Abstract
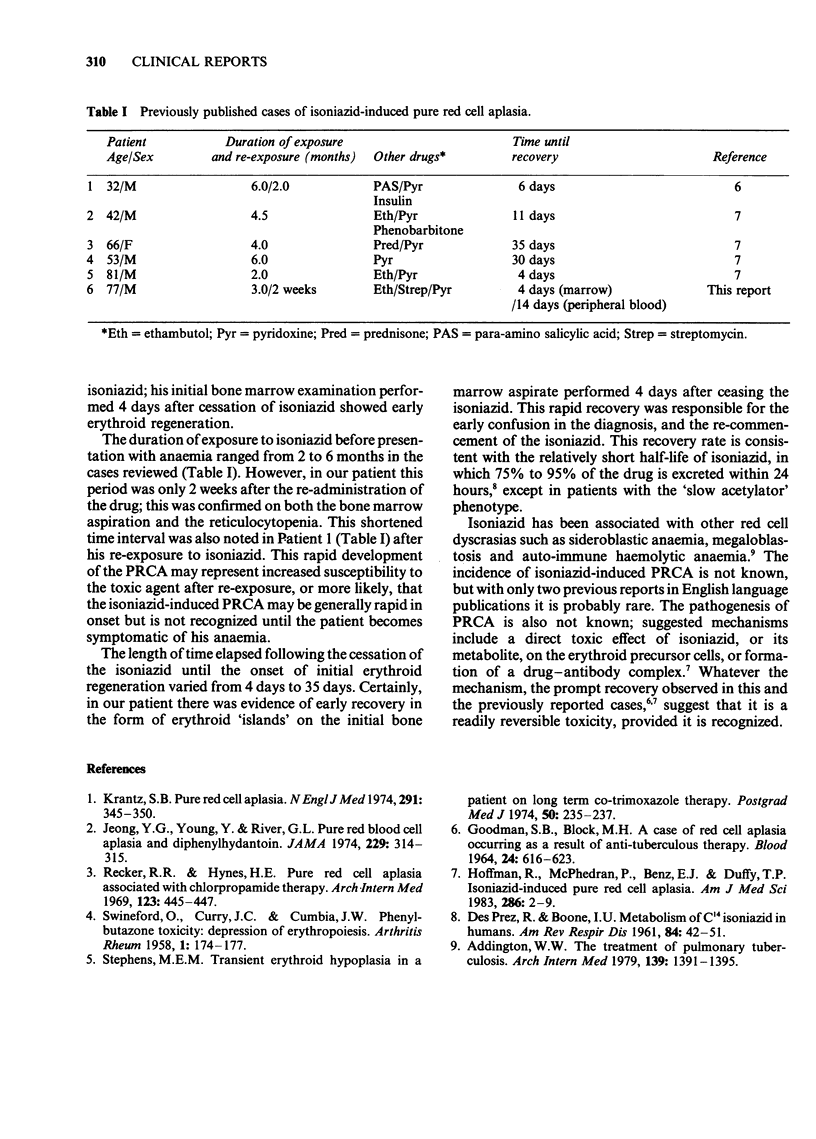
We describe a 77 year old man who developed pure red cell aplasia while receiving antituberculous therapy including isoniazid. Prompt recovery occurred following cessation of isoniazid. In this paper we also review previously described case reports of isoniazid-induced pure red cell aplasia.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addington W. W. The treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. Current options. Arch Intern Med. 1979 Dec;139(12):1391–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DES PREZ R., BOONE I. U. Metabolism of C14-isoniazid in humans. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Jul;84:42–51. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.84.1.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN S. B., BLOCK M. H. A CASE OF RED CELL APLASIA OCCURRING AS A RESULT OF ANTITUBERCULOUS THERAPY. Blood. 1964 Nov;24:616–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeong Y. G., Jung Y., River G. L. Pure RBC aplasia and diphenylhydantoin. JAMA. 1974 Jul 15;229(3):314–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz S. B. Pure red-cell aplasia. N Engl J Med. 1974 Aug 15;291(7):345–350. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197408152910707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recker R. R., Hynes H. E. Pure red blood cell aplasia associated with chlorpropamide therapy. Patient summary and review of the literature. Arch Intern Med. 1969 Apr;123(4):445–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWINEFORD O., Jr, CURRY J. C., CUMBIA J. W. Phenylbutazone toxicity: depression of erythropoiesis; a case report. Arthritis Rheum. 1958 Apr;1(2):174–177. doi: 10.1002/art.1780010210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens M. E. Transient erythroid hypoplasia in a patient on long-term co-trimoxazole therapy. Postgrad Med J. 1974 Apr;50(582):235–237. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.50.582.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


