Abstract
Although extrapyramidal features in normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) are not uncommon, presentations with Parkinson's syndrome as the predominant feature are rare and may give rise to diagnostic difficulties. Failure of patients with parkinsonism to respond to therapy, should alert one to the possibility of NPH.
Full text
PDF
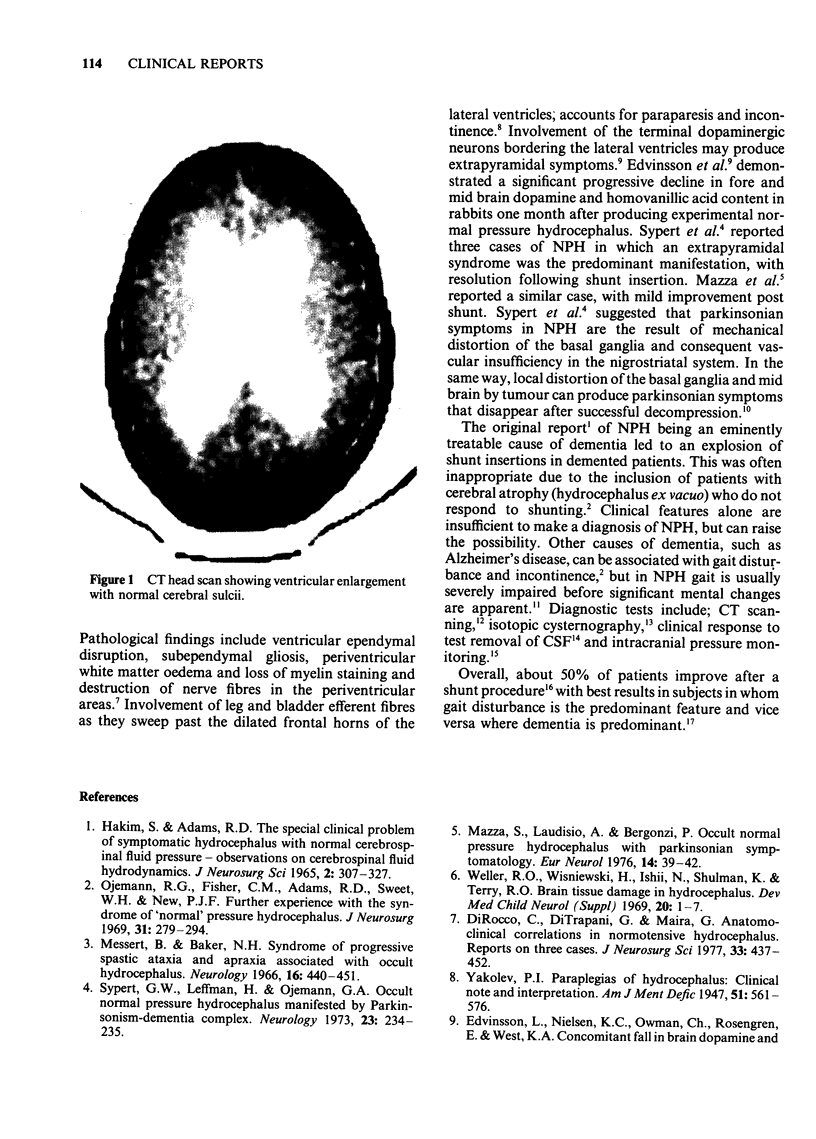

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black P. M. Idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Results of shunting in 62 patients. J Neurosurg. 1980 Mar;52(3):371–377. doi: 10.3171/jns.1980.52.3.0371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chawla J. C., Hulme A., Cooper R. Intracranial pressure in patients with dementia and communicating hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg. 1974 Mar;40(3):376–380. doi: 10.3171/jns.1974.40.3.0376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakim S., Adams R. D. The special clinical problem of symptomatic hydrocephalus with normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Observations on cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics. J Neurol Sci. 1965 Jul-Aug;2(4):307–327. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(65)90016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs L., Conti D., Kinkel W. R., Manning E. J. "Normal-pressure" hydrocephalus. Relationship of clinical and radiographic findings to improvement following shunt surgery. JAMA. 1976 Feb 2;235(5):510–512. doi: 10.1001/jama.235.5.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman R. Normal pressure hydrocephalus. Contemp Neurol Ser. 1977;15:69–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazza S., Laudisio A., Bergonzi P. Occult normal pressure hydrocephalus with parkinsonian symptomatology. Eur Neurol. 1976;14(1):39–42. doi: 10.1159/000114724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messert B., Baker N. H. Syndrome of progressive spastic ataxia and apraxia associated with occult hydrocephalus. Neurology. 1966 May;16(5):440–452. doi: 10.1212/wnl.16.5.440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley I. F., Radü E. W. Factors influencing the development of periventricular lucencies in patients with raised intracranial pressure. Neuroradiology. 1979 Feb 26;17(2):65–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00556020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVER L. Parkinsonism due to midbrain compression. Lancet. 1959 Nov 14;2(7107):817–819. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)90754-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojemann R. G., Fisher C. M., Adams R. D., Sweet W. H., New P. F. Further experience with the syndrome of "normal" pressure hydrocephalus. J Neurosurg. 1969 Sep;31(3):279–294. doi: 10.3171/jns.1969.31.3.0279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sypert G. W., Leffman H., Ojemann G. A. Occult normal pressure hydrocephalus manifested by parkinsonism-dementia complex. Neurology. 1973 Mar;23(3):234–238. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.3.234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller R. O., Wisniewski H., Ishii N., Shulman K., Terry R. D. Brain tissue damage in hydrocephalus. Dev Med Child Neurol Suppl. 1969;20:1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1969.tb09237.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]