Abstract
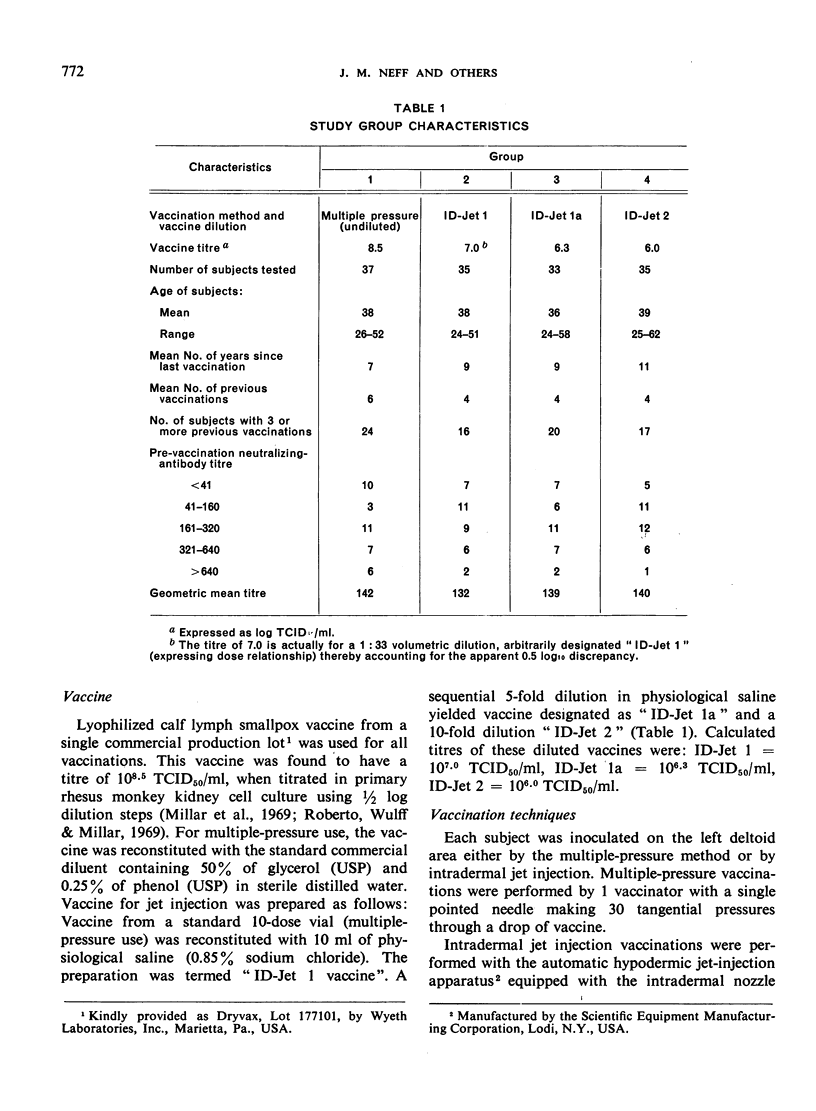
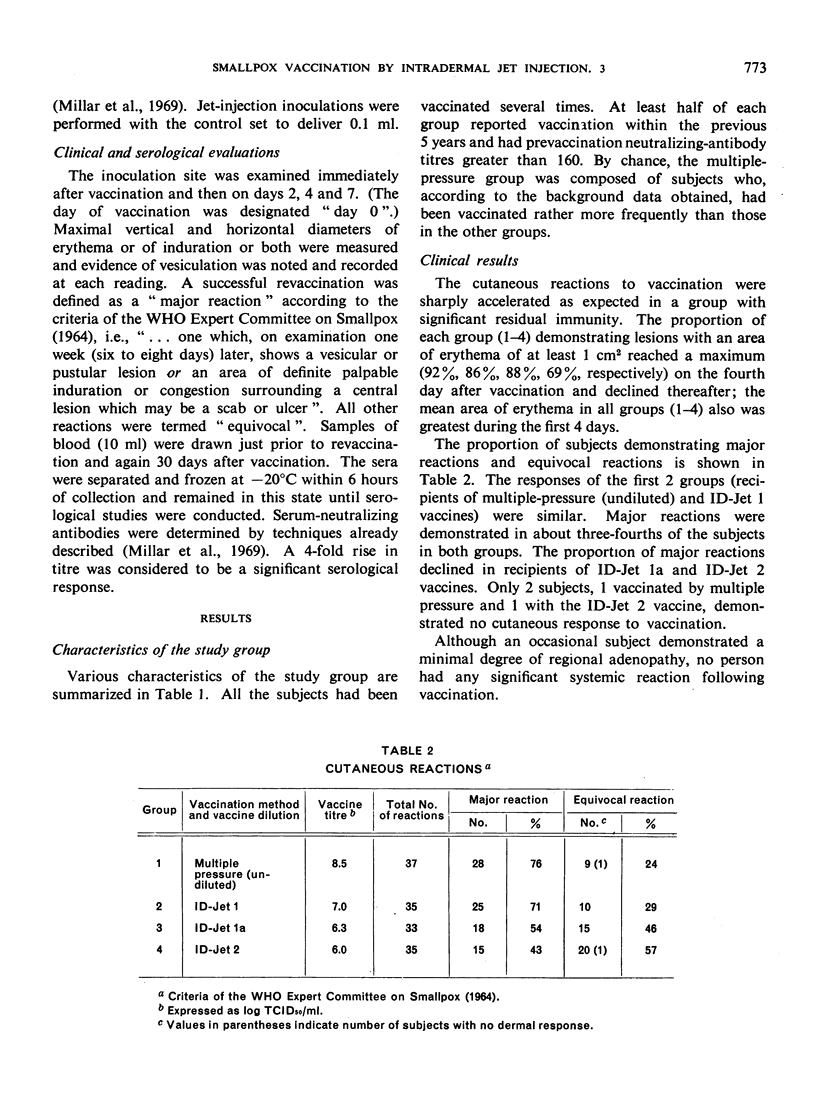
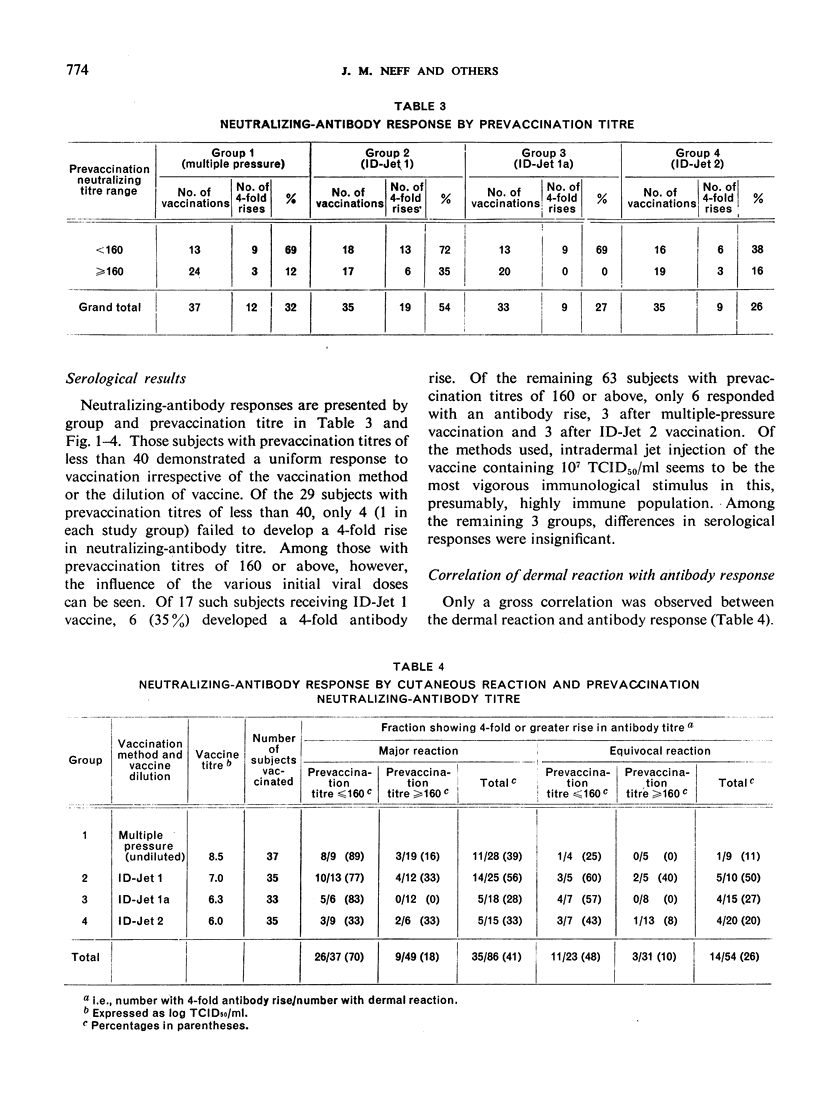
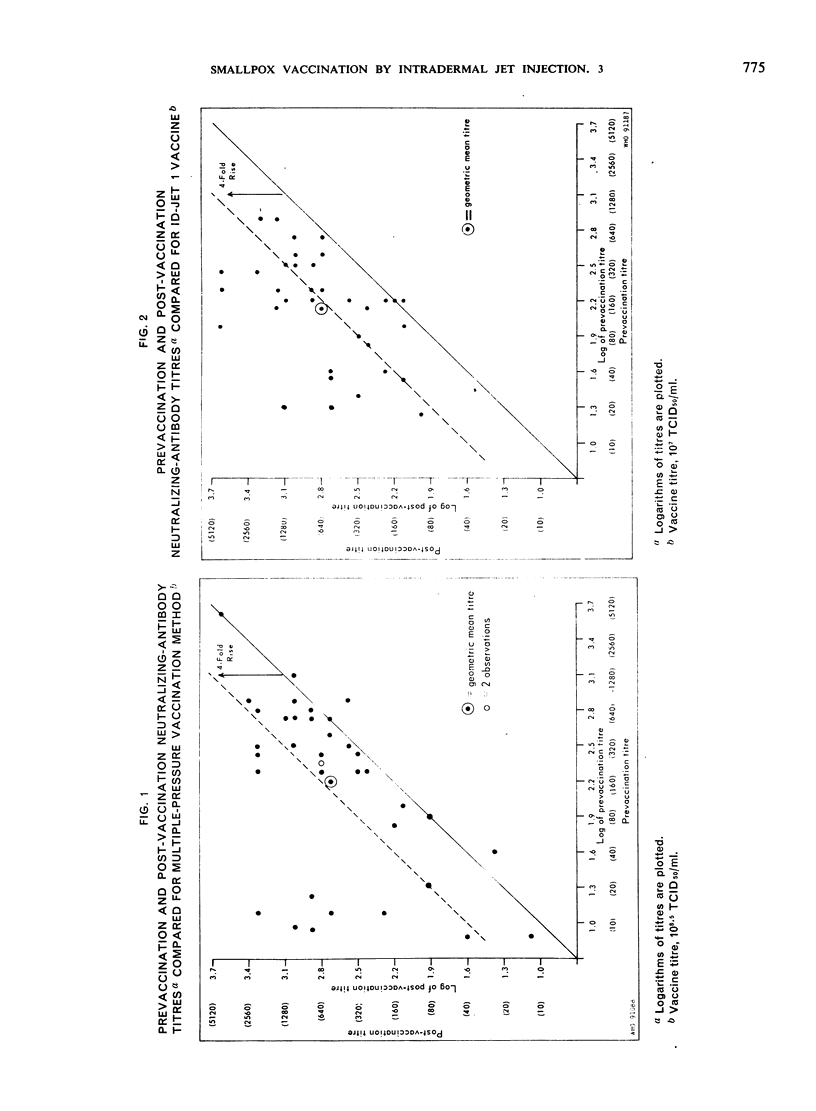
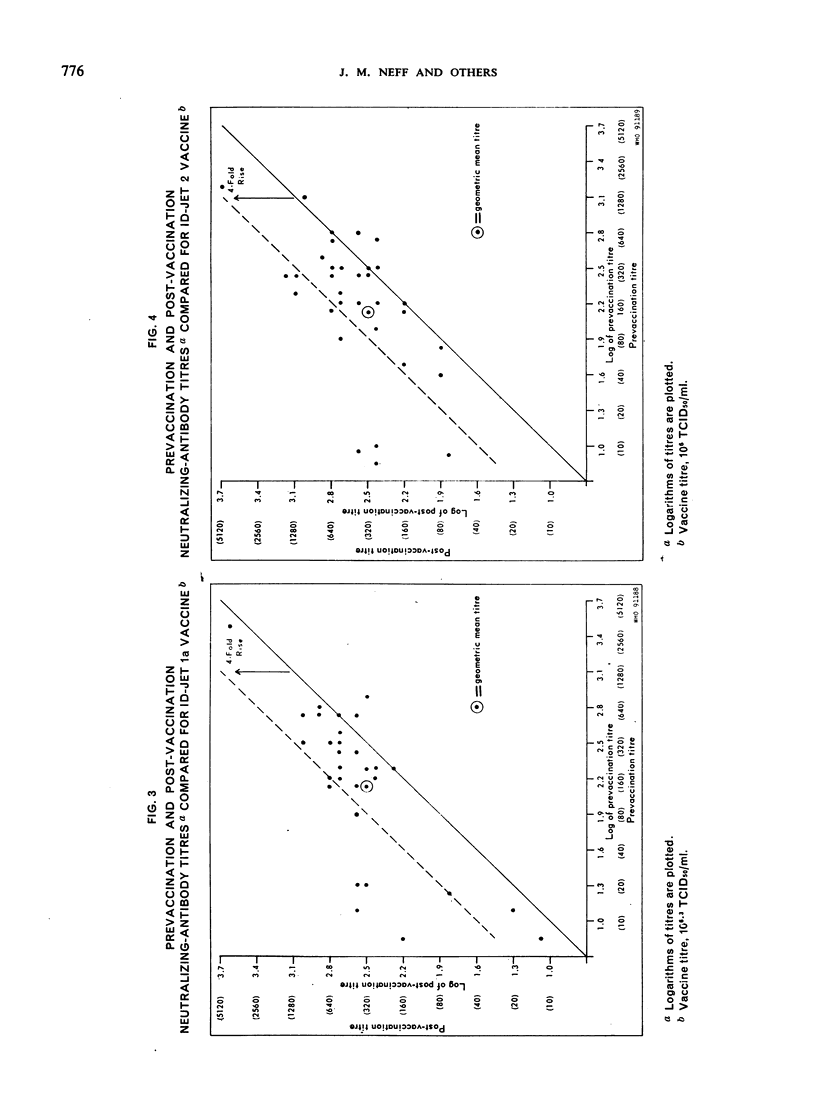
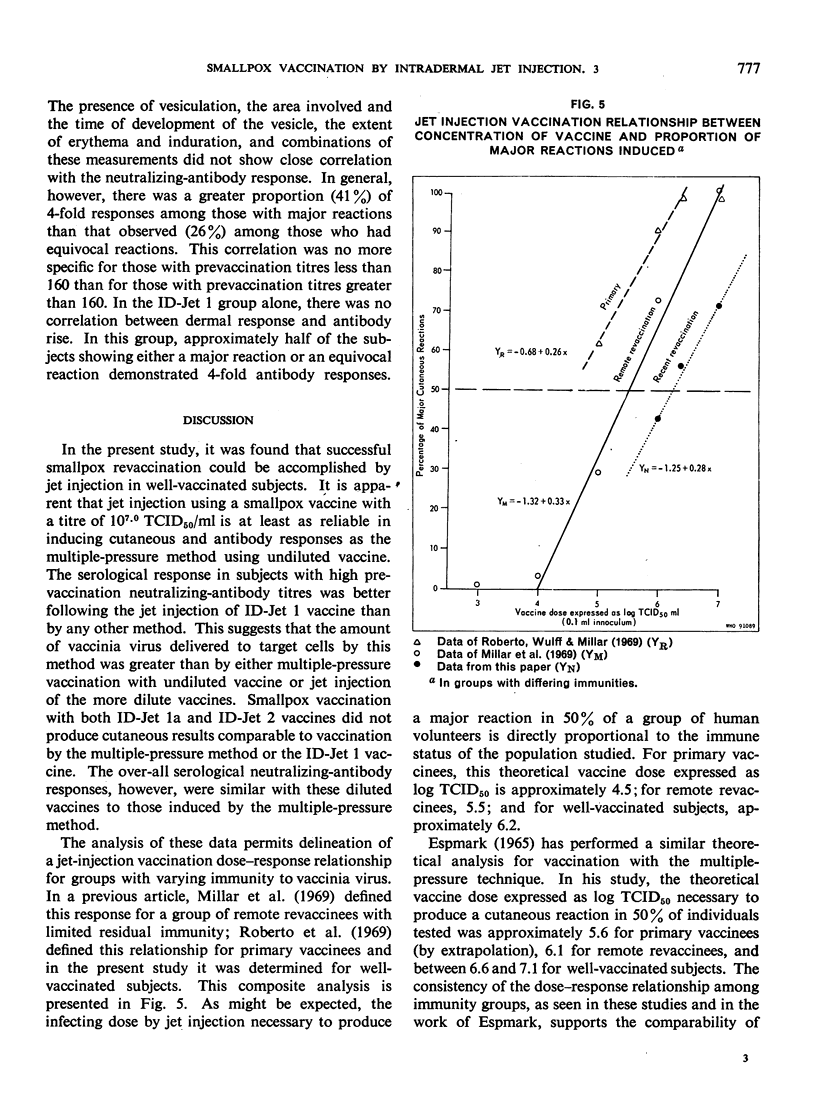
Smallpox vaccinations were performed in a well-vaccinated prison population by multiple-pressure technique and by intradermal jet injection using serial dilutions of vaccine. A total of 140 subjects were divided into groups, and each group was vaccinated by the multiple-pressure technique or by jet injection using 1 of 3 vaccine dilutions with the following calculated titres: ID-Jet 1 = 107.0 TCID50/ml, ID-Jet 1a = 106.3 TCID50/ml, ID-Jet 2 = 106.0 TCID50/ml. Clinical observations were made at intervals during the first week after vaccination. Prevaccination and post-vaccination serum samples were obtained immediately before and 30 days after the vaccination. Results based on clinical and serological evaluations indicated that smallpox vaccination by jet injection with the ID-Jet 1 vaccine was at least as efficacious as vaccination by the standard multiple-pressure technique.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ESPMARK J. A. SMALLPOX VACCINATION STUDIES WITH SERIAL DILUTIONS OF VACCINE. 2. STATISTICAL EVALUATION OF QUANTAL RESPONSE DATA. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;63:116–126. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.63.1.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar J. D., Roberto R. R., Wulff H., Wenner H. A., Henderson D. A. Smallpox vaccination by intradermal jet injection. I. Introduction, background and results of pilot studies. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;41(6):749–760. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberto R. R., Wulff H., Millar J. D. Smallpox vaccination by intradermal jet injection. 2. Cutaneous and serological responses to primary vaccination in children. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;41(6):761–769. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


