Abstract
The study of toxicology and other related fields has been largely based on in vitro techniques. These methods have provided quantitative information on the effects of inhibitors on enzymes, but none on the localized effects of inhibitors on selected sites of action within the animal. Histochemical study of frozen sections does provide data on the site of action of toxicants. The utility of histochemistry in conjunction with in vitro methods is discussed.
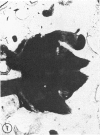
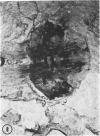
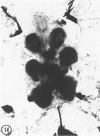
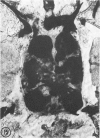
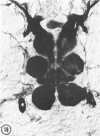
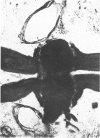
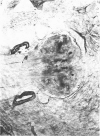
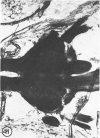
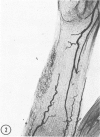
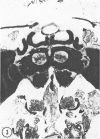
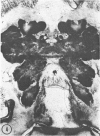
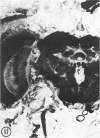
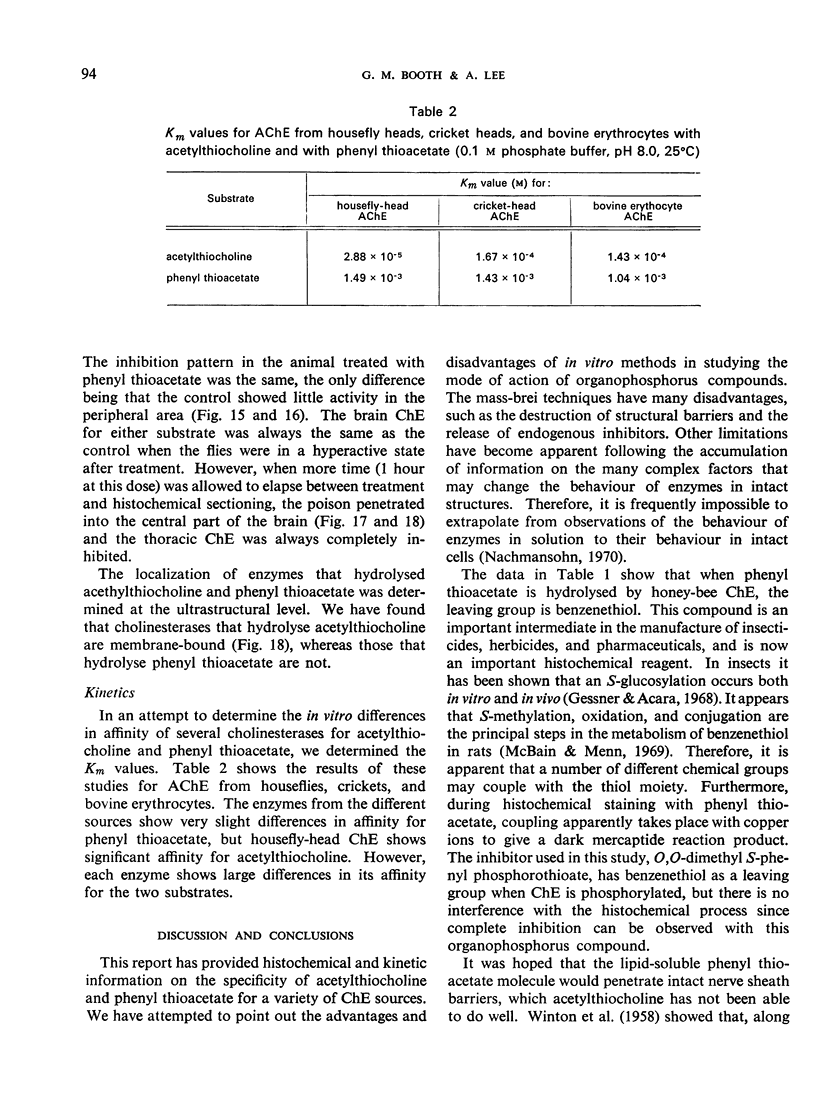
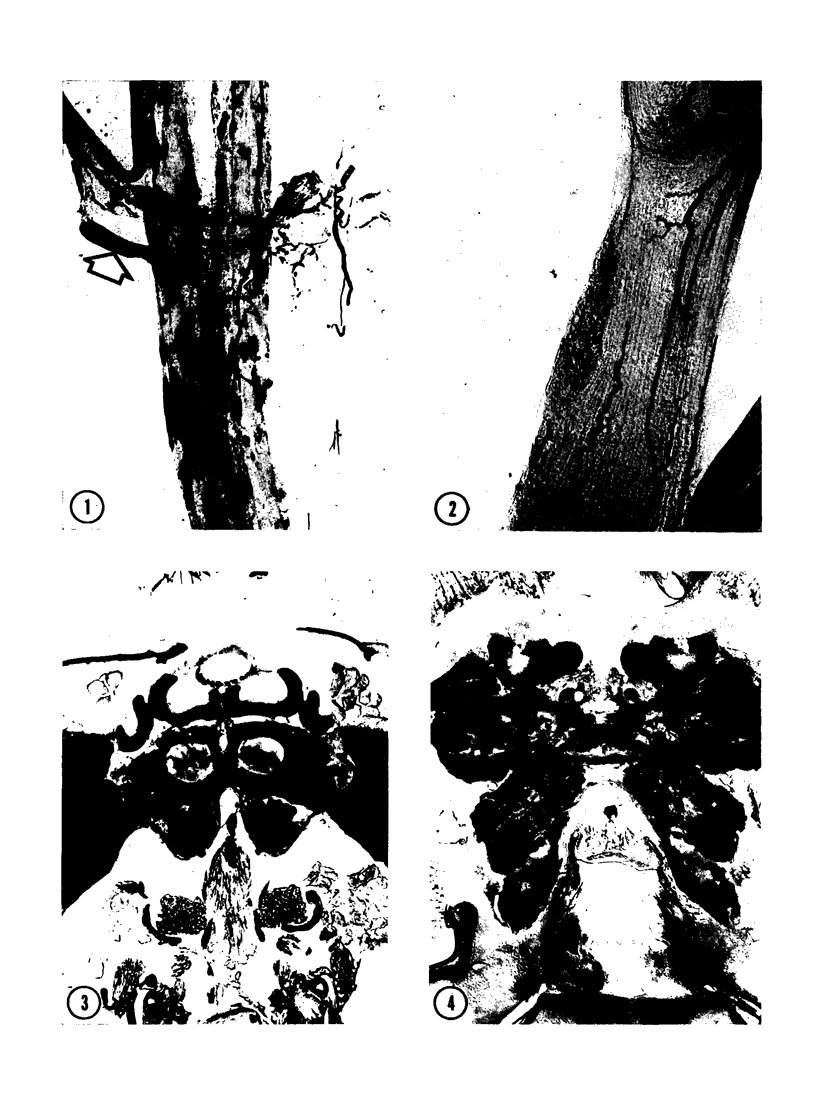
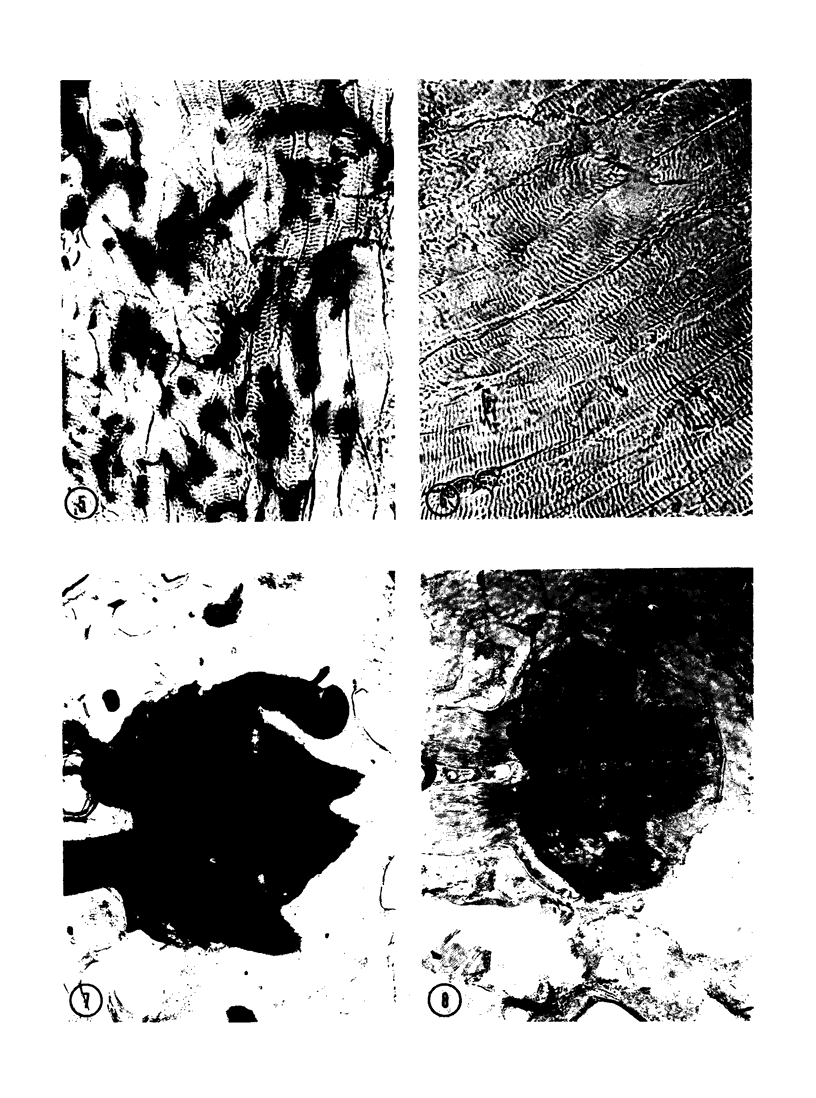
The substrates acetylthiocholine and phenyl thioacetate were utilized in demonstrating cholinesterase. Neither substrate penetrated well into freshly dissected nerve cord preparations, but both compounds were hydrolysed by sectioned tissue. The leaving group of phenyl thioacetate was demonstrated to be benzenethiol. In general, acetylthiocholine was hydrolysed slightly more rapidly by insect cholinesterases. A unique cholinesterase was found in motor end-plates of cricket muscle, which hydrolyses acetylthiocholine and which was inhibited by physostigmine. No other insect muscle preparation showed this activity. Topical application of insecticides showed that a vital site of action in flies is the peripheral area of the thoracic ganglia and that in crickets the brain and nerve cord are involved at knock-down. Kinetic data indicate that acetylthiocholine has a greater affinity than does phenyl thioacetate for a variety of enzyme sources. Ultrastructural evidence shows that cholinesterases that hydrolyse acetylthiocholine are membrane-bound. Phenyl thioacetate was found to be useful as a model in designing new insecticides.
Full text
PDF



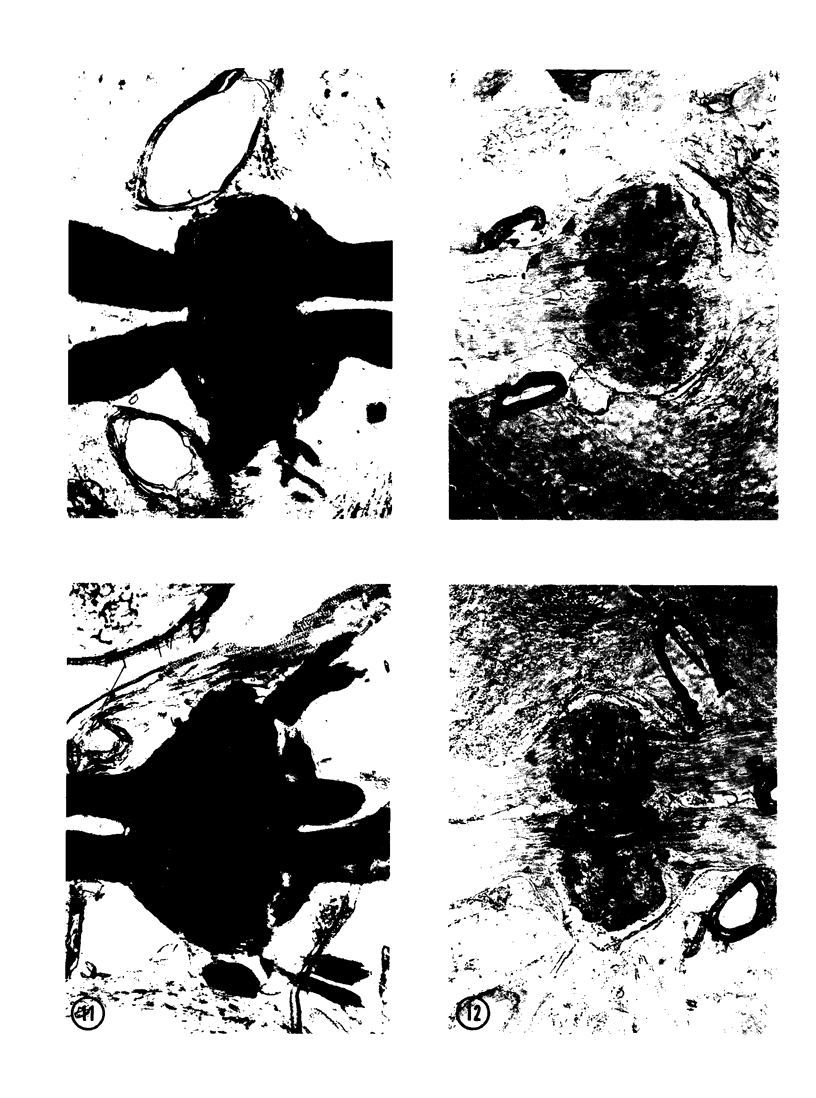
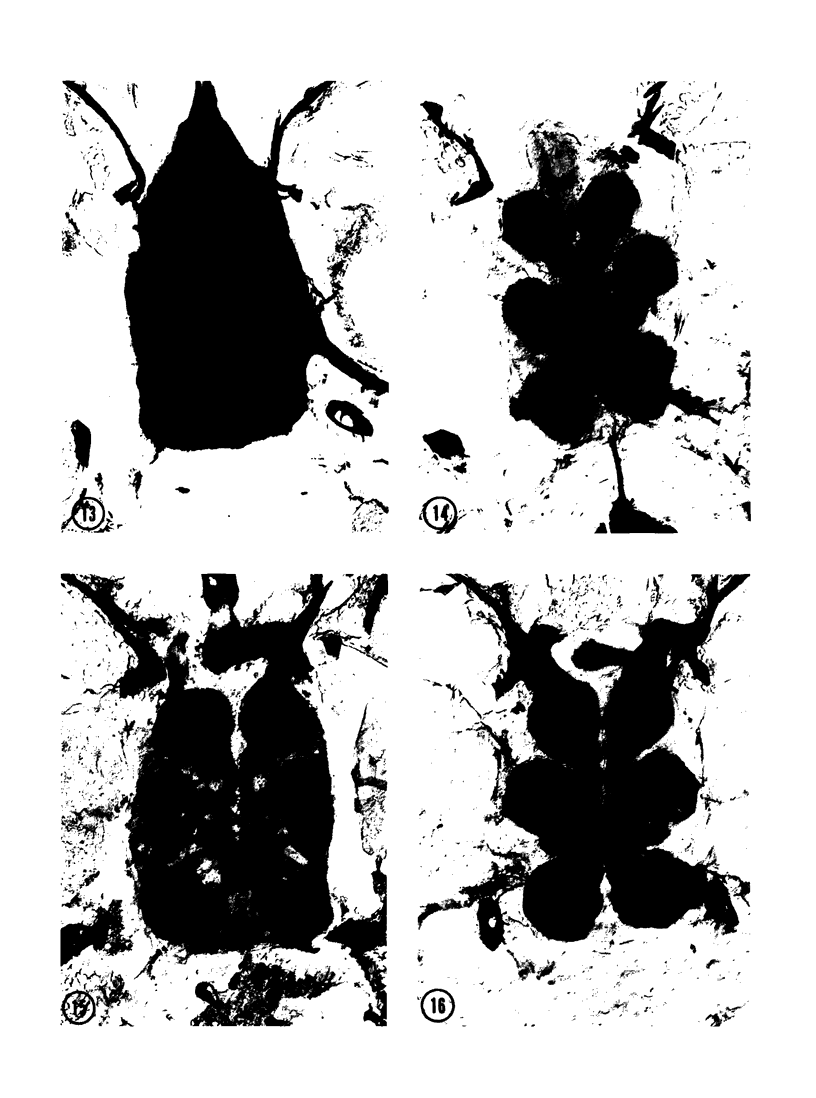
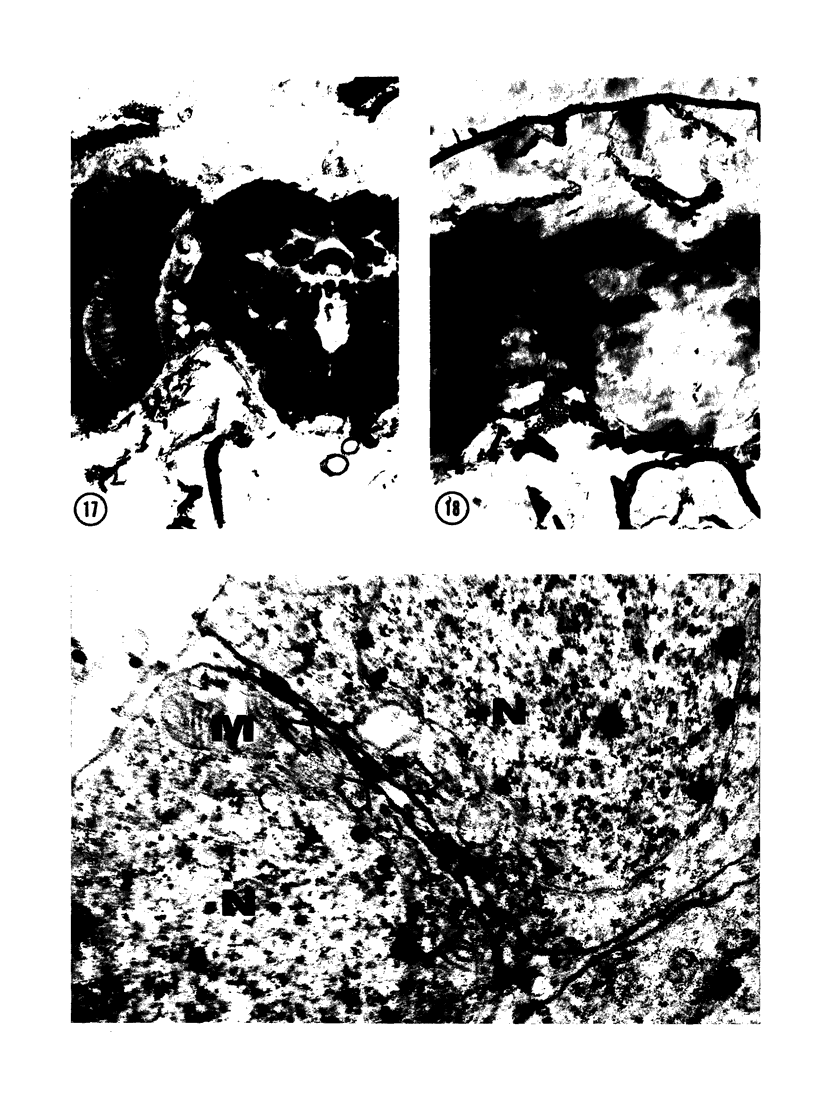




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booth G. M., Metcalf R. L. Histochemical evidence for localized inhibition of cholinesterase in the house fly. Ann Entomol Soc Am. 1970 Jan;63(1):197–204. doi: 10.1093/aesa/63.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth G. M., Metcalf R. L. Phenylthioacetate: a useful substrate for the histochemical and colorimetric detection of cholinesterase. Science. 1970 Oct 23;170(3956):455–457. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3956.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady U. E., Sternburg J. Studies on in vivo cholinesterase inhibition and poisoning symptoms in houseflies. J Insect Physiol. 1967 Jan;13(3):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(67)90078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLHOUN E. H. Physiological events in organophosphorus poisoning. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Sep;37:1127–1134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L., COURTNEY K. D., ANDRES V., Jr, FEATHER-STONE R. M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 Jul;7:88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham A. W., Gregory G. E., Sawick R. M. Bioassay and histochemical studies of the poisoning and recovery of house-flies (Musca domestica L.) treated with diazinon and diazoxon. Bull Entomol Res. 1966 Nov;57(1):107–116. doi: 10.1017/s0007485300052755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessner T., Acara M. Metabolism of thiols. S-Glucosylation. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jun 10;243(11):3142–3147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALMGREN H., SYLVEN B. On the chemistry of the thiocholine method of Koelle. J Histochem Cytochem. 1955 Nov;3(6):441–445. doi: 10.1177/3.6.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYNARD E. A., MAYNARD D. M. Cholinesterase in the crustacean muscle receptor organ. J Histochem Cytochem. 1960 Sep;8:376–379. doi: 10.1177/8.5.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBain J. B., Menn J. J. S-methylation, oxidation, hydroxylation and conjugation of thiophenol in the rat. Biochem Pharmacol. 1969 Sep;18(9):2282–2285. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(69)90340-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachmansohn D. Proteins in excitable membranes: their properties and function in bioelectricity are discussed. Science. 1970 May 29;168(3935):1059–1066. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3935.1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C., Booth G. M. Inhibition of choline acetylase from the house fly (Musca domestica L.) and mouse. Life Sci II. 1971 Mar 22;10(6):337–347. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zettler J. L., Brady U. E. In vivo cholinesterase inhibition in Tribolium castaneum with organophosphate insecticides. J Econ Entomol. 1970 Oct;63(5):1628–1631. doi: 10.1093/jee/63.5.1628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]