Abstract
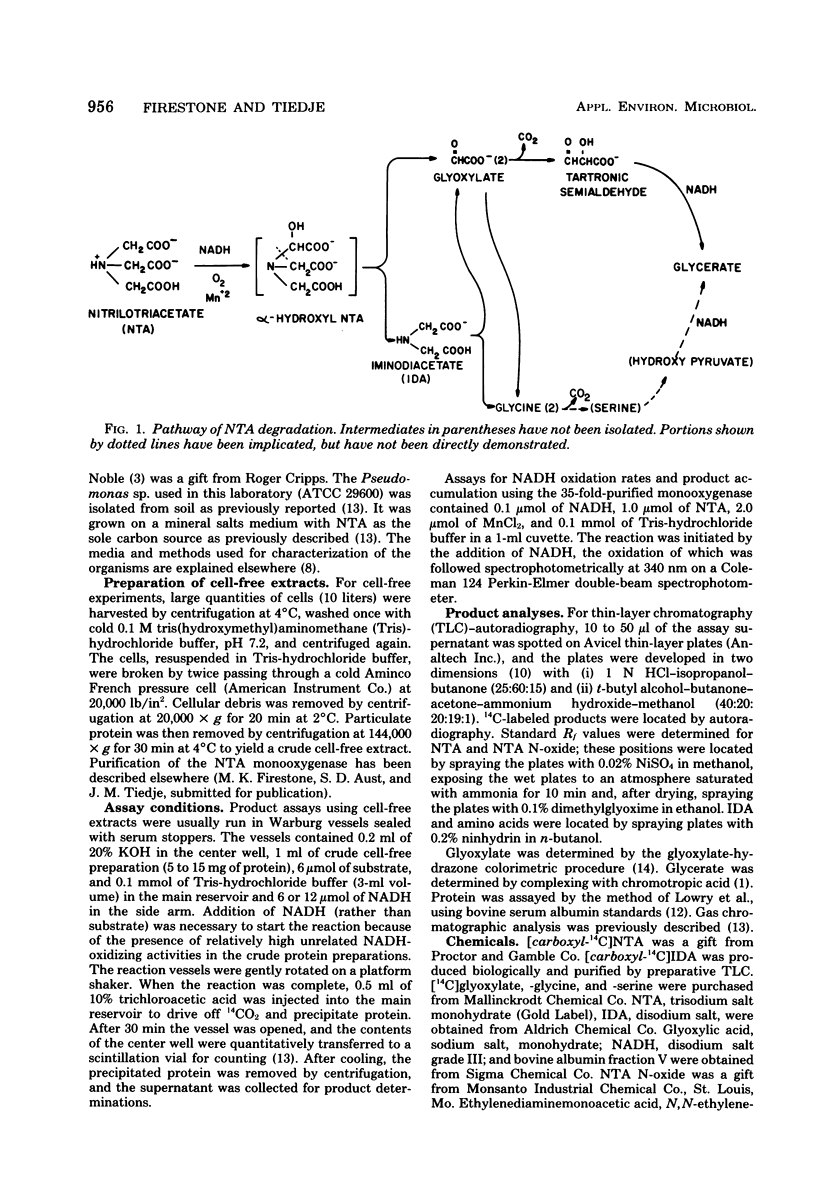
The pathway of degradation of nitrilotriacetate (NTA) was determined by using cell-free extracts and a 35-fold purification of NTA monooxygenase. The first step in the breakdown was an oxidative cleavage of the tertiary amine by the monooxygenase to form the aldo acid, glyoxylate, and the secondary amine, iminodiacetate (IDA). NTA N-oxide acted as a substrate analog for induction of the monooxygenase and was slowly metabolized by the enzyme, but was not an intermediate in the pathway. No intermediate before IDA was found, but an unstable alpha-hydroxy-NTA intermediate was postulated. IDA did undergo cleavage in the presence of the purified monooxygenase to give glyoxylate and glycine, but was not metabolized in cell-free extracts. Glyoxylate was further metabolized by cell-free extracts to yield CO2 and glycerate or glycine, products also found from NTA metabolism. Of the three bacterial isolates in which the NTA pathway has been studied, two strains, one isolated from a British soil and ours from a Michigan soil, appear to be almost identical.
Full text
PDF

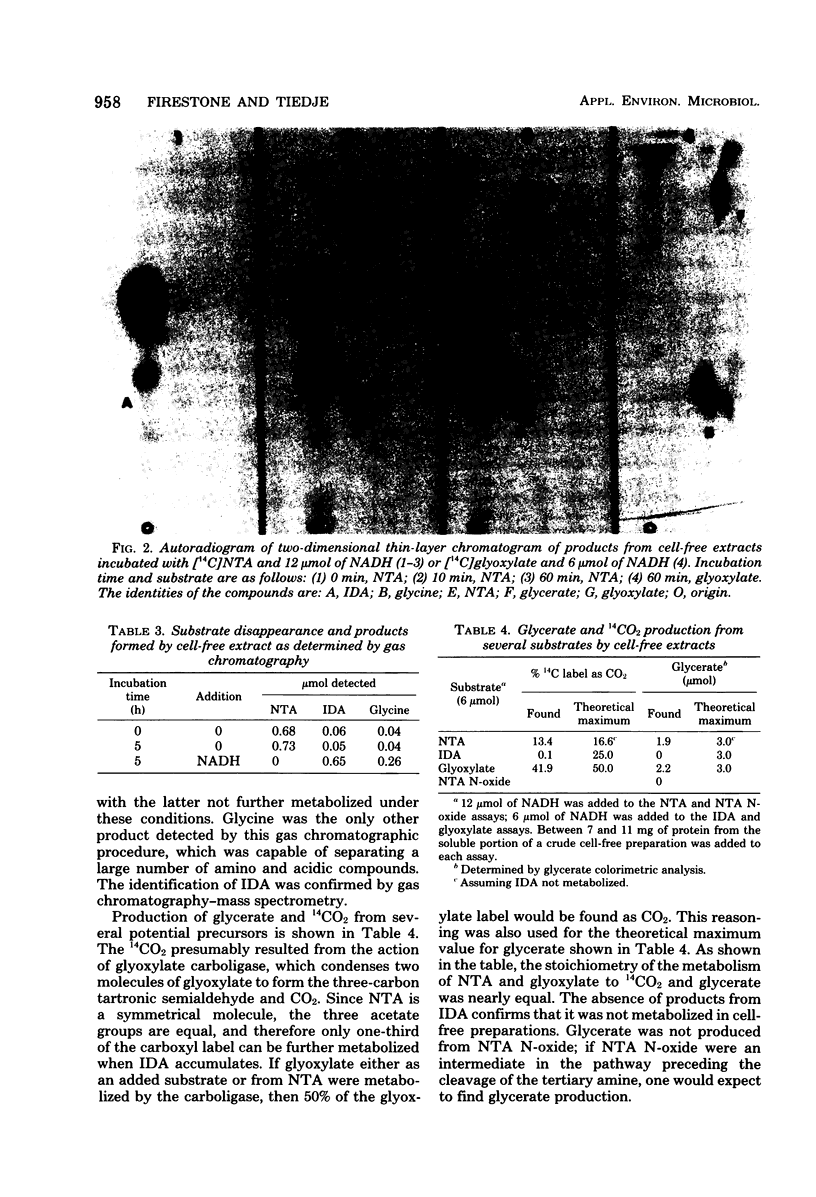



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Colorimetric assay methods for free and phosphorylated glyceric acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):469–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulton C. A., Crabbe M. J., Large P. J. Microbial oxidation of amines. Partial purification of a trimethylamine mono-oxygenase from Pseudomonas aminovorans and its role in growth on trimethylamine. Biochem J. 1974 May;140(2):253–263. doi: 10.1042/bj1400253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripps R. E., Noble A. S. The metabolism of nitrilotriacetate by a pseudomonad. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;136(4):1059–1068. doi: 10.1042/bj1361059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Focht D. D., Joseph H. A. Bacterial degradation of nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA). Can J Microbiol. 1971 Dec;17(12):1553–1556. doi: 10.1139/m71-247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamble T. N., Betlach M. R., Tiedje J. M. Numerically dominant denitrifying bacteria from world soils. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):926–939. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.926-939.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorrod J. W., Temple D. J. The formation of an N-hydroxymethyl intermediate in the N-demethylation of N-methylcarbazole in vivo and in vitro. Xenobiotica. 1976 May;6(5):265–274. doi: 10.3109/00498257609151638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiedje J. M., Mason B. B., Warren C. B., Malec E. J. Metabolism of nitrilotriacetate by cells of Pseudomonas species. Appl Microbiol. 1973 May;25(5):811–818. doi: 10.1128/am.25.5.811-818.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trijbels F., Vogels G. D. Degradation of allantoin by Pseudomonas acidovorans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 14;113(2):292–301. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]