Abstract
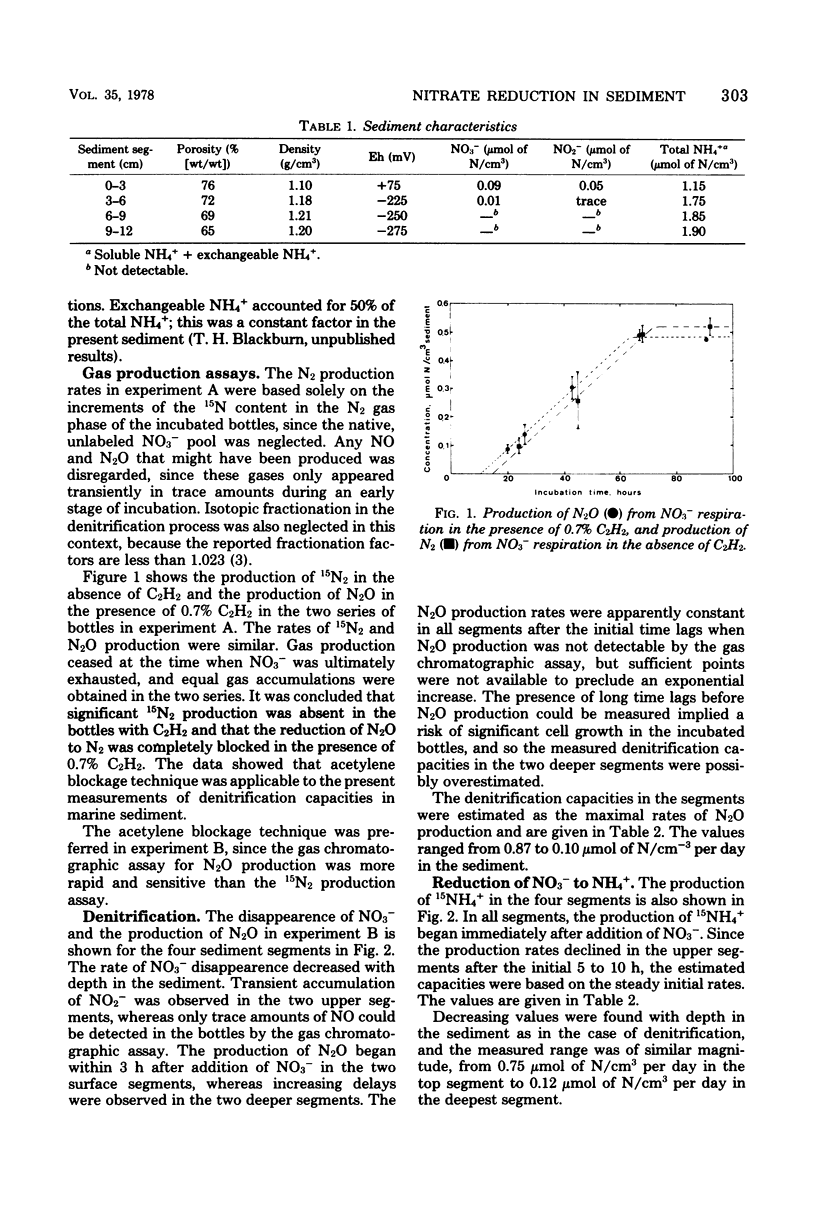
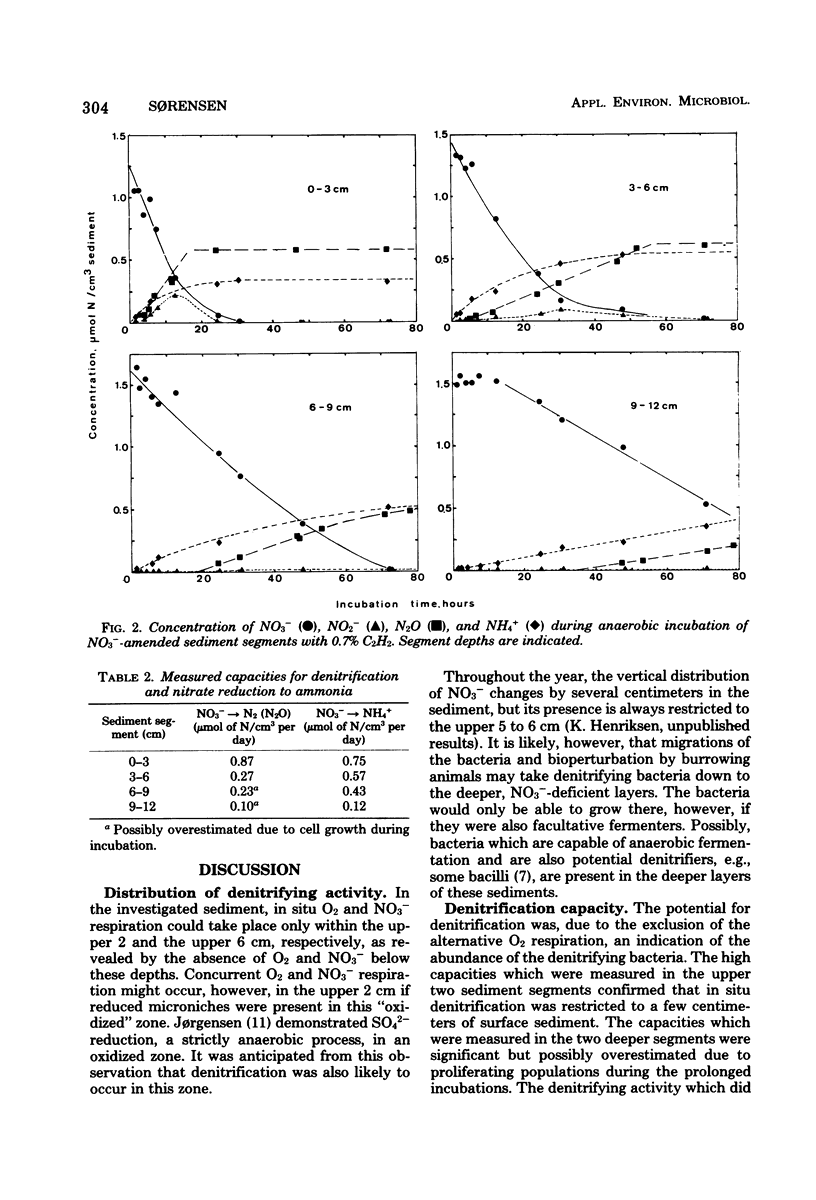
The capacity for dissimilatory reduction of NO3− to N2 (N2O) and NH4+ was measured in 15NO3−-amended marine sediment. Incubation with acetylene (7 × 10−3 atmospheres [normal]) caused accumulation of N2O in the sediment. The rate of N2O production equaled the rate of N2 production in samples without acetylene. Complete inhibition of the reduction of N2O to N2 suggests that the “acetylene blockage technique” is applicable to assays for denitrification in marine sediments. The capacity for reduction of NO3− by denitrification decreased rapidly with depth in the sediment, whereas the capacity for reduction of NO3− to NH4+ was significant also in deeper layers. The data suggested that the latter process may be equally as significant as denitrification in the turnover of NO3− in marine sediments.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balderston W. L., Sherr B., Payne W. J. Blockage by acetylene of nitrous oxide reduction in Pseudomonas perfectomarinus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Apr;31(4):504–508. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.4.504-508.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorova R. I., Milekhina E. I., Il'iukhina N. I. O vozmozhnosti metoda "gazoobmena" dlia obnaruzheniia zhizni vne zemli--identifikatsiia azotfiksiruiushchikh mikroorganizmov. Izv Akad Nauk SSSR Biol. 1973 Nov-Dec;6:797–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan S. M., Hall J. B. The physiological function of nitrate reduction in Clostridium perfringens. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Mar;87(1):120–128. doi: 10.1099/00221287-87-1-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. J. Reduction of nitrogenous oxides by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Dec;37(4):409–452. doi: 10.1128/br.37.4.409-452.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichinoty F. Les nitrate-réductases bactériennes. IV. Régulation de la biosynthèse et de l'activité de l'enzyme B. Arch Mikrobiol. 1970;71(2):116–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshinari T., Knowles R. Acetylene inhibition of nitrous oxide reduction by denitrifying bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Apr 5;69(3):705–710. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90932-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


