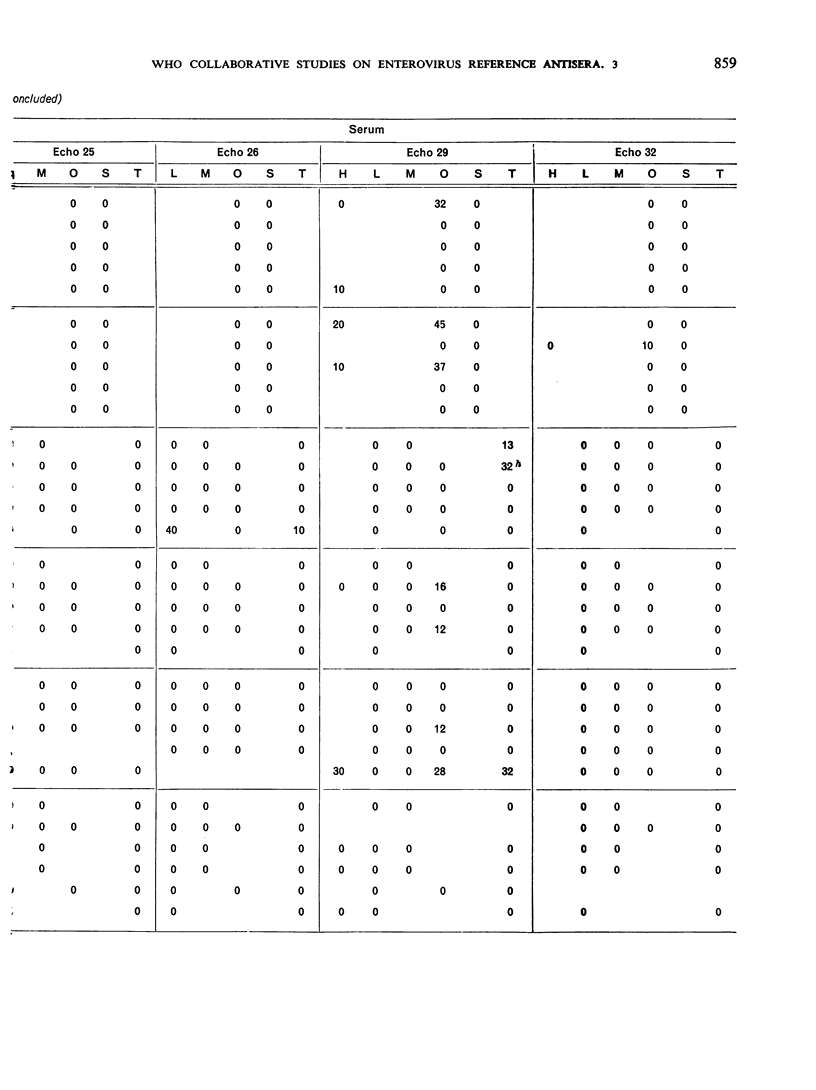
This paper smmarizes the results of the third part of co-operative studies undertaken by the WHO International Reference Centre for Enteroviruses and a number of WHO Regional Virus Reference Centres and WHO Virus Collaborating Laboratories and other laboratories in a comprehensive testing programme of enterovirus equine antisera prepared for long-term use as reference antisera. The studies were designed to appraise the specificity of the immune serum of horses inoculated with prototype enteroviruses (coxsackie-viruses A1, A5, A6, A12 and A22 and echoviruses 5, 6, 13-16, 18-20, 22-26, 29 and 32). Tests for neutralizing antibody were performed not only against the homologous viruses but also against regional homotypic strains. Tests for heterotypic antibody were made against the entire group of enteroviruses (except enterovirus 68), reoviruses 1-3, and adenoviruses 1-11, 13-17 and 19-22. Final vials of the dried serum were provided for the tests. Each serum sample represented a pool of the individual bleedings taken from a group of horses before and after immunization with each virus antigen. The results showed that the homologous geometric mean titres of 9 of 16 echovirus immune sera were 10 000 or above while the other 7 ranged from 2000 to 8000. The homologous antibody titre of one coxsackievirus type A serum was about 2000 while the titres of the other 4 type A sera ranged from about 5000 to 15 000. All corresponding pre-inoculation sera were negative. The results of the homotypic tests, though limited in number, showed the usefulness of the sera. Data on heterotypic antibody titres, if any, are recorded for gidance in the use of the sera. Co-operative testing of 19 additional enterovirus equine sera is now in progress.
Full text
PDF













Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hampil B., Melnick J. L. WHO collaborative studies on enterovirus reference antisera: second report. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;38(4):577–593. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampil B., Melnick J. L., Wallis C., Brown R. W., Braye E. T., Adams R. R., Jr Preparation of antiserum to enteroviruses in large animals. J Immunol. 1965 Nov;95(5):895–908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMITSUKA P. S., LOU T. Y., FABIYI A., WENNER H. A. PREPARATION AND STANDARDIZATION OF COXSACKIEVIRUS REFERENCE ANTISERA. I. FOR TWENTY-FOUR GROUP A VIRUSES. Am J Epidemiol. 1965 May;81:283–306. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIM K. A., BENYESH-MELNICK M. Typing of viruses by combinations of antiserum pools. Application to typing of enteroviruses (Coxsackie and ECHO). J Immunol. 1960 Mar;84:309–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIDULLA M., WALLIS C., MELNICK J. L. ENTEROVIRUS IMMUNIZING ANTIGENS IN THE FORM OF CATION-STABILIZED AND CONCENTRATED VIRUS PREPARATIONS. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:9–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J. L., Hampil B. WHO collaborative studies on enterovirus reference antisera. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;33(6):761–772. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOHIER R., PEILLARD, GINESTE J., FREYDIER J. Micro-méthode en tubes pour la réaction de fixation du complément appliquée au diagnostic des infections a virus. Ann Biol Clin (Paris) 1956 Mar-Apr;14(3-4):281–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Virus aggregation as the cause of the non-neutralizable persistent fraction. J Virol. 1967 Jun;1(3):478–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.3.478-488.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


