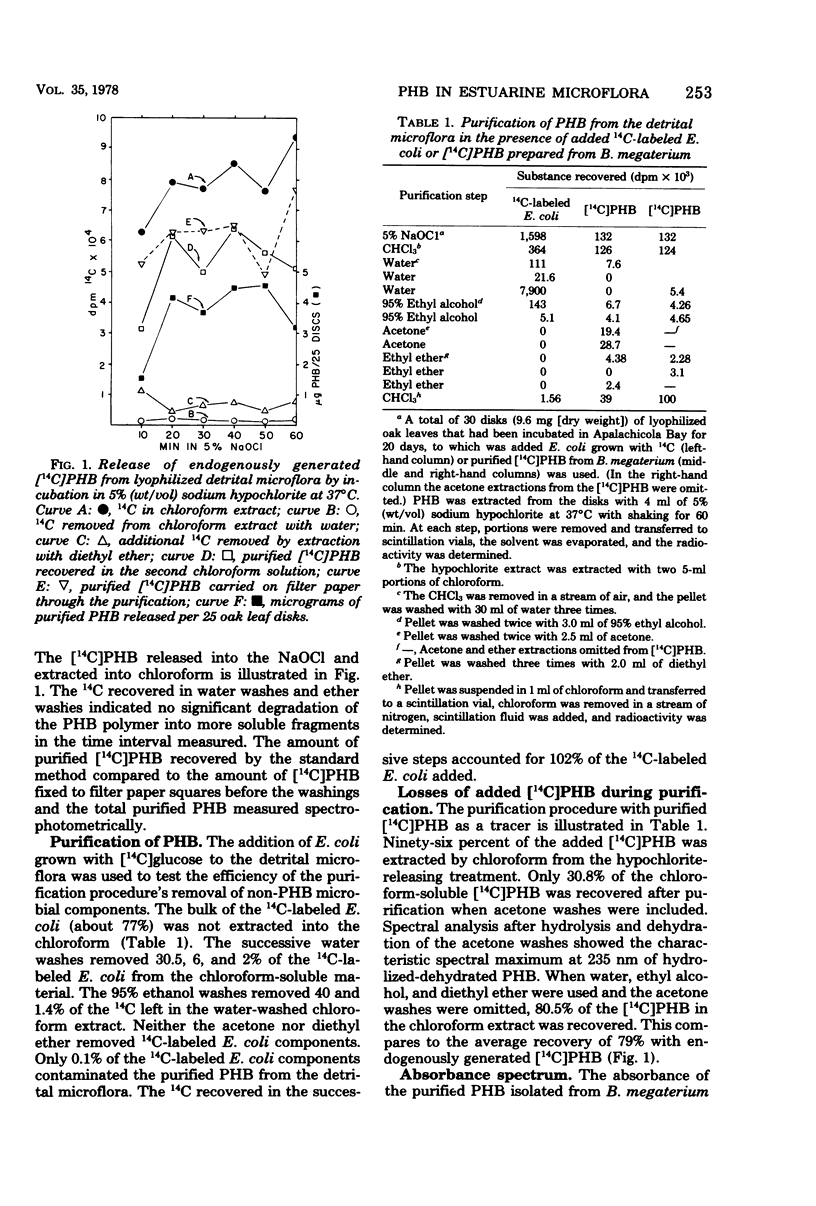
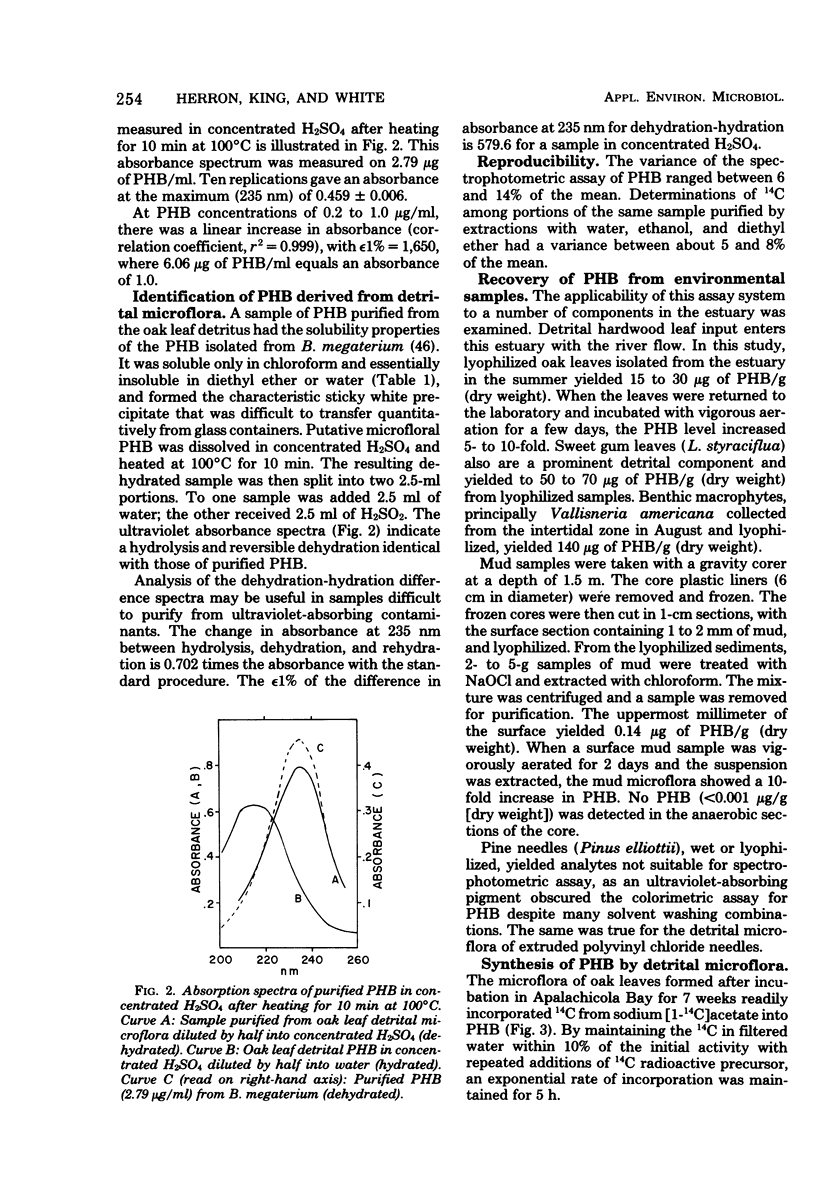
Abstract
Poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) is a uniquely procaryotic endogenous storage polymer whose metabolism has been shown to reflect environmental perturbations in laboratory monocultures. When hydrolyzed for 45 min in 5% sodium hypochlorite, PHB can be isolated from estuarine detrital microflora in high yield and purified free from non-PHB microbial components. Lyophilization of frozen estuarine samples shortens the exposure time to NaOCl necessary for maximal recovery. Lyophilized samples of hardwood leaves, Vallisneria, and the aerobic upper millimeter of estuarine muds yielded PHB. The efficiency of incorporation of sodium [1-14C]acetate into PHB is very high and is stimulated by aeration. PHB was not recovered from the anaerobic portions of sediments unless they were aerated for a short time. Levels of PHB in the detrital microbial community do not correlate with the microbial biomass as measured by the extractible lipid phosphate, suggesting that PHB-like eucaryotic endogenous storage materials may more accurately reflect the metabolic status of the population than its biomass.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobbie R. J., Morrison S. J., White D. C. Effects of substrate biodegradability on the mass and activity of the associated estuarine microbiota. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):179–184. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.179-184.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosshard-Heer E., Bachofen R. Synthese von Specicherstoffen aus Pyruvat durch Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;65(1):61–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdon K. L. Fatty Material in Bacteria and Fungi Revealed by Staining Dried, Fixed Slide Preparations. J Bacteriol. 1946 Dec;52(6):665–678. doi: 10.1128/jb.52.6.665-678.1946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRABTREE K., MCCOY E., BOYLE W. C., ROHLICH G. A. ISOLATION, IDENTIFICATION, AND METABOLIC ROLE OF THE SUDANOPHILIC GRANULES OF ZOOGLOEA RAMIGERA. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:218–226. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.218-226.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr N. G. The occurrence of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate in the blue-green alga, Chlorogloea fritschii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 8;120(2):308–310. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90353-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree K., Boyle W., McCoy E., Rohlich G. A. A mechanism of floc formation by Zoogloea ramigera. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1966 Dec;38(12):1968–1980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. B. CELLULAR LIPIDS OF A NOCARDIA GROWN ON PROPANE AND N-BUTANE. Appl Microbiol. 1964 Jul;12:301–304. doi: 10.1128/am.12.4.301-304.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOUDOROFF M., STANIER R. Y. Role of poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid in the assimilation of organic carbon by bacteria. Nature. 1959 May 23;183(4673):1440–1442. doi: 10.1038/1831440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes E. A., Senior P. J. The role and regulation of energy reserve polymers in micro-organisms. Adv Microb Physiol. 1973;10:135–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deinema M. H. Bacterial flocculation and production of poly- -hydroxybutyrate. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Dec;24(6):857–858. doi: 10.1128/am.24.6.857-858.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeruwa A. C., Hawirko R. Z. Poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate metabolism during growth and sporulation of Clostridium botulinum. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):989–993. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.989-993.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK G. DIE BIOSYNTHESE DER POLY-BETA-HYDROXYBUTTERSAEURE DURCH KNALLGASBAKTERIEN. II. VERWERTUNG ORGANISCHER SAEUREN. Arch Mikrobiol. 1964 Feb 21;47:230–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson F. A., Dawes E. A. Regulation of the tricarboxylic acid cycle and poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate metabolism in Azotobacter beijerinckii grown under nitrogen or oxygen limitation. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Dec;97(2):303–312. doi: 10.1099/00221287-97-2-303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannan L. V., Rehacek Z. Formation of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate by Actinomycetes. Indian J Biochem. 1970 Jun;7(2):126–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. D., White D. C. Muramic acid as a measure of microbial biomass in estuarine and marine samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):777–783. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.777-783.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. D., White D. C., Taylor C. W. Use of lipid composition and metabolism to examine structure and activity of estuarine detrital microflora. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1177–1183. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1177-1183.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kominek L. A., Halvorson H. O. Metabolism of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate and acetoin in Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1251–1259. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1251-1259.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAW J. H., SLEPECKY R. A. Assay of poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82:33–36. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.1.33-36.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDGREN D. G., ALPER R., SCHNAITMAN C., MARCHESSAULT R. H. CHARACTERIZATION OF POLY-BETA-HYDROXYBUTYRATE EXTRACTED FROM DIFFERENT BACTERIA. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:245–251. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.245-251.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACRAE R. M., WILKINSON J. F. Poly-beta-hyroxybutyrate metabolism in washed suspensions of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus megaterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Aug;19(1):210–222. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-1-210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakata H. M. Role of acetate in sporogenesis of Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):784–788. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.784-788.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuti M. P., De Bertoldi M., Lepidi A. A. Influence of phenylacetic acid on poly- -hydroxybutyrate (PHB) polymerization and cell elongation in Azotobacter chroococcum Beij. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Aug;18(8):1257–1261. doi: 10.1139/m72-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raman Kutty M., Kannan L. V., Rehacek Z. Effect of phosphate on biosynthesis of antimycin A and production and utilization of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate by Streptomyces antibioticus. Indian J Biochem. 1969 Dec;6(4):230–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHLEGEL H. G., GOTTSCHALK G., VON BARTHA R. Formation and utilization of poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid by Knallgas bacteria (Hydrogenomonas). Nature. 1961 Jul 29;191:463–465. doi: 10.1038/191463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIERRA G., GIBBONS N. E. Role and oxidation pathway of poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid in Micrococcus halodenitrificans. Can J Microbiol. 1962 Apr;8:255–269. doi: 10.1139/m62-032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH-WHITE S., PEACOCK W. J., TURNER B., DEN DULK G. M. A ring chromosome in man. Nature. 1963 Jan 5;197:102–103. doi: 10.1038/197102b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster E., Schlegel H. G. Chemolithotrophes Wachstum von Hydrogenomonas H16 im Chemostaten mit elektrolytischer Knallgaserzeugung. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;58(4):380–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short S. A., White D. C., Aleem M. I. Phospholipid metabolism in Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):142–150. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.142-150.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slepecky R. A., Law J. H. SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION OF POLY-beta-HYDROXYBUTYRIC ACID IN CONNECTION WITH SPORULATION OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82(1):37–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.1.37-42.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobek J. M., Charba J. F., Foust W. N. Endogenous metabolism of Azotobacter agilis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):687–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.687-695.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Doudoroff M., Kunisawa R., Contopoulou R. THE ROLE OF ORGANIC SUBSTRATES IN BACTERIAL PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Aug;45(8):1246–1260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.8.1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson L. H., Socolofsky M. D. Cyst formation and poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid accumulation in Azotobacter. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):304–310. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.304-310.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokes J. L., Powers M. T. Stimulation of poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate oxidation in Sphaerotilus discophorus by manganese and magnesium. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):295–301. doi: 10.1007/BF00406343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uffen R. L., Sybesma C., Wolfe R. S. Mutants of Rhodospirrillum rubrum obtained after long-term anaerobic, dark growth. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1348–1356. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1348-1356.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON D. H., WILKINSON J. F. The isolation and estimation of the poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate inclusions of Bacillus species. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Aug;19(1):198–209. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-1-198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward A. C., Dawes E. A. A disk assay for poly- -hydroxybutyrate. Anal Biochem. 1973 Apr;52(2):607–613. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Tucker A. N. Phospholipid metabolism during changes in the proportions of membrane-bound respiratory pigments in Haemophilus parainfluenzae. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):199–209. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.199-209.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zevenhuizen L. P., Ebbink A. G. Interrelations between glycogen, poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid and lipids during accumulation and subsequent utilization in a Pseudomonas. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1974;40(1):103–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00394558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


