Abstract
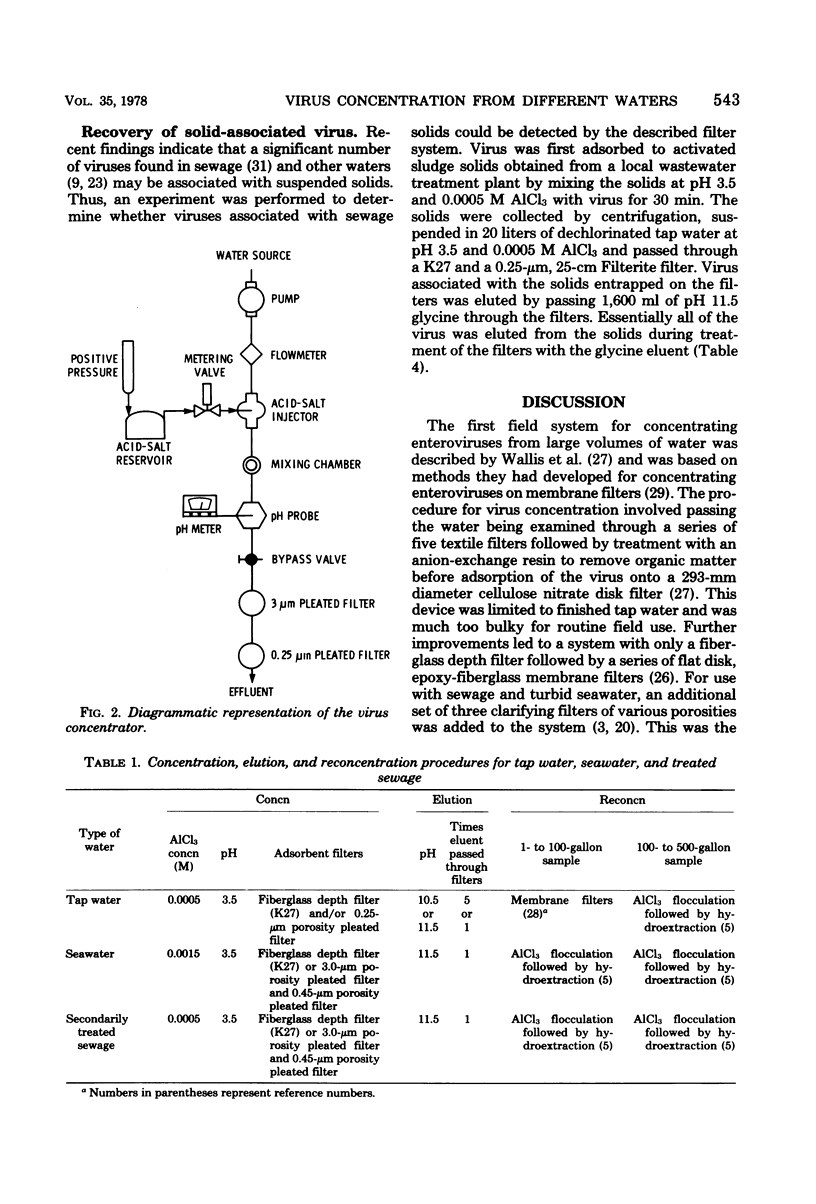
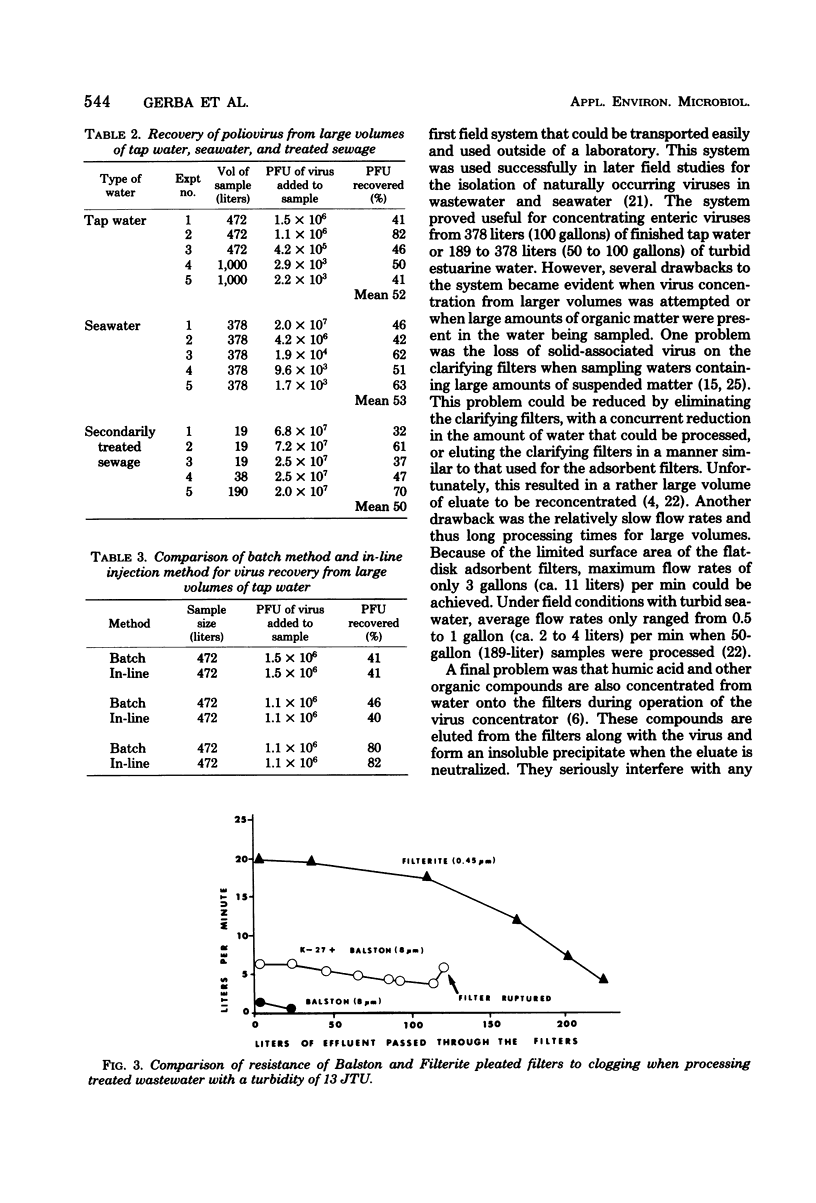
Methods are described for the efficient concentration of an enterovirus from large volumes of tap water, sewage, and seawater. Virus in acidified water (pH 3.5) in the presence of aluminum chloride was adsorbed to a 10-inch (ca. 25.4 cm) fiberglass depth cartridge and a 10-inch pleated epoxy-fiberglass filter in a series at flow rates of up to 37.8 liters (10 gallons) per min. Adsorbed viruses were eluted from the filters with glycine buffer (pH 10.5 to 11.5), and the eluate was reconcentrated by using a combination of aluminum flocculation followed by hydroextraction. With this procedure, poliovirus in large volumes of tap water, seawater, and sewage could be concentrated with an average efficiency of 52, 53, and 50%, respectively. It was demonstrated that this method is capable of detecting surface solid-associated viruses originating from sewage treatment plants. No difference in virus recovery between laboratory batch studies and a set-up with acid-salt injection was found. This unified scheme for the concentration of viruses has many advantages over previously described systems. These include: high operating flow rates, low weight and small size, effectiveness with a variety of waters with widely varying qualities, and filters with a high resistance to clogging.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barron A. L., Olshevsky C., Cohen M. M. Characteristics of the BGM line of cells from African green monkey kidney. Brief report. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1970;32(4):389–392. doi: 10.1007/BF01250067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrah S. R., Gerba C. P., Goyal S. M., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Regeneration of pleated filters used to concentrate enteroviruses from large volumes of tap water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):308–311. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.308-311.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrah S. R., Gerba C. P., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Concentration of viruses from large volumes of tap water using pleated membrane filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):221–226. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.221-226.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrah S. R., Goyal S. M., Gerba C. P., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Concentration of enteroviruses from estuarine water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1192–1196. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1192-1196.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrah S., Wallis C., Shaffer P. T., Melnick J. L. Reconcentration of poliovirus from sewage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Nov;32(5):653–658. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.5.653-658.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerba C. P., Schaiberger G. E. Effect of particulates on virus survival in seawater. J Water Pollut Control Fed. 1975 Jan;47(1):93–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert R. G., Rice R. C., Bouwer H., Gerba C. P., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Wastewater renovation and reuse: virus removal by soil filtration. Science. 1976 Jun 4;192(4243):1004–1005. doi: 10.1126/science.1273580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson M., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Concentration and purification of enteroviruses by membrane chromatography. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Nov;32(5):689–693. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.5.689-693.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. F., Jr, Akin E. W., Benton W. H., Mayhew C. J., Metcalf T. G. Recovery of poliovirus from turbid estuarine water on microporous filters by the use of celite. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Mar;27(3):506–512. doi: 10.1128/am.27.3.506-512.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. F., Jr, Akin E. W., Benton W. H., Metcalf T. G. Virus in water. II. Evaluation of membrane cartridge filters for recovering low multiplicities of poliovirus from water. Appl Microbiol. 1972 May;23(5):880–888. doi: 10.1128/am.23.5.880-888.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill W. F., Jr, Jakubowski W., Akin E. W., Clarke N. A. Detection of virus in water: sensitivity of the tentative standard method for drinking water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):254–261. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.254-261.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowski W., Hill W. F., Jr, Clarke N. A. Comparative study of four microporous filters for concentrating viruses from drinking water. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jul;30(1):58–65. doi: 10.1128/am.30.1.58-65.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowski W., Hoff J. C., Anthony N. C., Hill W. F., Jr Epoxy-fiberglass adsorbent for concentrating viruses from large volumes of potable water. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Sep;28(3):501–502. doi: 10.1128/am.28.3.501-502.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenelson E., Fattal B., Hostovesky T. Organic flocculation: an efficient second-step concentration method for the detection of viruses in tap water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):638–639. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.638-639.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf T. G., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Environmental factors influencing isolation of enteroviruses from polluted surface waters. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):920–926. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.920-926.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaub S. A., Sagik B. P. Association of enteroviruses with natural and artificially introduced colloidal solids in water and infectivity of solids-associated virions. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Aug;30(2):212–222. doi: 10.1128/am.30.2.212-222.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Gerba C. P., Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Concentration of enteroviruses from large volumes of turbid estuary water. Can J Microbiol. 1977 Jun;23(6):770–778. doi: 10.1139/m77-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Wallis C., Henderson M., Melnick J. L. Concentration of enteroviruses from large volumes of water. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Oct;26(4):529–534. doi: 10.1128/am.26.4.529-534.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Concentration of enteroviruses on membrane filters. J Virol. 1967 Jun;1(3):472–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.3.472-477.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis C., Melnick J. L. Concentration of viruses on aluminum and calcium salts. Am J Epidemiol. 1967 May;85(3):459–468. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellings F. M., Lewis A. L., Mountain C. W. Demonstration of solids-associated virus in wastewater and sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):354–358. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.354-358.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



