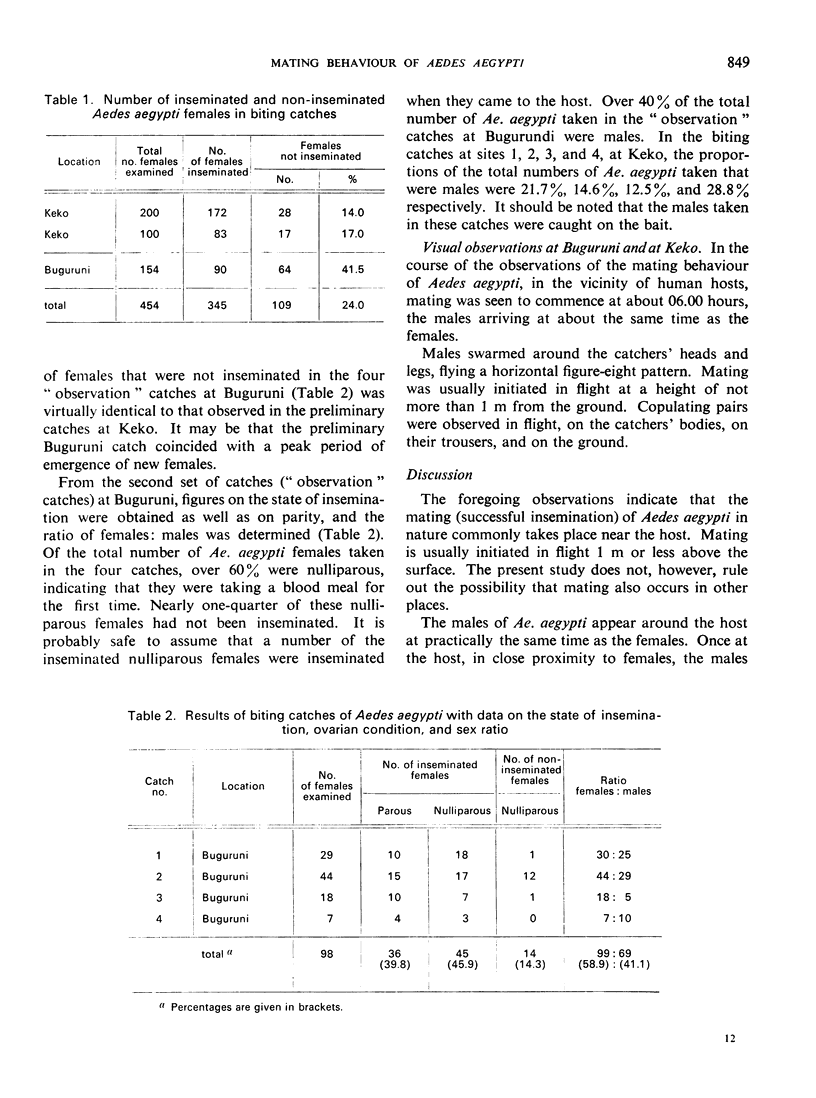
Full text
PDF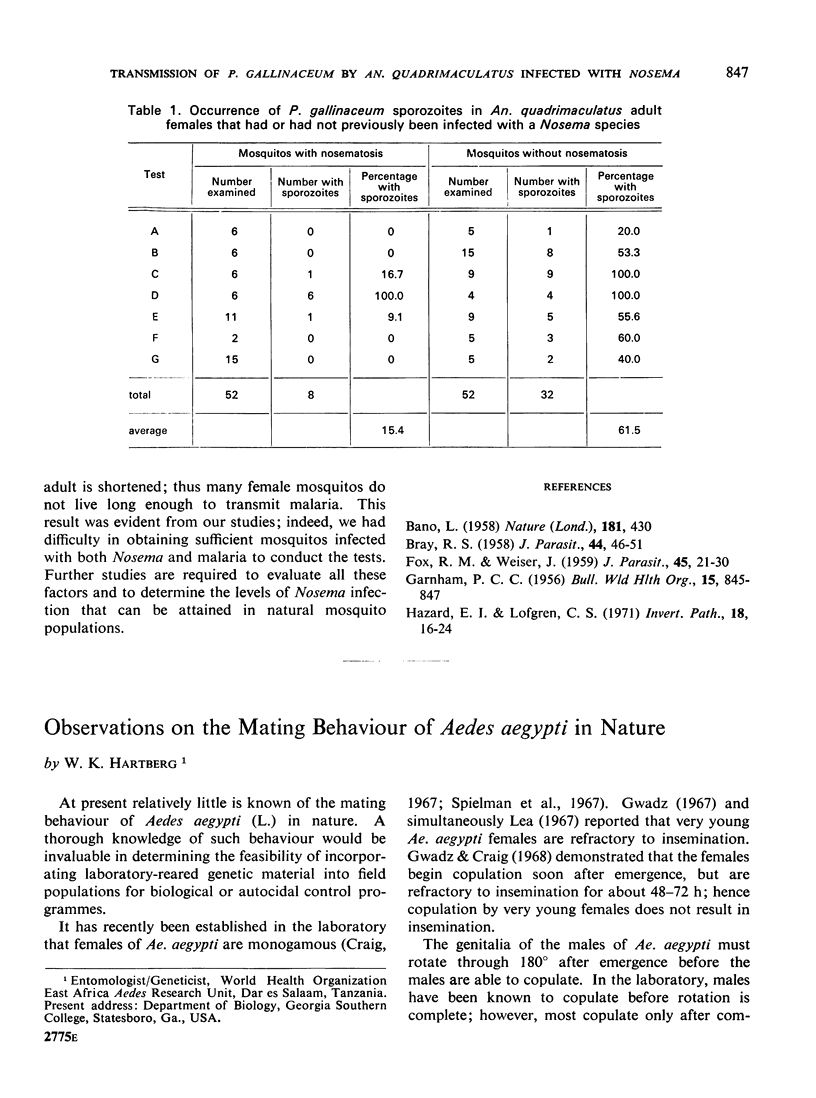


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Craig G. B., Jr Mosquitoes: female monogamy induced by male accessory gland substance. Science. 1967 Jun 16;156(3781):1499–1501. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3781.1499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant G. G. Dioxane and dioxaspiro derivatives as attractants for male yellow-fever mosquitoes. J Econ Entomol. 1969 Aug;62(4):786–789. doi: 10.1093/jee/62.4.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRPIS M. [New information on a method for the study of the activity of mosquitoes]. Biologia (Bratisl) 1962;17:123–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuno M., Tonn R. J. A study of biting habits of Aedes aegypti in Bangkok, Thailand. Bull World Health Organ. 1970;43(2):319–325. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


