Abstract
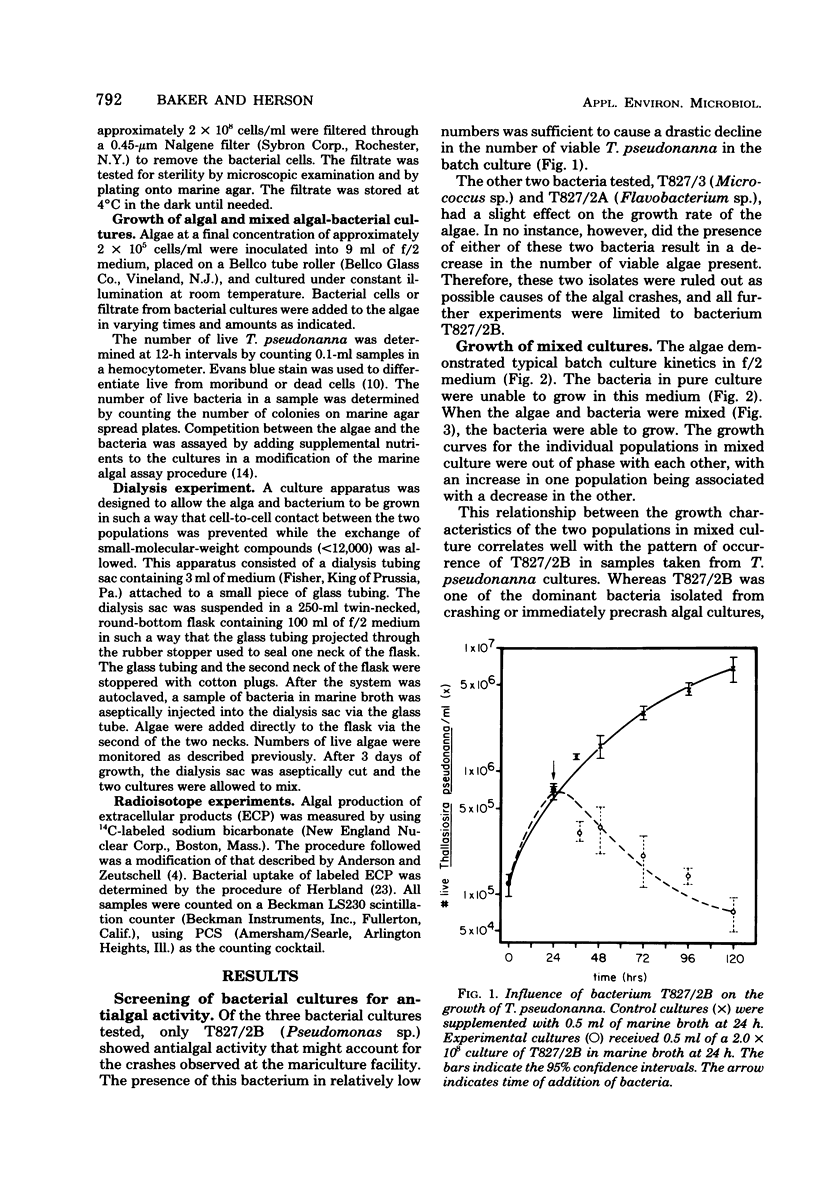
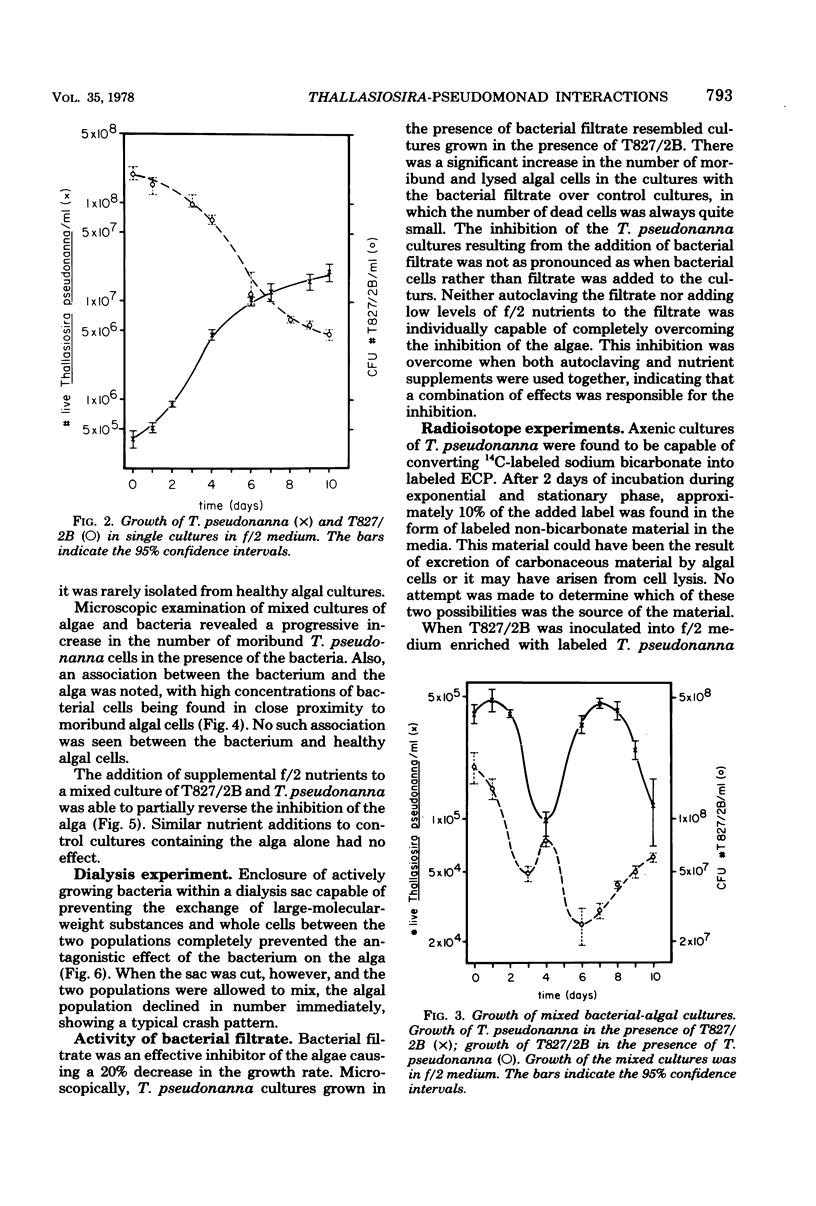
The marine diatom Thallasiosira pseudonanna (3H) and several bacteria associated with it were isolated from batch cultures at the University of Delaware mariculture facility. The interaction between the algae and each of the bacteria was investigated. One of the isolates, T827/2B (Pseudomonas sp.), was incapable of surviving in f/2 culture medium unless the algae were present. When the algae and T827/2B were grown together in the f/2 medium, the bacterial growth was stimulated and the algal growth was inhibited. Bacterial filtrate had a similar effect on the algae, indicating that the bacterial effect is an indirect one most likely resulting from the excretion of a harmful compound into the medium. Preliminary characterization of the material excreted by the bacteria indicates that it s proteinaceous in nature. The interactions observed does not fit into any single category of interactions but can be explained as a combination of competition and indirect parasitism.
Full text
PDF
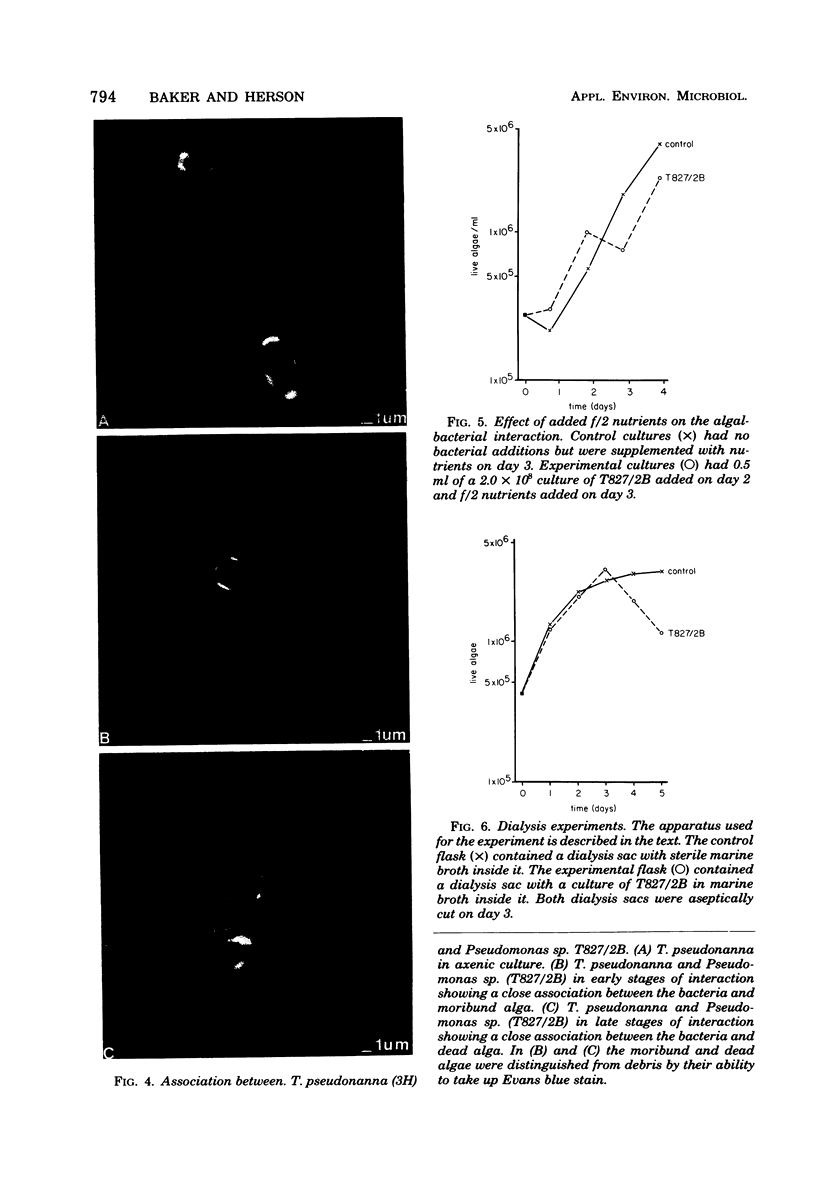


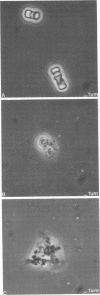
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN M. B., DAWSON E. Y. Production of antibacterial substances by benthic tropical marine algae. J Bacteriol. 1960 Mar;79:459–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.79.3.459-460.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLEN M. B. Excretion of organic compounds by Chlamydomonas. Arch Mikrobiol. 1956;24(2):163–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00408630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon R. E., Shane M. S., Bush V. N. Lysogeny of a blue-green alga, Plectonema boryanum. Virology. 1971 Jul;45(1):149–153. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90121-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crippen R. W., Perrier J. L. The use of neutral red and Evans blue for live-dead determinations of marine plankton (with comments on the use of rotenone for inhibition of grazing). Stain Technol. 1974 Mar;49(2):97–104. doi: 10.3109/10520297409116949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff D. C., Bruce D. L., Antia N. J. The antibacterial activity of marine planktonic algae. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Oct;12(5):877–884. doi: 10.1139/m66-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOGG G. E. The production of extracellular nitrogenous substances by a blue-green alga. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1952 Apr 24;139(896):372–397. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1952.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson A. G. Behavior of mixed cultures of microorganisms. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:63–87. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUILLARD R. R., RYTHER J. H. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt, and Detonula confervacea (cleve) Gran. Can J Microbiol. 1962 Apr;8:229–239. doi: 10.1139/m62-029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granhall U., Berg B. Antimicrobial effects of Cellvibrio on blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(3):234–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00425201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating K. I. Allelopathic influence on blue-green bloom sequence in a eutrophic lake. Science. 1977 May 20;196(4292):885–887. doi: 10.1126/science.196.4292.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. Role of predators in the reversal of imbalances in microbial ecosystems. Nature. 1971 Mar 26;230(5291):257–258. doi: 10.1038/230257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Shilo M., Kislev N. Isolation of "cyanophages" from freshwater ponds and their interaction with Plectonema boryanum. Virology. 1967 Jun;32(2):234–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90273-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reim R. L., Shane M. S., Cannon R. E. The characterization of a Bacillus capable of blue-green bactericidal activity. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Jul;20(7):981–986. doi: 10.1139/m74-152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg S. C., Shilo M. Early host damage in the infection cycle of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):149–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.149-160.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryther J. H., Goldman J. C. Microbes as food in mariculture. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:429–443. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoener T. W. Alternatives to Lotka-Volterra competition: models of intermediate complexity. Theor Popul Biol. 1976 Dec;10(3):309–333. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(76)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilo M. Lysis of blue-green algae by myxobacter. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):453–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.453-461.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. R., Brown R. M., Jr Cytophaga that kills or lyses algae. Science. 1969 Jun 27;164(3887):1523–1524. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3887.1523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]