Abstract
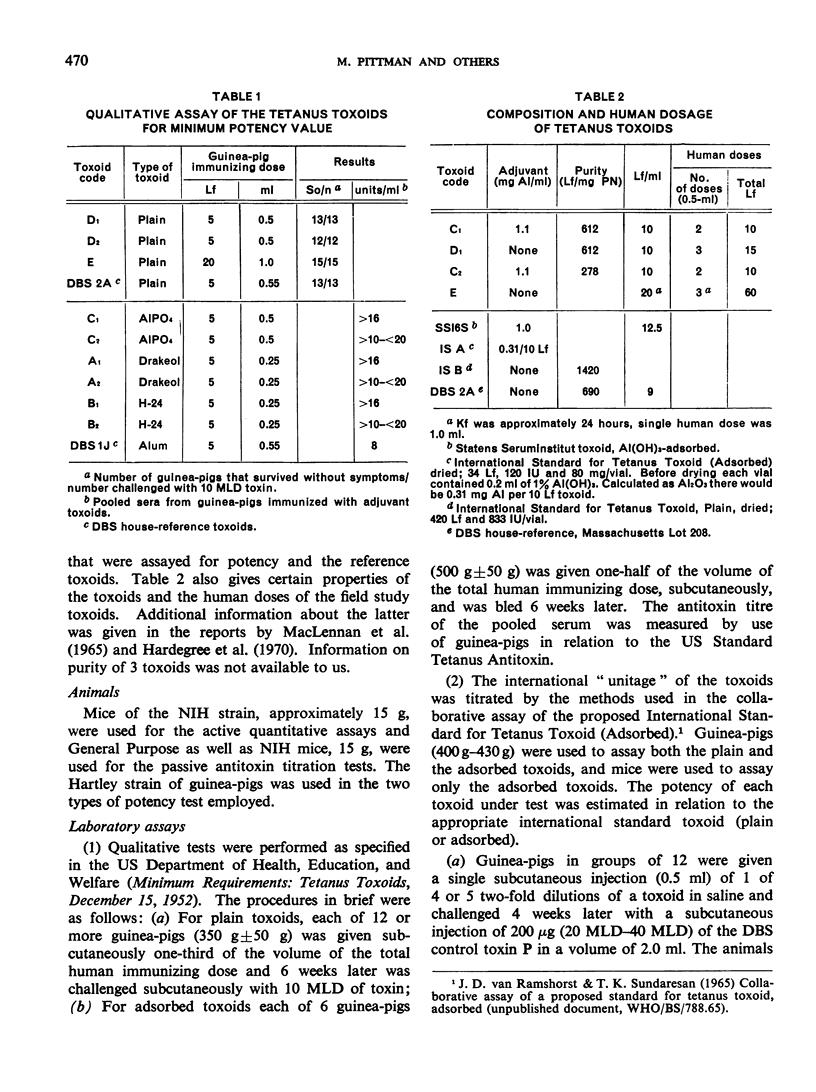
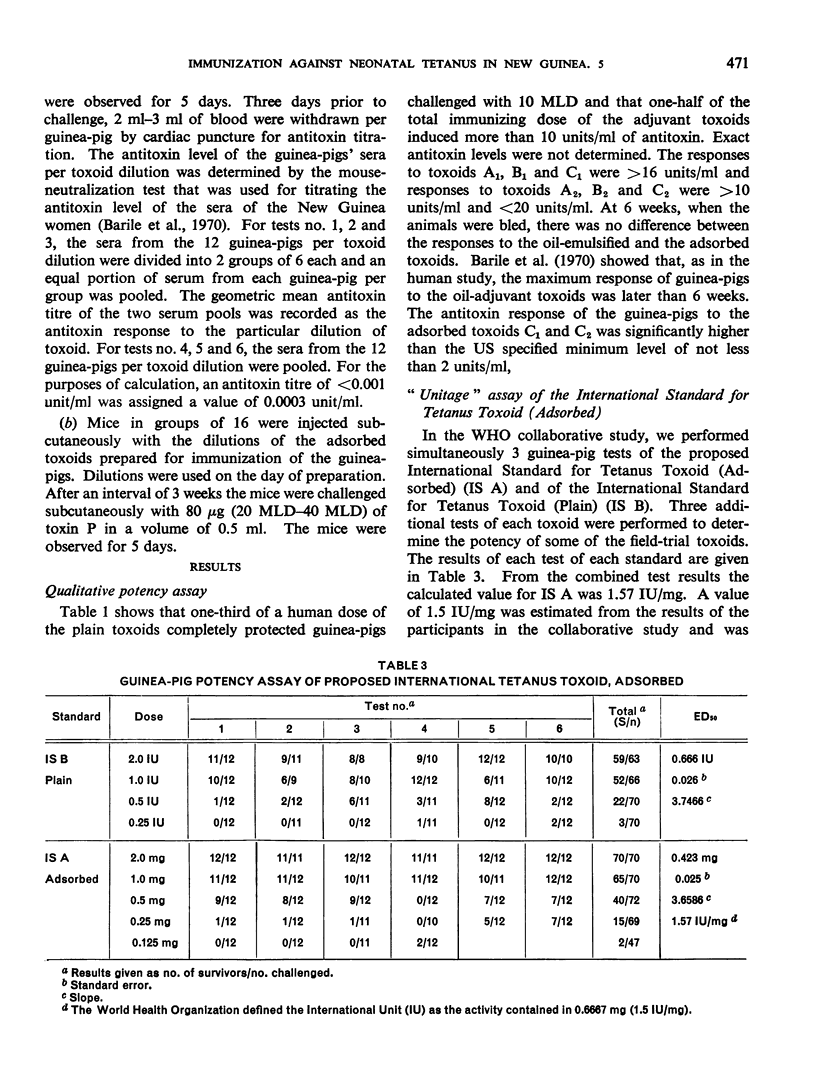
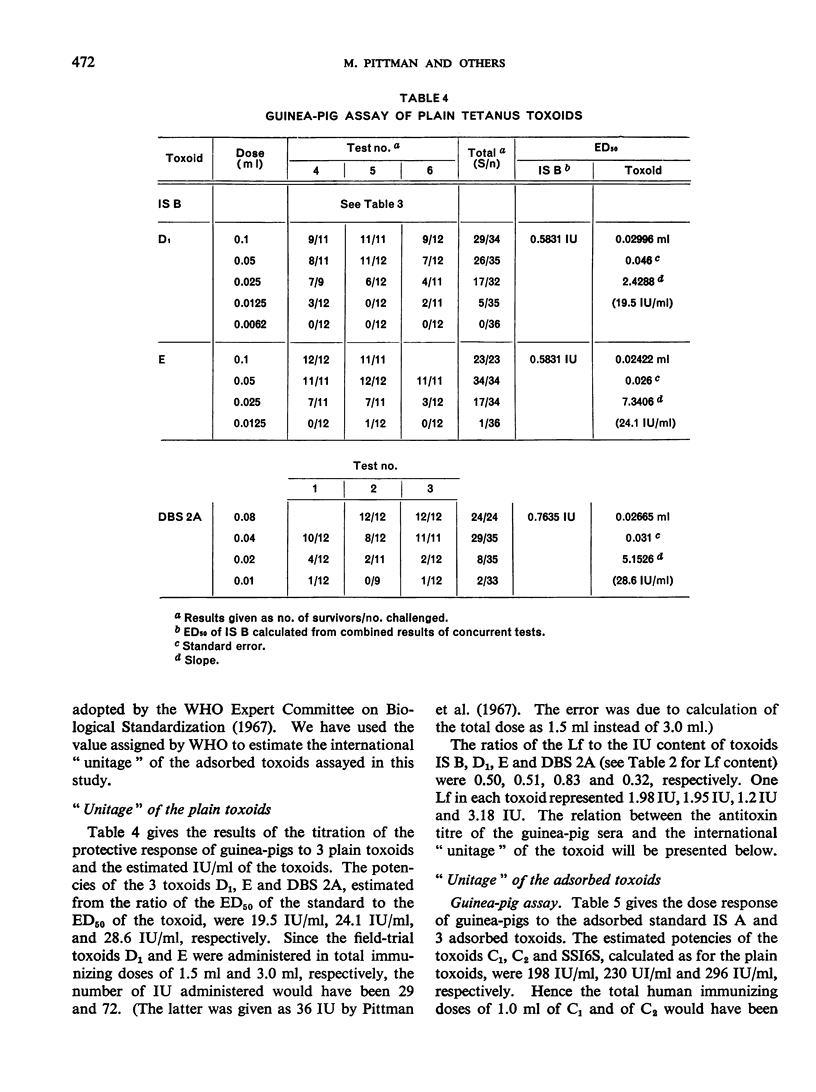
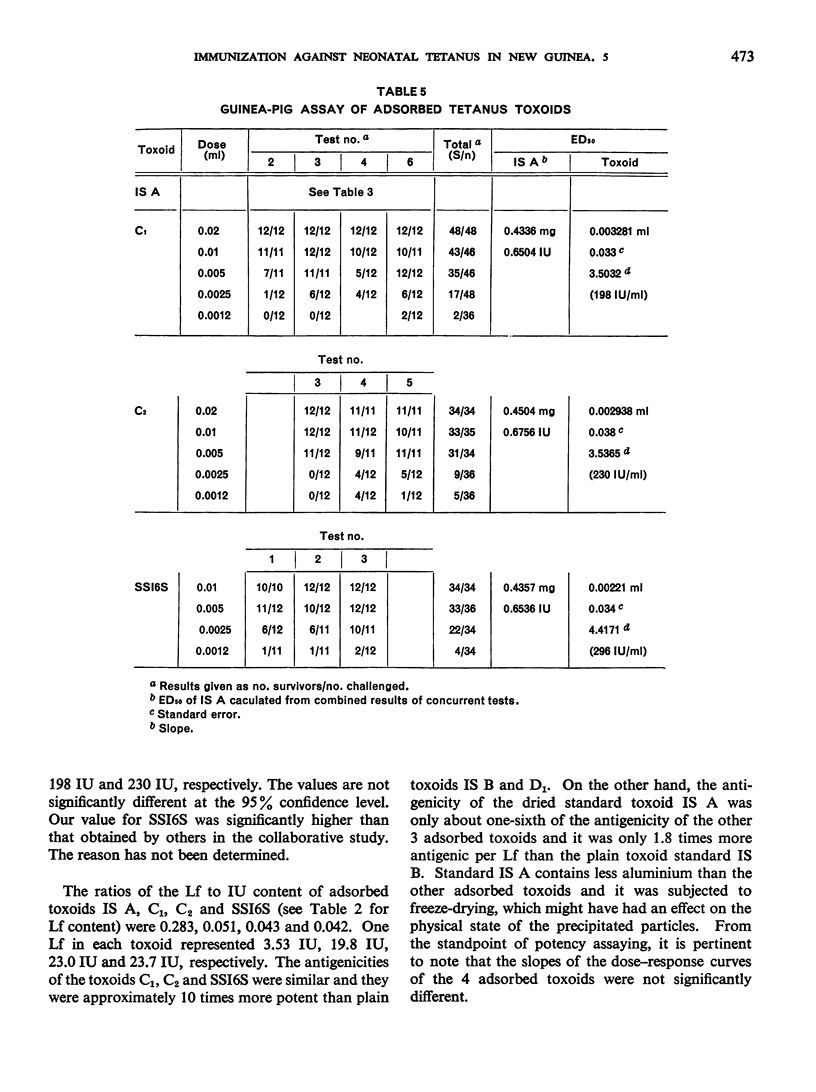
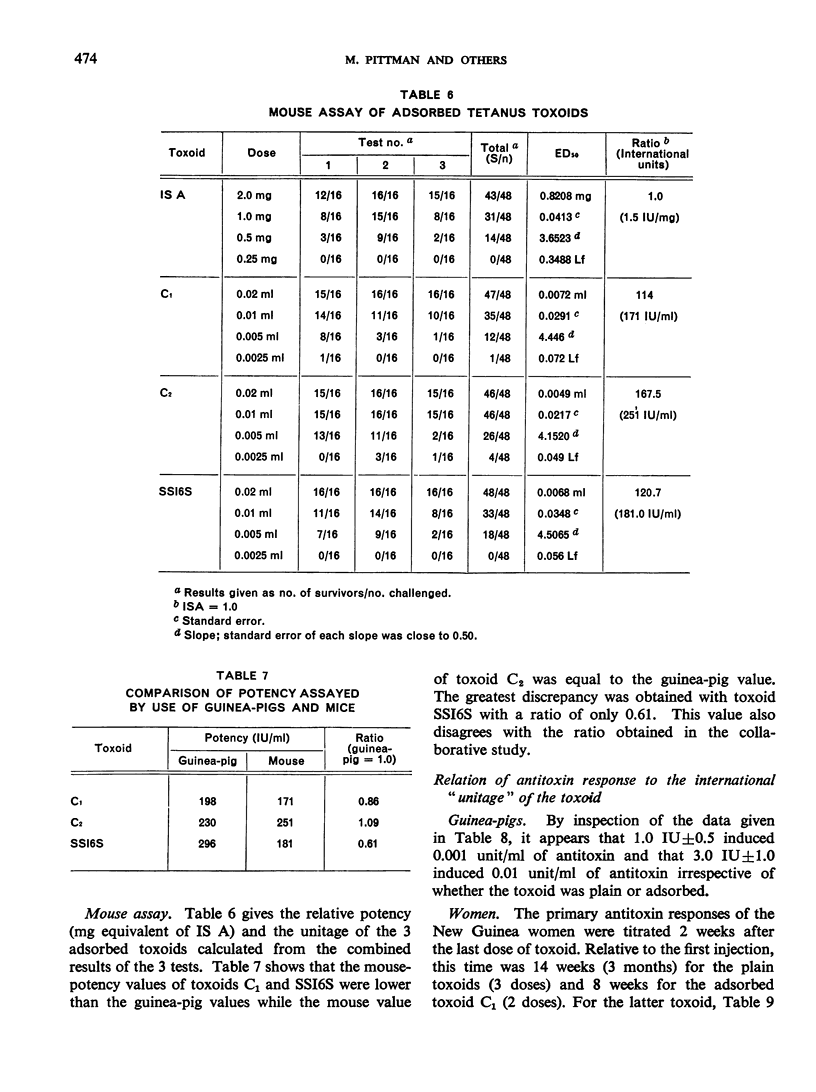
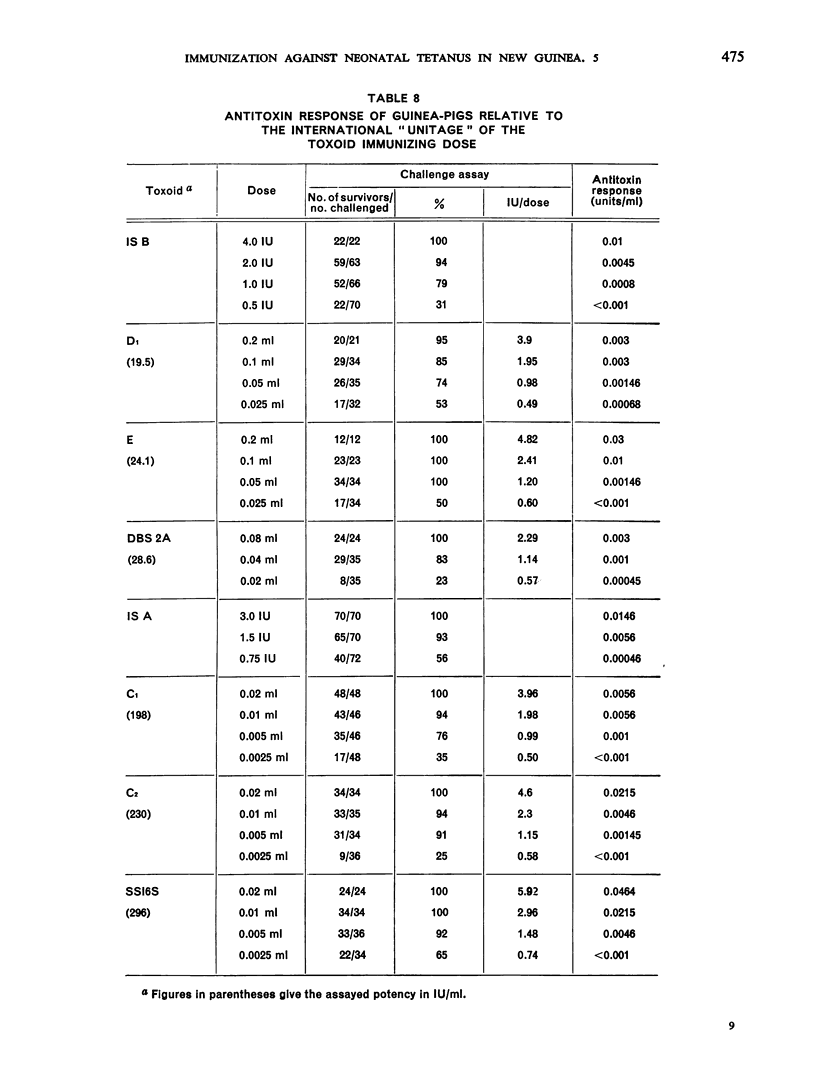
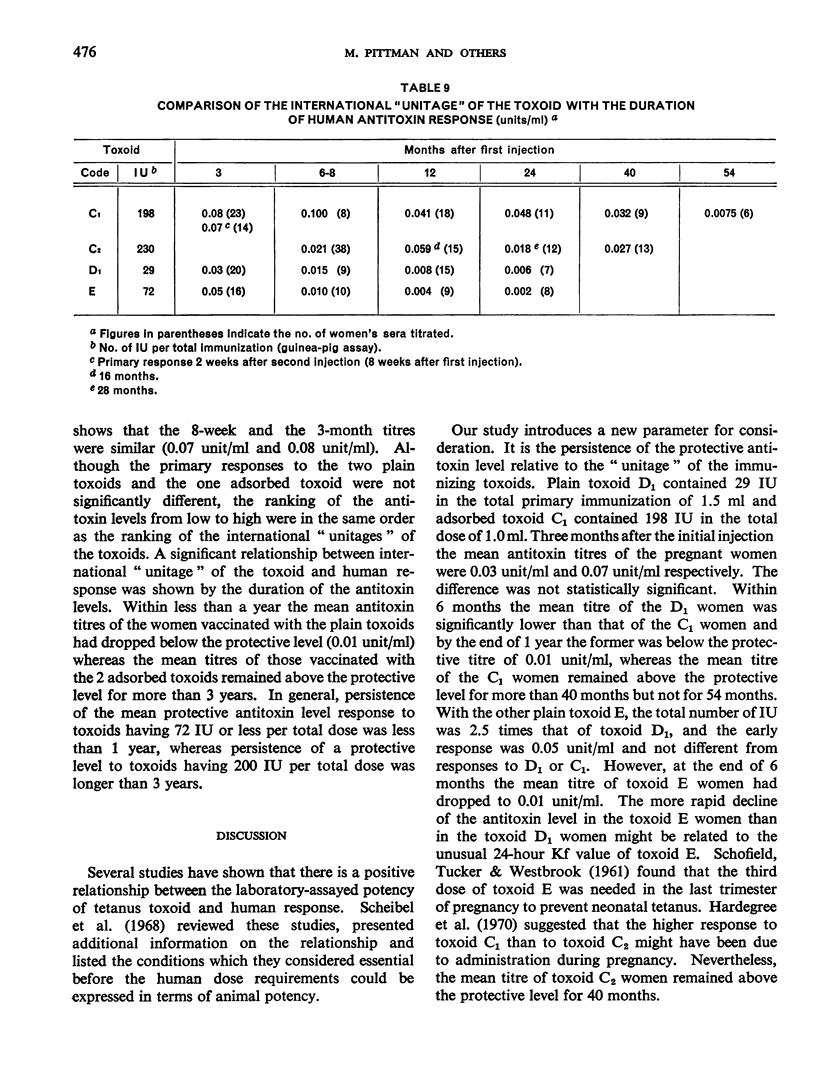
Previous papers in this series have shown that plain toxoids induced early primary antitoxin levels in women in New Guinea that were not significantly different from those induced by adsorbed toxoids but that at the end of 1 year the antitoxin levels differed significantly. Protective levels (not less than 0.01 unit/ml) induced by adsorbed toxoids persisted for more than 3 years. Results of laboratory assays of the toxoids reported in this paper show that per total human immunizing dose, the plain toxoids had 72 or less international units (IU) whereas the adsorbed toxoids had approximately 200 IU. The international ”unitage” of these toxoids reflected the persistence of the human protective antitoxin level but not the early primary response. The assay results were in agreement with findings of other workers that the mouse as well as the guinea-pig may be satisfactory for potency assay of adsorbed toxoids. The need for determination of the international unitage of tetanus toxoids used in human studies and the confirmation of relationship of this value to persistence of antitoxin levels is emphasized.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROWN J. H., GERWE E. G., GREENBERG L., HENDRY J. L., HOHENADEL J., MASUCCI P., NEWMAN C., TAYLOR E. M. Precision of potency assay of alum-precipitated tetanus toxoid in mice; an inter-institutional study. J Immunol. 1953 Feb;70(2):171–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barile M. F., Hardegree M. C., Pittman M. Immunization against neonatal tetanus in New Guinea. 3. The toxin-neutralization test and the response of guinea-pigs to the toxoids as used in the immunization schedules in New Guinea. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(3):453–459. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN H., VAN RAMSHORST J., TASMAN A. Consistency in potency assay of tetanus toxoid in mice. Bull World Health Organ. 1959;20:1133–1150. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBERG L., BENOIT R. Control of potency and the dosage of diphtheria and tetanus toxoids. J Am Med Assoc. 1956 Jan 14;160(2):108–113. doi: 10.1001/jama.1956.02960370018005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardegree M. C., Barile M. F., Pittman M., Schofield F. D., Maclennan R., Kelly A. Immunization against neonatal tetanus in New Guinea. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(3):439–451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan R., Schofield F. D., Pittman M., Hardegree M. C., Barile M. F. Immunization against neonatal tetanus in New Guinea. Antitoxin response of pregnant women to adjuvant and plain toxoids. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32(5):683–697. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOFIELD F. D., TUCKER V. M., WESTBROOK G. R. Neonatal tetanus in New Guinea. Effect of active immunization in pregnancy. Br Med J. 1961 Sep 23;2(5255):785–789. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5255.785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheibel I., Chen B. L., Bentzon M. W., Zia K. Human response to four tetanus vaccines with differing potency when assayed in animals. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1968;73(1):115–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1968.tb00485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


