Abstract
A controlled field trial of oral killed typhoid vaccine was carried out in Delhi, India in 1968-69. Altogether, 13 374 children below the age of 17 years were included in the study. Two comparable groups of children were given either placebo or vaccine. Each tablet of vaccine contained 100×109 killed Salmonella typhi, and 3 tablets of vaccine or placebo were administered to each child. The vaccinated subjects were followed up from 10 June 1968 to 31 August 1969. The effectiveness of the vaccine was measured by comparing the incidence of typhoid fever (based only on bacteriologically positive cases) in the two groups. It was found that the difference in incidence of the disease in the two groups was not statistically significant. The oral killed typhoid vaccine in the dosage schedule used in the present trial was found not to be effective against the disease.
Full text
PDF
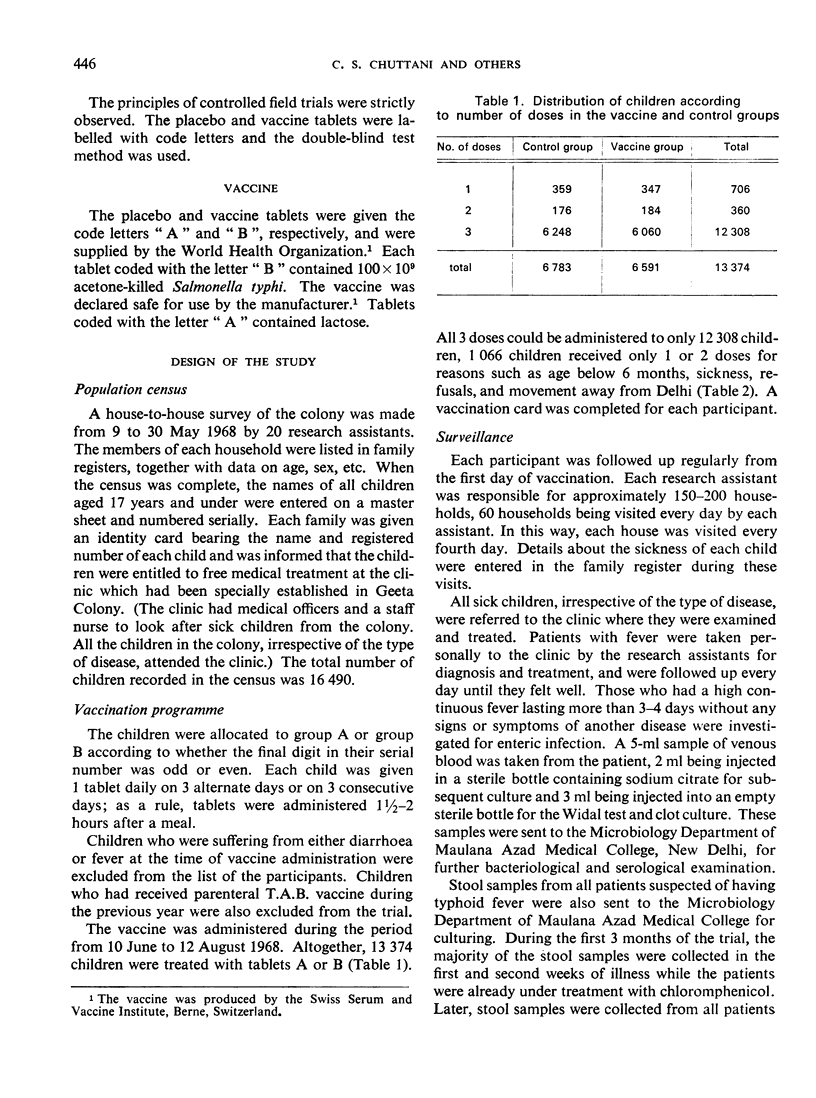

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CVJETANOVIC B., UEMURA K. THE PRESENT STATUS OF FIELD AND LABORATORY STUDIES OF TYPHOID AND PARATYPHOID VACCINES WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO STUDIES SPONSORED BY WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32:29–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hejfec L. B., Salmin L. V., Lejtman M. Z., Kuz'minova M. L., Vasil'eva A. V., Levina L. A., Bencianova T. G., Pavlova E. A., Antonova A. A. A controlled field trial and laboratory study of five typhoid vaccines in the USSR. Bull World Health Organ. 1966;34(3):321–339. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


