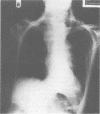
Abstract
We report an unusual case of bilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy caused by gross oesophageal distension due to achalasia.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gani J. S., Morrison J. M. Simple thyroid cyst: cause of acute bilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1987 May 2;294(6580):1128–1129. doi: 10.1136/bmj.294.6580.1128-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holl-Allen R. T. Laryngeal nerve paralysis and benign thyroid disease. Arch Otolaryngol. 1967 Mar;85(3):335–337. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1967.00760040337018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson V. G. The management of airway involvement in thyroid tumors. Arch Otolaryngol. 1983 Feb;109(2):86–90. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1983.00800160020005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]