Abstract
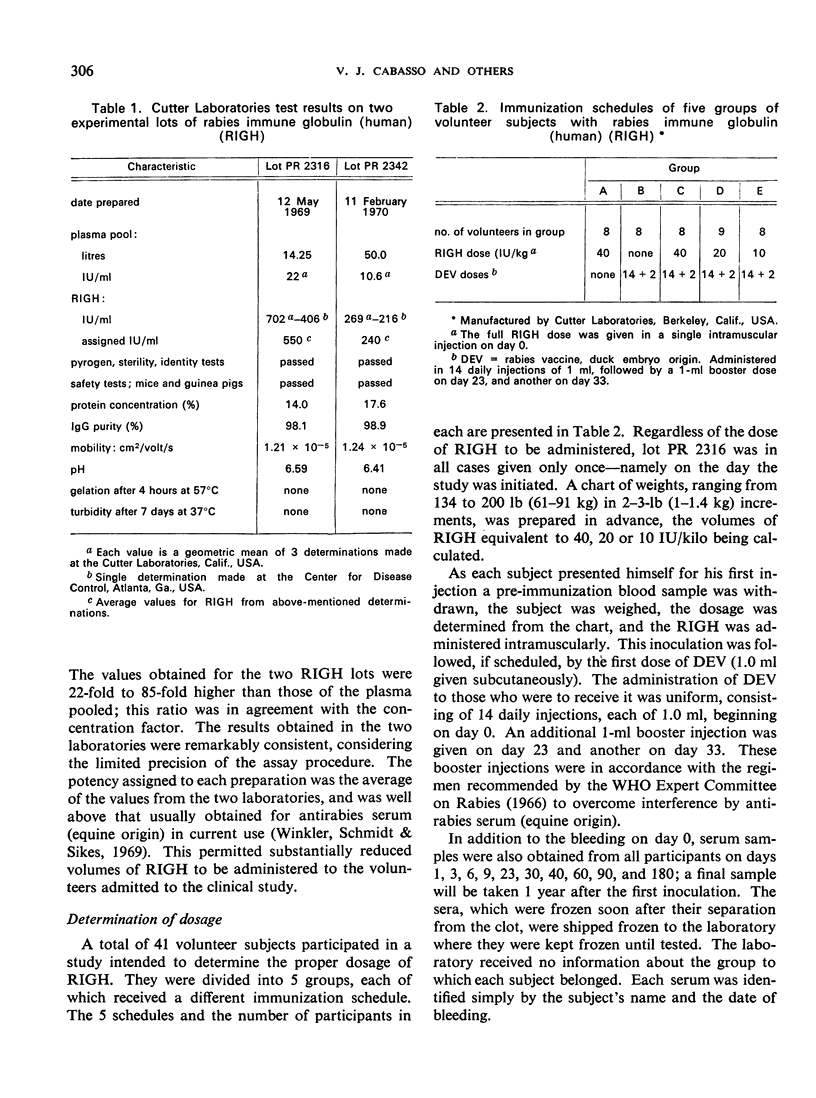
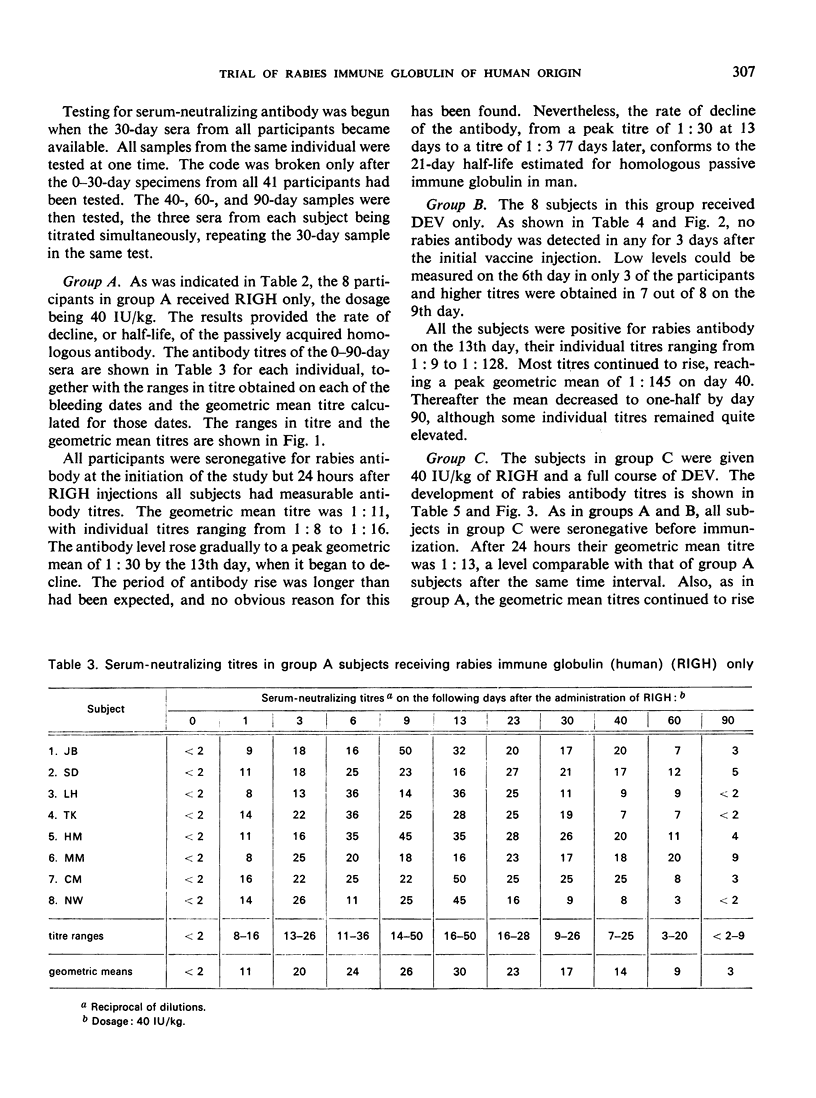
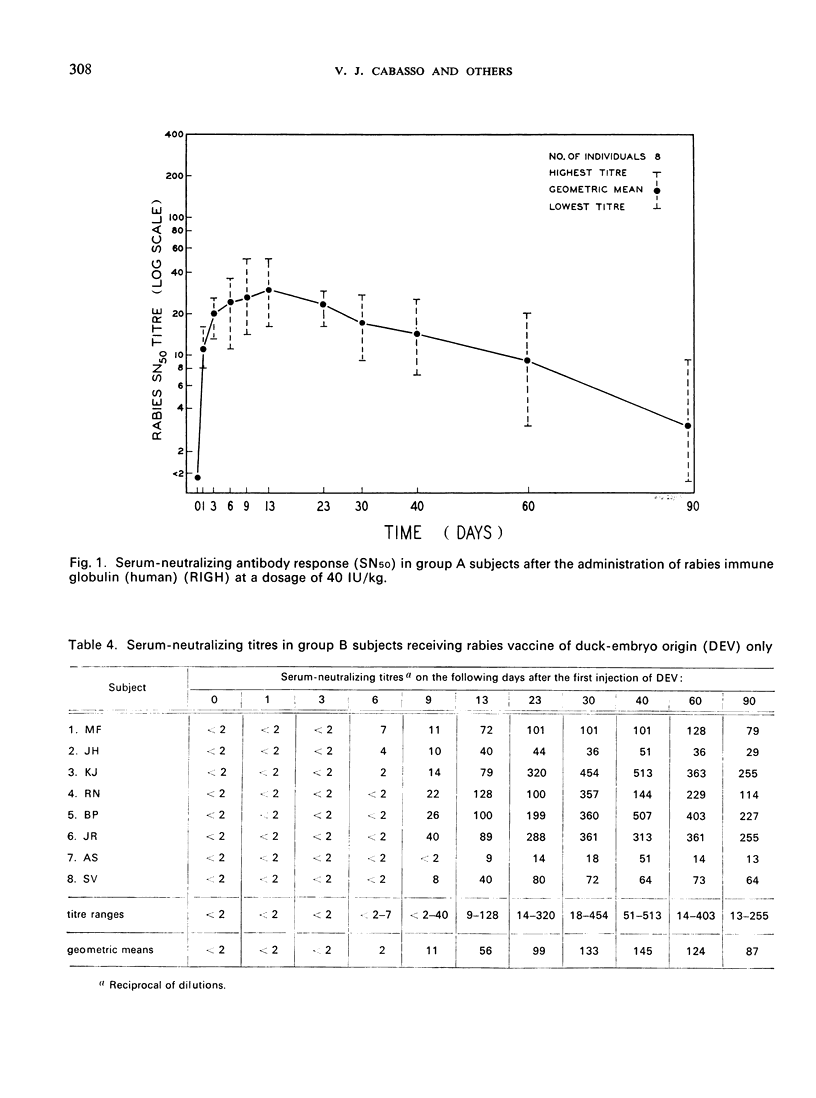
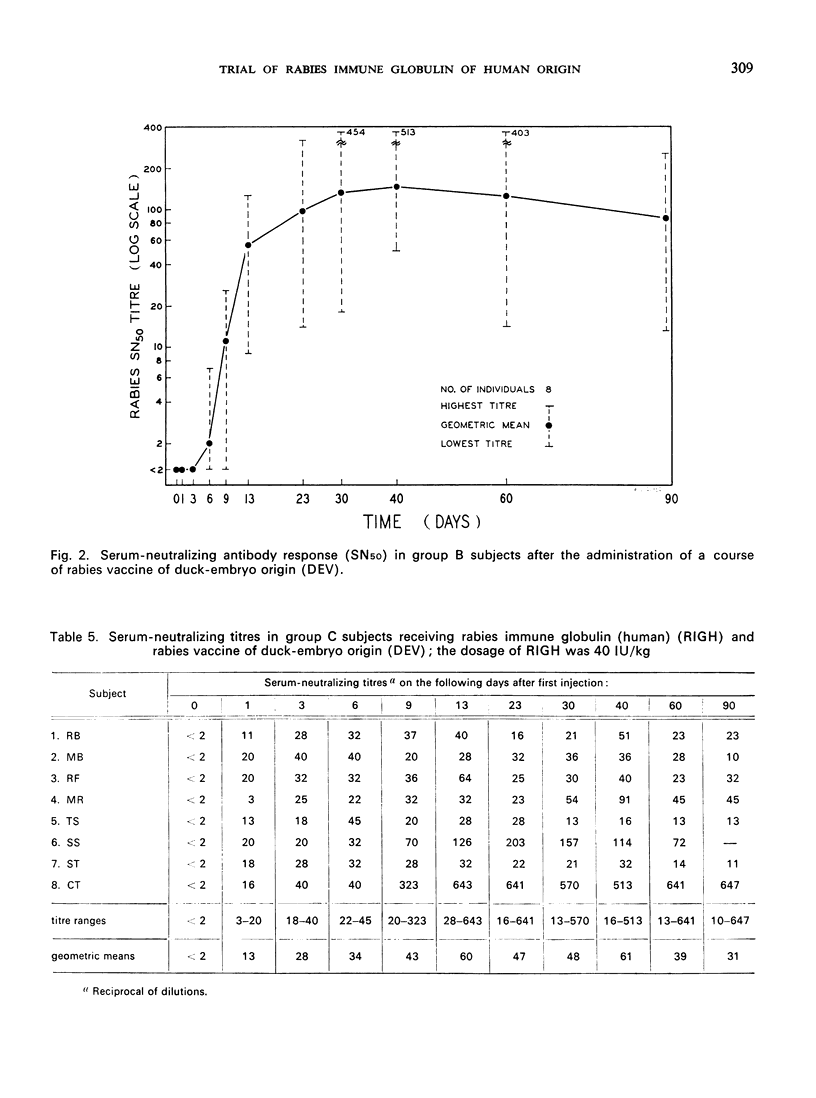
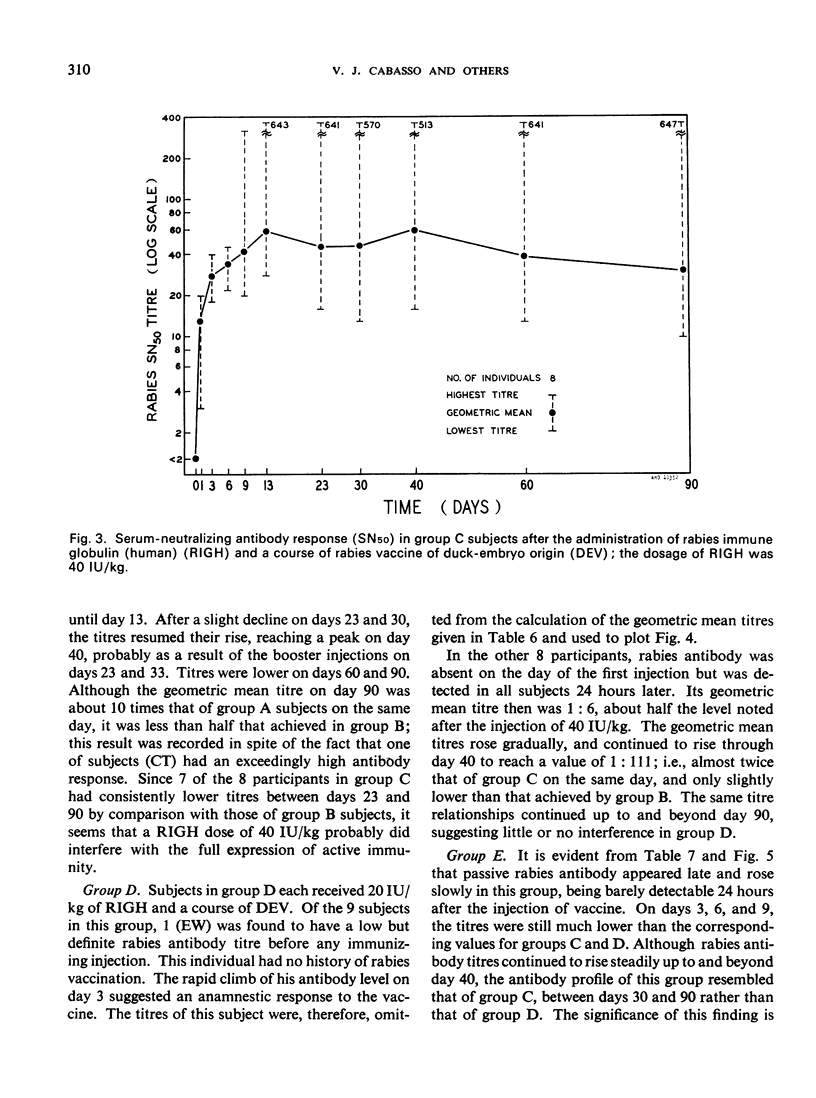
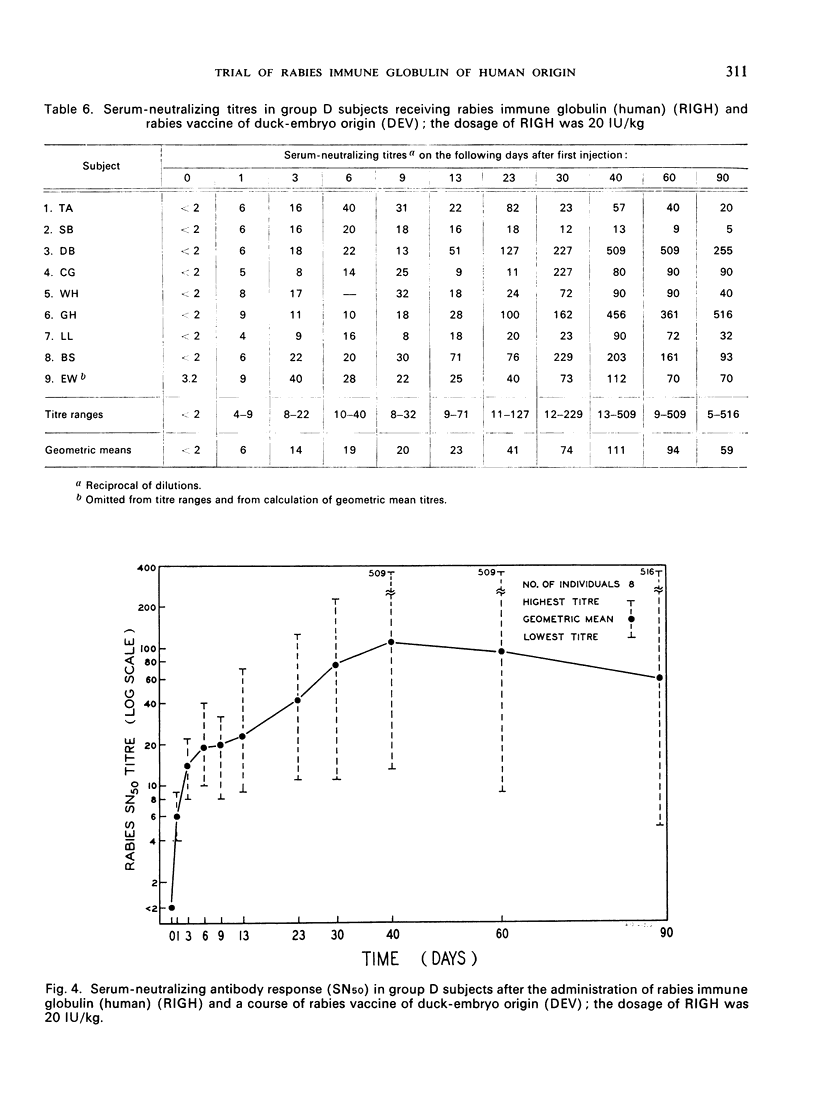
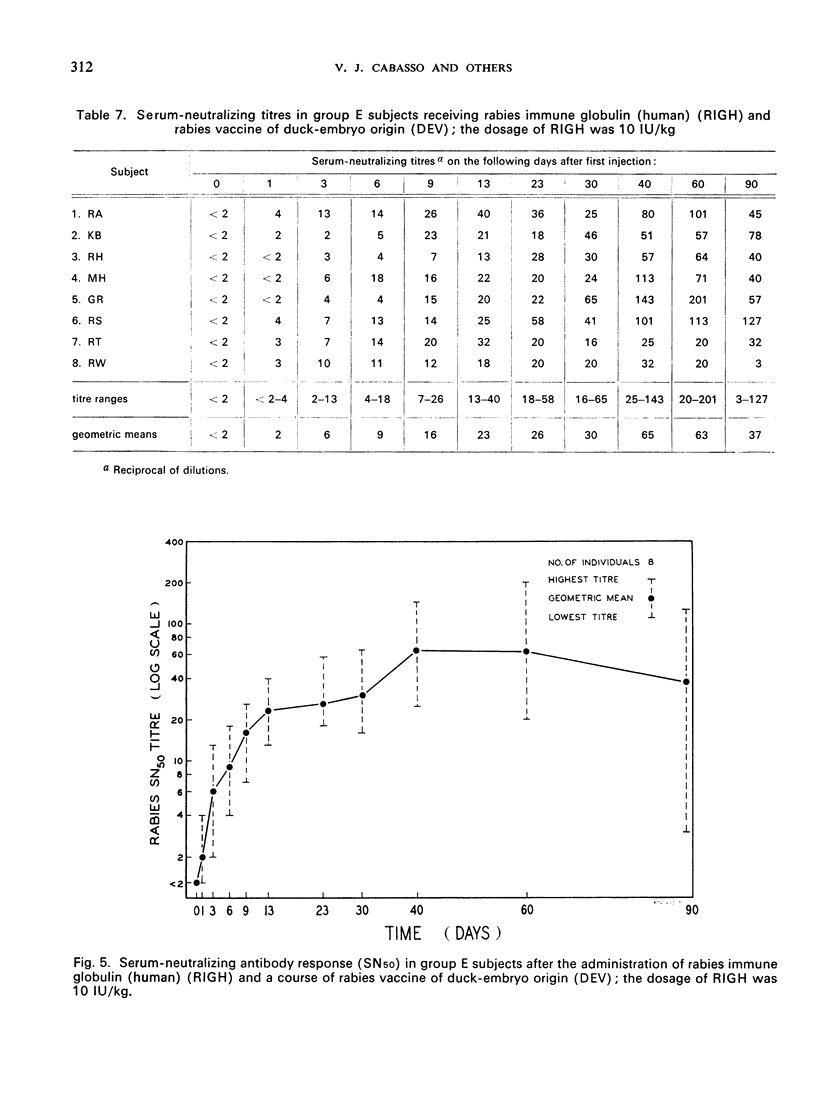
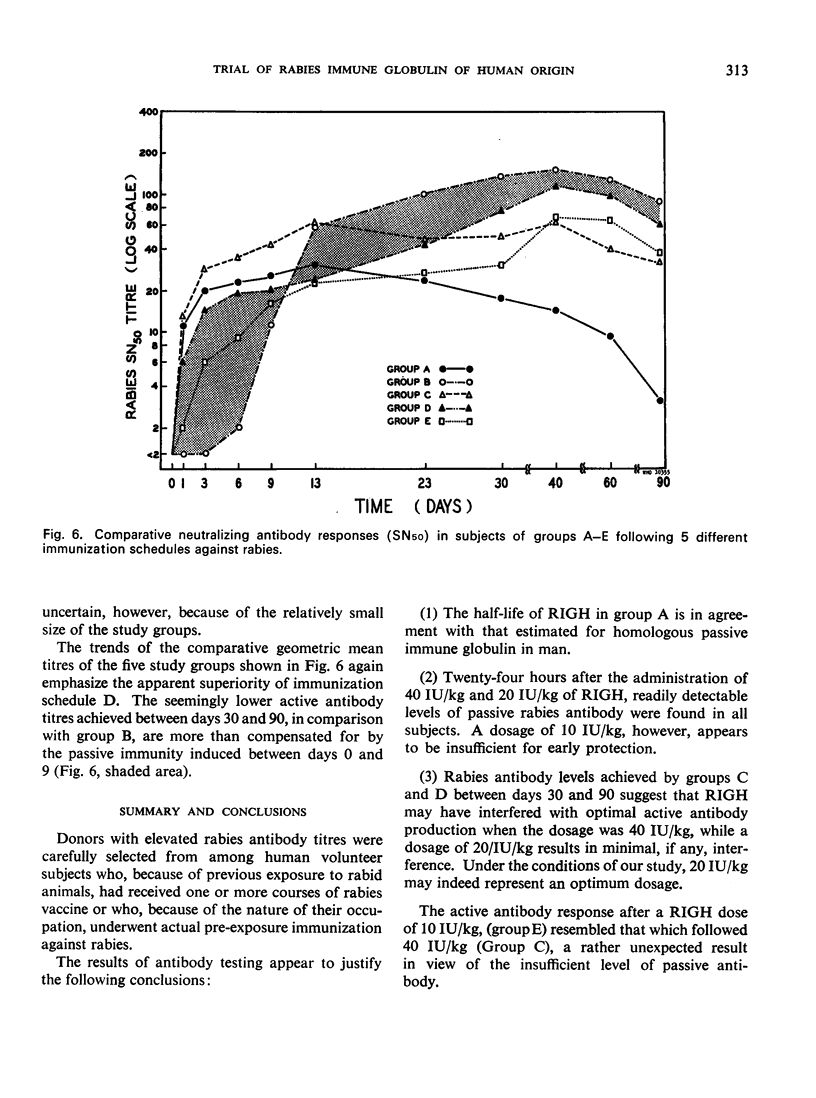
A clinical study was carried out in volunteer subjects to determine the proper dosage of rabies immune globulin (human) (RIGH) when used in conjunction with rabies vaccine of duck-embryo origin (DEV). Two lots of RIGH were prepared from plasma pools derived from donors with high titres of rabies-neutralizing antibody; both lots had potencies in excess of that accepted for antirabies serum of equine origin. The subjects had never received rabies vaccine but would oridinarily have been given pre-exposure rabies prophylaxis. Serological results obtained during a period of 90 days after the initiation of the study justify the following conclusions: (1) the half-life obtained with RIGH is in agreement with that estimated for homologous passive immune globulin in man; (2) readily detectable levels of rabies antibody were found in all subjects 24 hours after the administration of 40 and 20 international units per kg of RIGH, but not after the administration of 10 international units/kg; and (3) there was an indication that 40 international units/kg may have interfered with optimal active antibody production by the vaccine, and that interference was absent or minimal after doses of 20 intenational units/kg.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ATANASIU P., BAHMANYAR M., BALTAZARD M., FOX J. P., HABEL K., KAPLAN M. M., KISSLING R. E., KOMAROV A., KOPROWSKI H., LEPINE P. Rabies neutralizing antibody response to different schedules of serum and vaccine inoculations in non-exposed persons. II. Bull World Health Organ. 1957;17(6):911–932. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ATANASIU P., BAHMANYAR M., BALTAZARD M., FOX J. P., HABEL K., KAPLAN M. M., KISSLING R. E., KOMAROV A., KOPROWSKI H., LEPINE P. Rabies neutralizing antibody response to different schedules of serum and vaccine inoculations in non-exposed persons. Bull World Health Organ. 1956;14(4):593–611. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ATANASIU P., CANNON D. A., DEAN D. J., FOX J. P., HABEL K., KAPLAN M. M., KISSLING R. E., KOPROWSKI H., LEPINE P., PEREZ GALLARDO F. Rabies neutralizing antibody response to different schedules of serum and vaccine inoculations in non-exposed persons. 3. Bull World Health Organ. 1961;25:103–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer B. G., Dierks R. E. Effects of homologous or heterologous antiserum on neutralizing-antibody response to rabies vaccine. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(3):407–417. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atanasiu P., Dean D. J., Habel K., Kaplan M. M., Koprowski H., Lépine P., Serié C. Rabies neutralizing antibody response to different schedules of serum and vaccine inoculations in non-exposed persons. 4. Bull World Health Organ. 1967;36(3):361–365. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTAZARD M., BAHMANYAR M. Essai pratique du sérum antirabique chez les mordus par loups enragés. Bull World Health Organ. 1955;13(5):747–772. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEAN D. J., BAER G. M., THOMPSON W. R. Studies on the local treatment of rabies-infected wounds. Bull World Health Organ. 1963;28(4):477–486. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABEL K., KOPROWSKI H. Laboratory data supporting the clinical trial of anti-rabies serum in persons bitten by a rabid wolf. Bull World Health Organ. 1955;13(5):773–779. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOSTY T. S., KISSLING R. E., SCHAEFFER M., WALLACE G. A., DIBBLE E. H. Human antirabies gamma globulin. Bull World Health Organ. 1959;20:1111–1119. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. M., COHEN D., KOPROWSKI H., DEAN D., FERRIGAN L. Studies on the local treatment of wounds for the prevention of rabies. Bull World Health Organ. 1962;26:765–775. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOPROWSKI H., BLACK J. Studies on chick-embryo-adapted rabies virus. V. Protection of animals with antiserum and living attenuated virus after exposure to street strain of rabies virus. J Immunol. 1954 Jan;72(1):85–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOPROWSKI H., COX H. R. Recent developments in the prophylaxis of rabies. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1951 Dec;41(12):1483–1489. doi: 10.2105/ajph.41.12.1483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOPROWSKI H., VAN DER SCHEER J., BLACK J. Use of hyperimmune anti-rabies serum concentrates in experimental rabies. Am J Med. 1950 Apr;8(4):412–420. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(50)90224-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ONCLEY J. L., MELIN M. The separation of the antibodies, isoagglutinins, prothrombin, plasminogen and beta1-lipoprotein into subfractions of human plasma. J Am Chem Soc. 1949 Feb;71(2):541–550. doi: 10.1021/ja01170a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELIMOV M., BOLTUCIJ L., SEMENOVA E., KOBRINSKIJ G., ZMUSKO L. [The use of antirabies gamma globulin in subjects severely bitten by rabid wolves or other animals]. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1959;3:168–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler W. G., Schmidt R. C., Sikes R. K. Evaluation of human rabies immune globulin and homologous and heterologous antibody. J Immunol. 1969 May;102(5):1314–1321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


