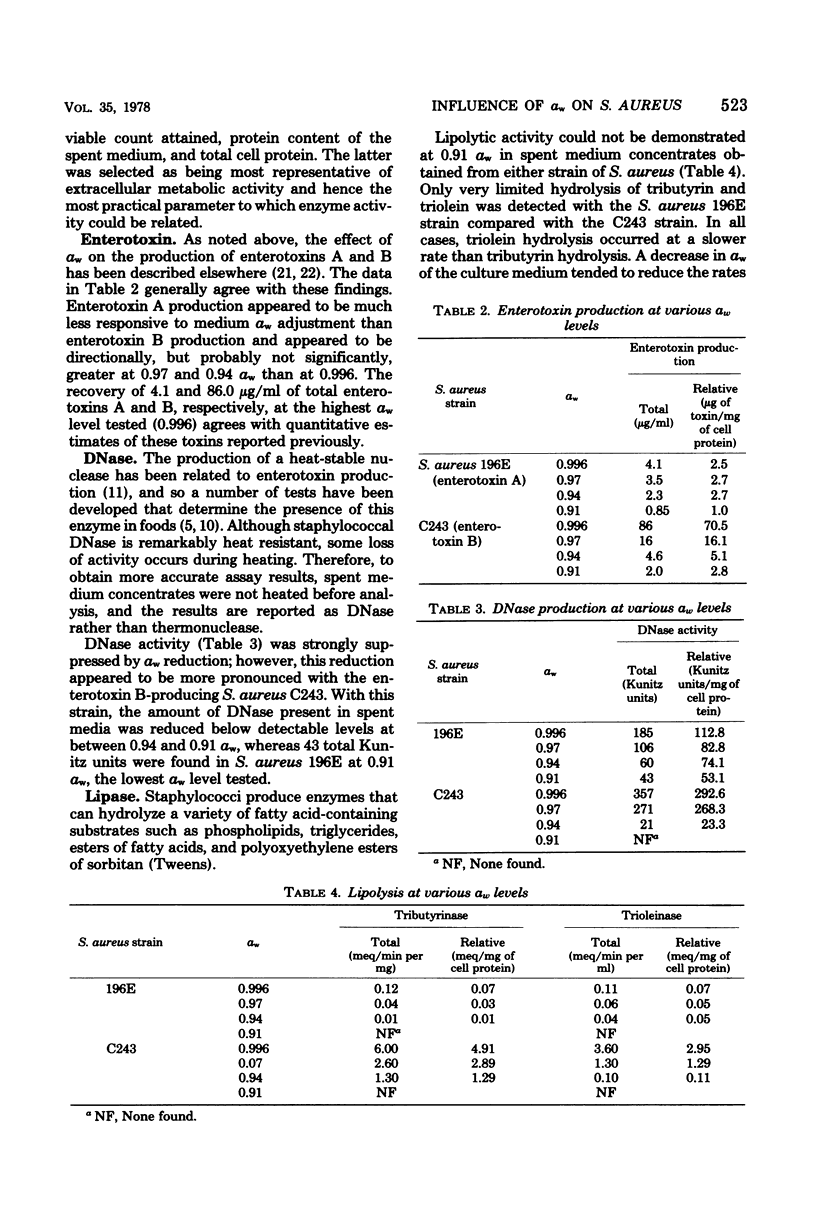
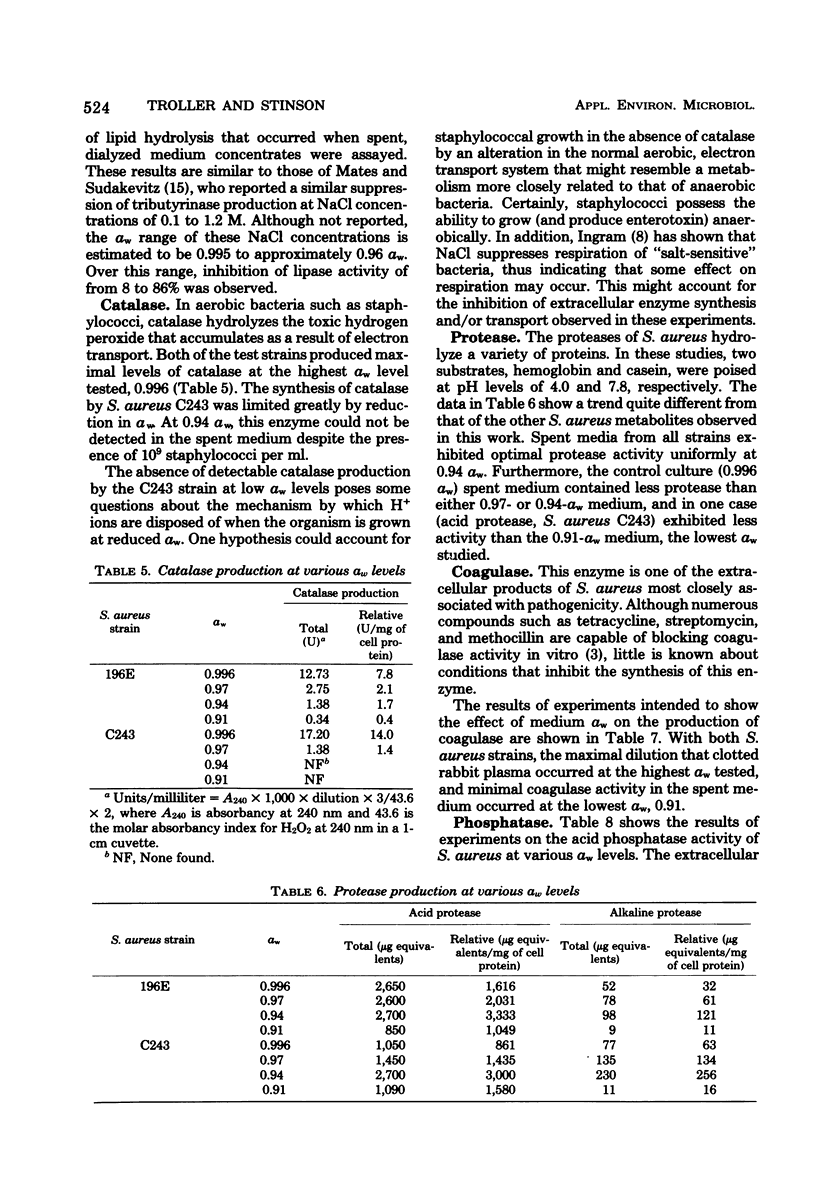
Abstract
Two enterotoxigenic strains of Staphylococcus aureus were examined for their ability to produce a number of extracellular enzymes at various water activity (alphaw) levels. Supernatant, dialyzed culture media were analyzed for total and relative levels of enzyme activity. With the exception of protease, enzyme activity was greatest in spent media obtained from cultures grown at 0.996 alphaw, the highest level tested. Enzyme activity in spent media from an enterotoxin B-producing strain was generally more sensitive to alphaw reduction than activity from an enterotoxin A-producing strain. Unlike the other enzymes assayed, acid and alkaline protease activities were greatest when the organism was grown at 0.94 alphaw.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEERS R. F., Jr, SIZER I. W. A spectrophotometric method for measuring the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide by catalase. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):133–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. The sodium and potassium content of non-halophilic bacteria in relation to salt tolerance. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 May;25:97–102. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagnari L., Mocci A. Ricerche in vitro sull'effetto di vari antibiotici nei confronti dell'attivita' coagulasica dello stafilococco. G Batteriol Virol Immunol. 1965 Jan-Feb;58(1):7–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A., Deibel R. H. Turbidimetric assay of staphylococcal nuclease. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Mar;25(3):337–341. doi: 10.1128/am.25.3.337-341.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNITZ M. Crystalline desoxyribonuclease; isolation and general properties; spectrophotometric method for the measurement of desoxyribonuclease activity. J Gen Physiol. 1950 Mar;33(4):349–362. doi: 10.1085/jgp.33.4.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Genigeorgis C., Hoeprich P. D. Metachromatic agar-diffusion methods for detecting staphylococcal nuclease activity. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Apr;21(4):585–587. doi: 10.1128/am.21.4.585-587.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malveaux F. J., San Clemente C. L. Elution of loosely bound acid phosphatase from Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jul;15(4):738–743. doi: 10.1128/am.15.4.738-743.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mates A., Sudakevitz D. Production of lipase by Staphylococcus aureus under various growth conditions. J Appl Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;36(2):219–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1973.tb04094.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean R. A., Lilly H. D., Alford J. A. Effects of meat-curing salts and temperature on production of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1207–1211. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1207-1211.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Measures J. C. Role of amino acids in osmoregulation of non-halophilic bacteria. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):398–400. doi: 10.1038/257398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAN Y. L., BLUMENTHAL H. J. Correlation between acid phosphatase and coagulase production or phage type of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82:124–129. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.1.124-129.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT W. J. Water relations of Staphylococcus aureus at 30 degrees C. Aust J Biol Sci. 1953 Nov;6(4):549–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperber W. H., Tatini S. R. Interpretation of the tube coagulase test for identification of Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Apr;29(4):502–505. doi: 10.1128/am.29.4.502-505.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troller J. A. Effect of water activity on enterotoxin A production and growth of Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Sep;24(3):440–443. doi: 10.1128/am.24.3.440-443.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troller J. A. Effect of water activity on enterotoxin B production and growth of Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Mar;21(3):435–439. doi: 10.1128/am.21.3.435-439.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor R., Lachica F., Weiss K. F., Deibel R. H. Relationships among coagulase, enterotoxin, and heat-stable deoxyribonuclease production by Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jul;18(1):126–127. doi: 10.1128/am.18.1.126-127.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weirether F. J., Lewis E. E., Rosenwald A. J., Lincoln R. E. Rapid quantitative serological assay of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.284-291.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



