Abstract
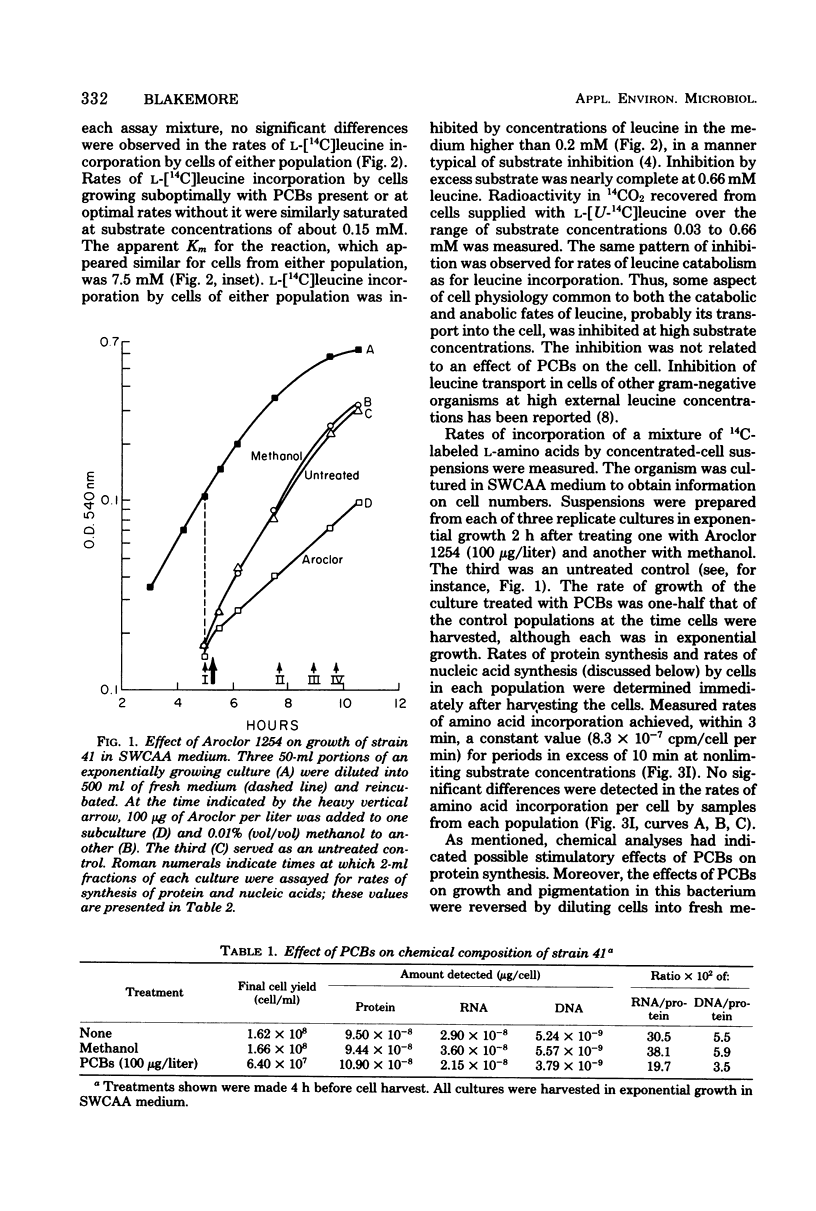
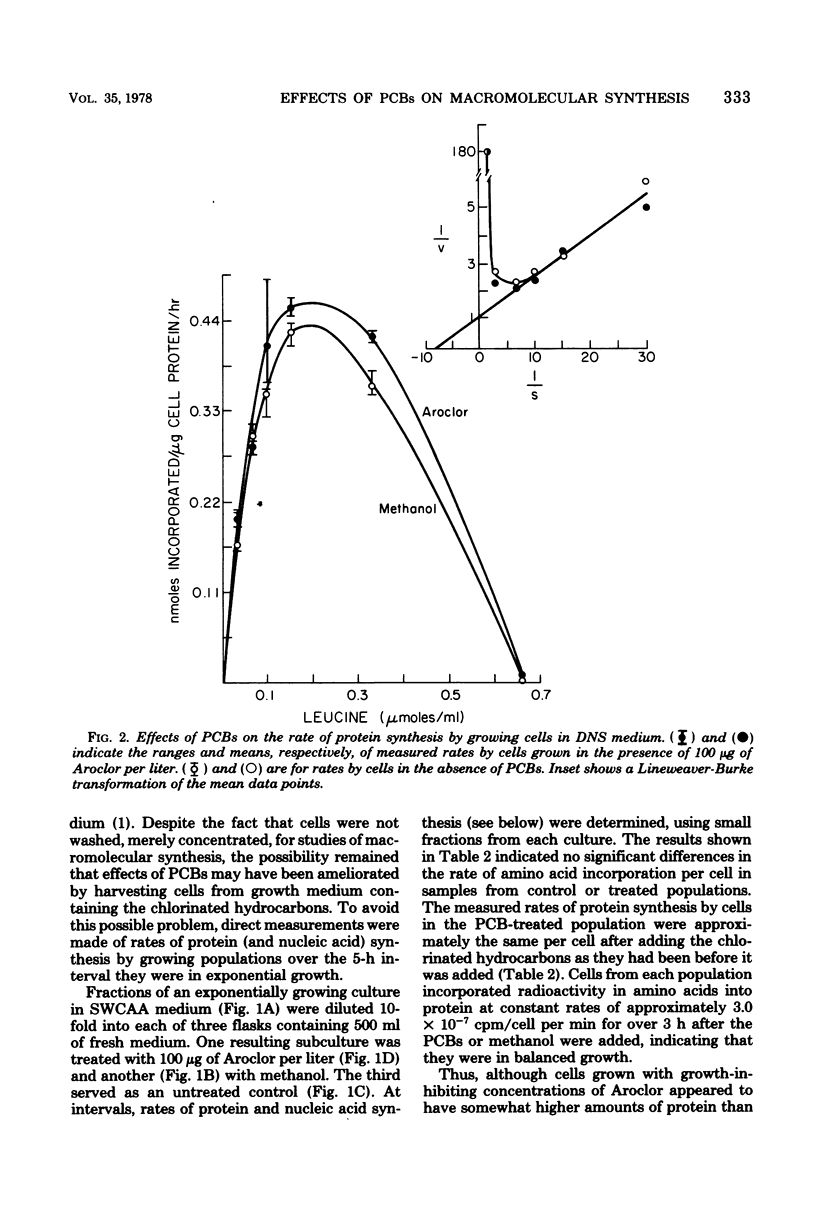
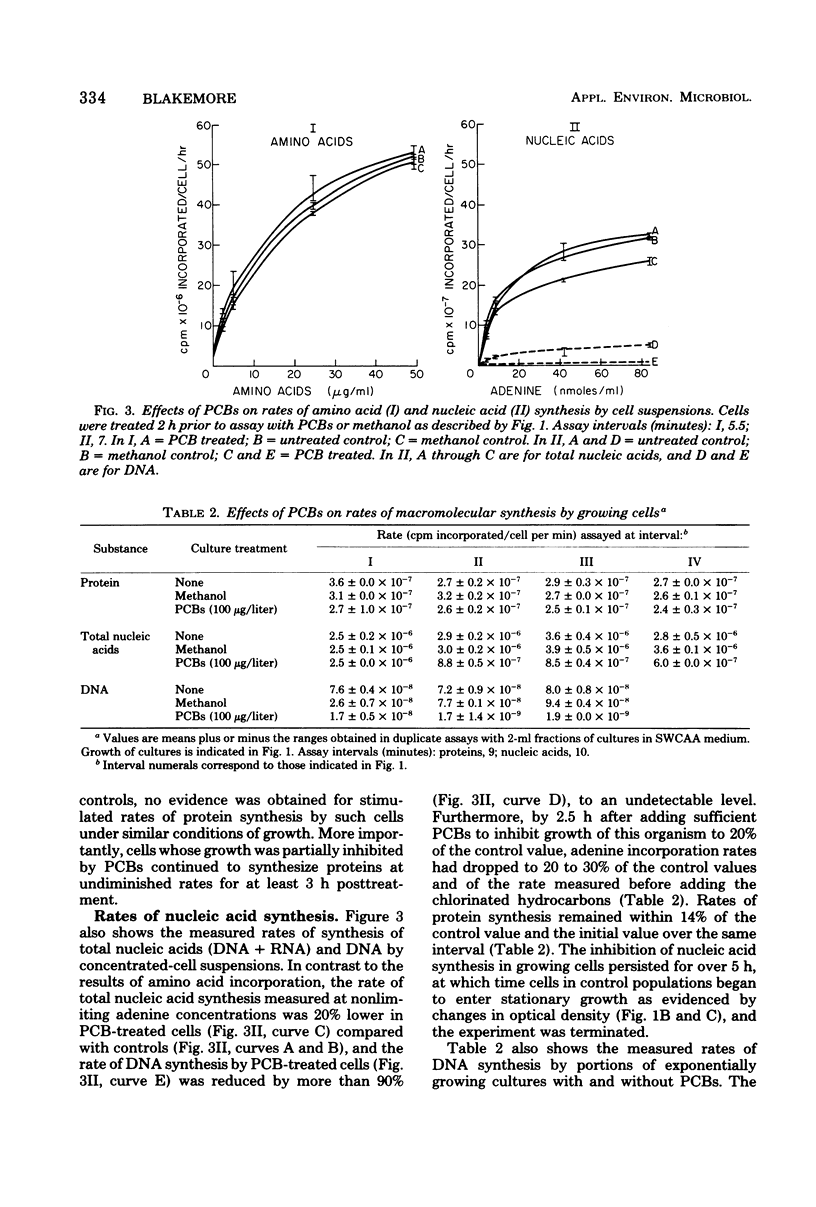
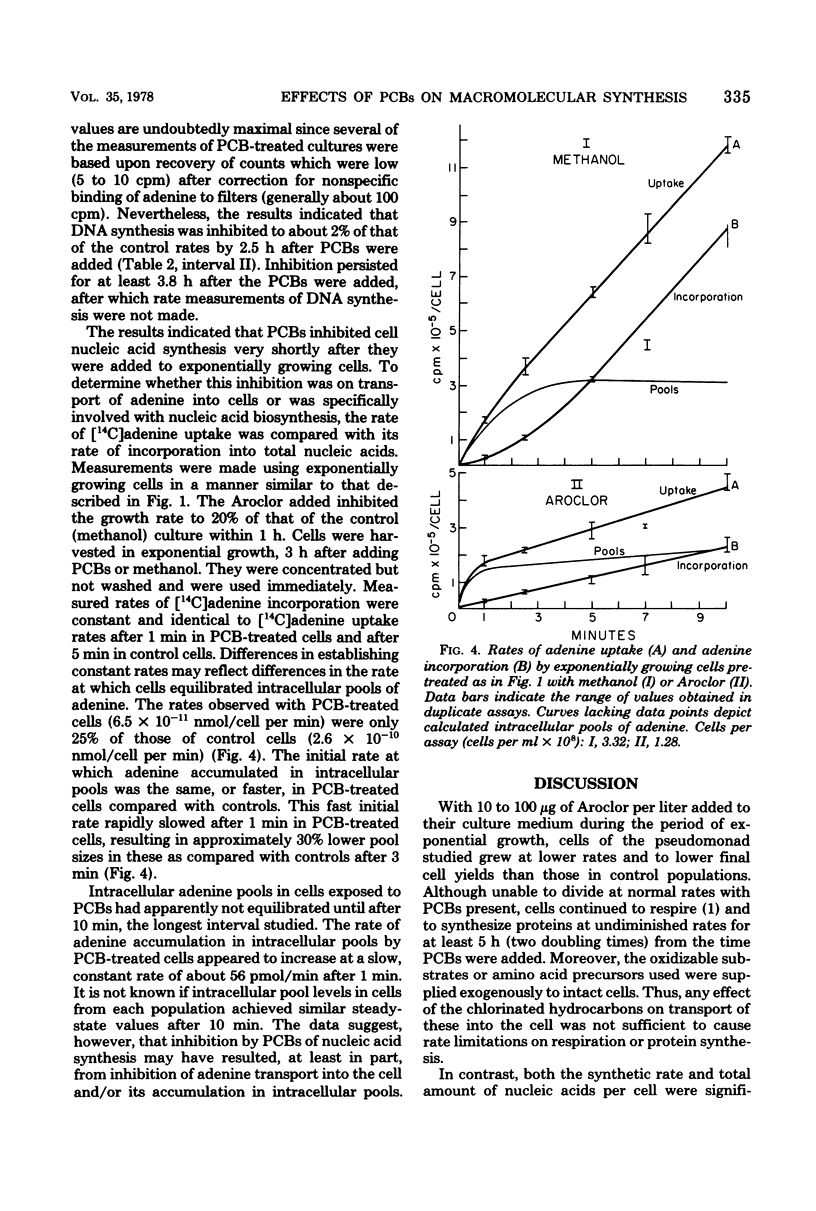
Growth rates and final cell yields of a polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)-sensitive pseudomonad isolated from the open ocean were reduced in a dose-dependent manner by 10 to 100 μg of Aroclor 1254 per liter, a commercial mixture of PCB isomers added to its culture medium. Effects on growth rates were detected within 1 h (approximately one doubling time) of treatment. By 4 h posttreatment, the amounts of deoxyribonucleic acid and ribonucleic acid per cell in exponentially growing populations treated with sublethal doses of Aroclor were detectably lower than in appropriate controls. Corresponding cell protein values were slightly higher than in controls. Selective degradation of cell proteins or nucleic acids was not detected in cells whose growth was totally suppressed for 4 h by PCBs. Cells whose growth rate was inhibited 20 to 50% by Aroclor synthesized protein at normal rates for periods in excess of 5 h from the time the chlorinated hydrocarbons were added. In contrast, rates per cell of adenine uptake and adenine incorporation into deoxyribonucleic acid and total nucleic acids by the cells treated with PCBs were significantly lower than in control cells. Intracellular adenine pools of cells whose growth was inhibited to 20% of the control rate by PCBs were 30% smaller and appeared to require a longer interval to equilibrate than those of untreated cells. This may indicate impaired transport and/or efflux of this nucleic acid precursor through the membrane of affected cells. Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis in this sensitive bacterium by PCBs could explain the observed inhibitory effects of the chlorinated hydrocarbons on its growth.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore R. P., Carey A. E. Effects of polychlorinated biphenyls on growth and respiration of heterotrophic marine bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):323–328. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.323-328.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degnen S. T., Newton A. Dependence of cell division on the completion of chromosome replication in Caulobacter. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):852–856. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.852-856.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A., Rosenberg E. Linkages between deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and cell division in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):69–79. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.69-79.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmanian M., Oxender D. L. Derepressed leucine transport activity in Escherichia coli. J Supramol Struct. 1972;1(1):55–59. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


