Abstract
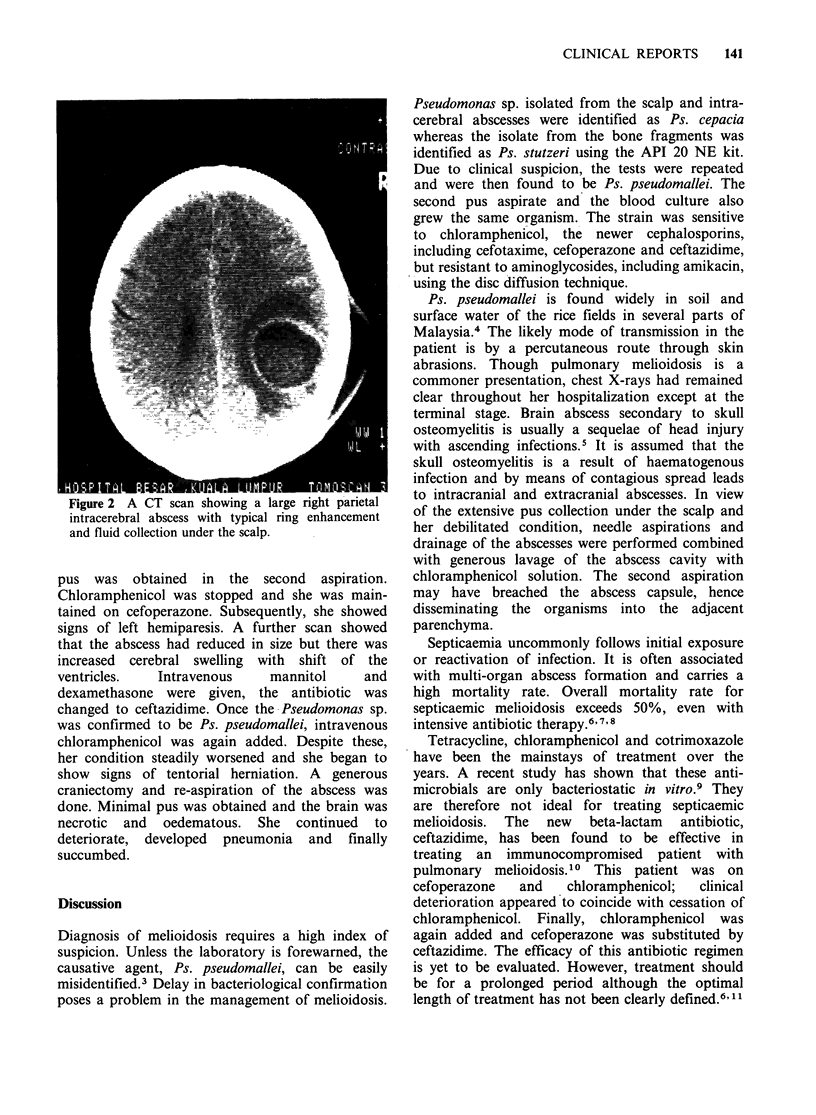
Central nervous system involvement in melioidosis is rare. We describe a 48 year old woman who developed septicaemia and a brain abscess due to Pseudomonas pseudomallei. Since there is a continuing practical problem in bacteriological confirmation of the aetiological agent, diagnosis of melioidosis has to be made on clinical suspicion.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashdown L. R. Identification of Pseudomonas pseudomallei in the clinical laboratory. J Clin Pathol. 1979 May;32(5):500–504. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.5.500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brundage W. G., Thuss C. J., Jr, Walden D. C. Four fatal cases of melioidosis in U. S. soldiers in Vietnam. Bacteriologic and pathologic characteristics. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1968 Mar;17(2):183–191. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1968.17.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau P. Y., Ng W. S., Leung Y. K., Lolekha S. In vitro susceptibility of strains of Pseudomonas pseudomallei isolated in Thailand and Hong Kong to some newer beta-lactam antibiotics and quinolone derivatives. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):167–170. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett E. D., Nelson R. A. Pulmonary melioidosis. Observations in thirty-nine cases. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Sep;112(3):331–340. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.112.3.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C., Sampath A., Spotnitz M. The pseudomallei group: a review. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124(6):598–606. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.6.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patamasucon P., Schaad U. B., Nelson J. D. Melioidosis. J Pediatr. 1982 Feb;100(2):175–182. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(82)80630-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puthucheary S. D., Lin H. P., Yap P. K. Acute septicaemic melioidosis: a report of seven cases. Trop Geogr Med. 1981 Mar;33(1):19–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]