Abstract
Because of the instability of Factor VIII (antihaemophilic factor) in plasma in vitro, and since evidence has accumulated that the level of activity varies significantly between samples of ”fresh normal plasma”, it is apparent that a stable biological standard is required.
Two freeze-dried preparations of Factor VIII, one plasma and one concentrate preparation, were prepared and have been assayed in a collaborative trial by 20 laboratories in 9 countries.
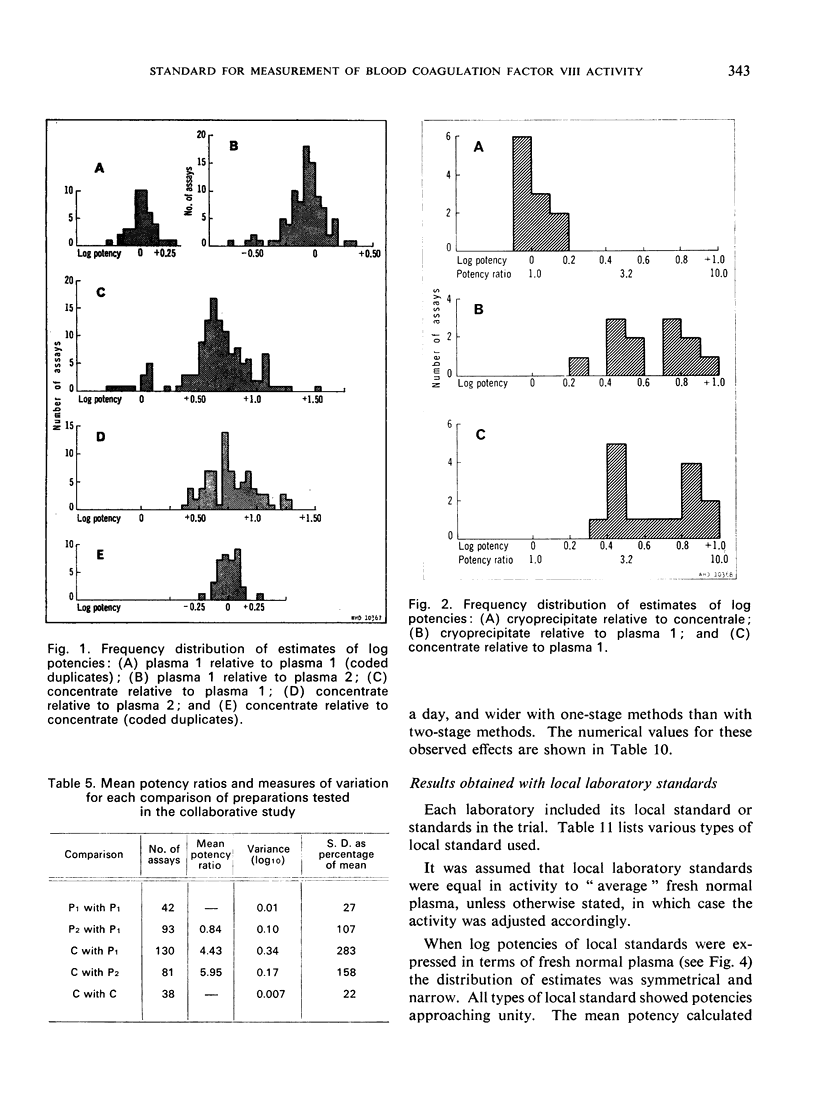
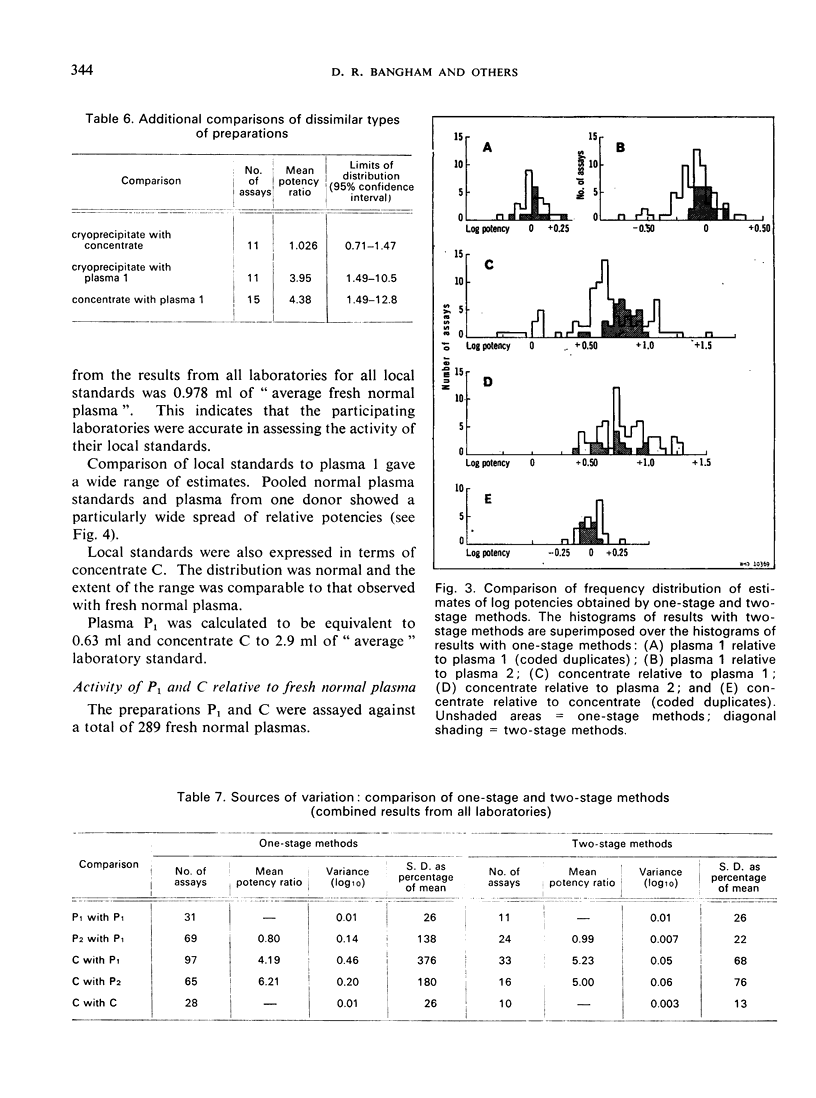
The laboratories used their own methods and altogether 248 assays were carried out. Comparison of materials of similar type gave precise estimates with all the methods used, but when materials dissimilar in type and in Factor VIII content were compared less precise results were obtained. Sources of variation, such as differences in method, differences between operators, and day-to-day variations, were analysed.
Accelerated degradation tests, carried out on the freeze-dried plasma and concentrate preparations, showed that Factor VIII activity was sufficiently stable in the concentrate for it to be used as a long-term standard but that the Factor VIII activity was less stable in the plasma preparation.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BIGGS R., MACFARLANE R. G., DENSON K. W., ASH B. J. THROMBIN AND THE INTERACTION OF FACTORS 8 AND 9. Br J Haematol. 1965 May;11:276–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb06588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. L., Hardisty R. M., Kosoy M. H., Bracken C. Antihaemophilic globulin: preparation by an improved cryoprecipitation method and clinical use. Br Med J. 1967 Apr 8;2(5544):79–85. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5544.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JERNE N. K., PERRY W. L. The stability of biological standards. Bull World Health Organ. 1956;14(1):167–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEKWICK R. A., WALTON P. L. AN ASSAY FOR ANTIHAEMOPHILIC FACTOR (FACTOR VIII) WITH SOME CONSIDERATIONS AFFECTING THE ESTABLISHMENT OF A STANDARD REFERENCE PREPARATION. Br J Haematol. 1964 Jul;10:299–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1964.tb00706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEKWICK R. A., WOLF P. A concentrate of human antihaemophilic factor; its use in six cases of haemophilia. Lancet. 1957 Mar 30;272(6970):647–650. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)91116-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael S. E., Tunnah G. W. The purification of factor 8 (antihaemophilic globulin). II. Further purification and some properities of factor 8. Br J Haematol. 1966 Mar;12(2):115–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1966.tb05616.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemetz J., Nossel H. L. Activated coagulation factors: in-vivo and in-vitro studies. Br J Haematol. 1969 Apr;16(4):337–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb00411.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POOL J. G., GERSHGOLD E. J., PAPPENHAGEN A. R. HIGH-POTENCY ANTIHAEMOPHILIC FACTOR CONCENTRATE PREPARED FROM CRYOGLOBULIN PRECIPITATE. Nature. 1964 Jul 18;203:312–312. doi: 10.1038/203312a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESTON A. E., BARR A. THE PLASMA CONCENTRATION OF FACTOR VIII IN THE NORMAL POPULATION. II. THE EFFECTS OF AGE, SEX AND BLOOD GROUP. Br J Haematol. 1964 Apr;10:238–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1964.tb00698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pool J. G., Shannon A. E. Production of high-potency concentrates of antihemophilic globulin in a closed-bag system. N Engl J Med. 1965 Dec 30;273(27):1443–1447. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196512302732701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston A. E. The factor-8 activity in fresh and stored plasma. Br J Haematol. 1967 Jan;13(1):42–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb08693.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPAPORT S. I., SCHIFFMAN S., PATCH M. J., AMES S. B. The importance of activation of antihemophilic globulin and proaccelerin by traces of thrombin in the generation of intrinsic prothrombinase activity. Blood. 1963 Feb;21:221–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPAET T. H., GARNER E. S. Studies on the storage lability of human antihemophilic factor. J Lab Clin Med. 1955 Jul;46(1):111–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelin G. M. Preparation and standardization of a stable AHF plasma. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1968 Jul 31;19(3):423–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstraete M., Olislaegers P., Van Itterbeek H., Waumans P., Lust A. Human plasma and plasma fractions as sources of factor VIII (antihaemophilic factor). Vox Sang. 1969 Apr;16(4):382–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1969.tb04765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGNER B. H., MCLESTER W. D., SMITH M., BRINKHOUS K. M. PURIFICATION OF ANTIHEMOPHILIC FACTOR (FACTOR VIII) BY AMINO ACID PRECIPITATION. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Apr 15;11:64–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


