Abstract
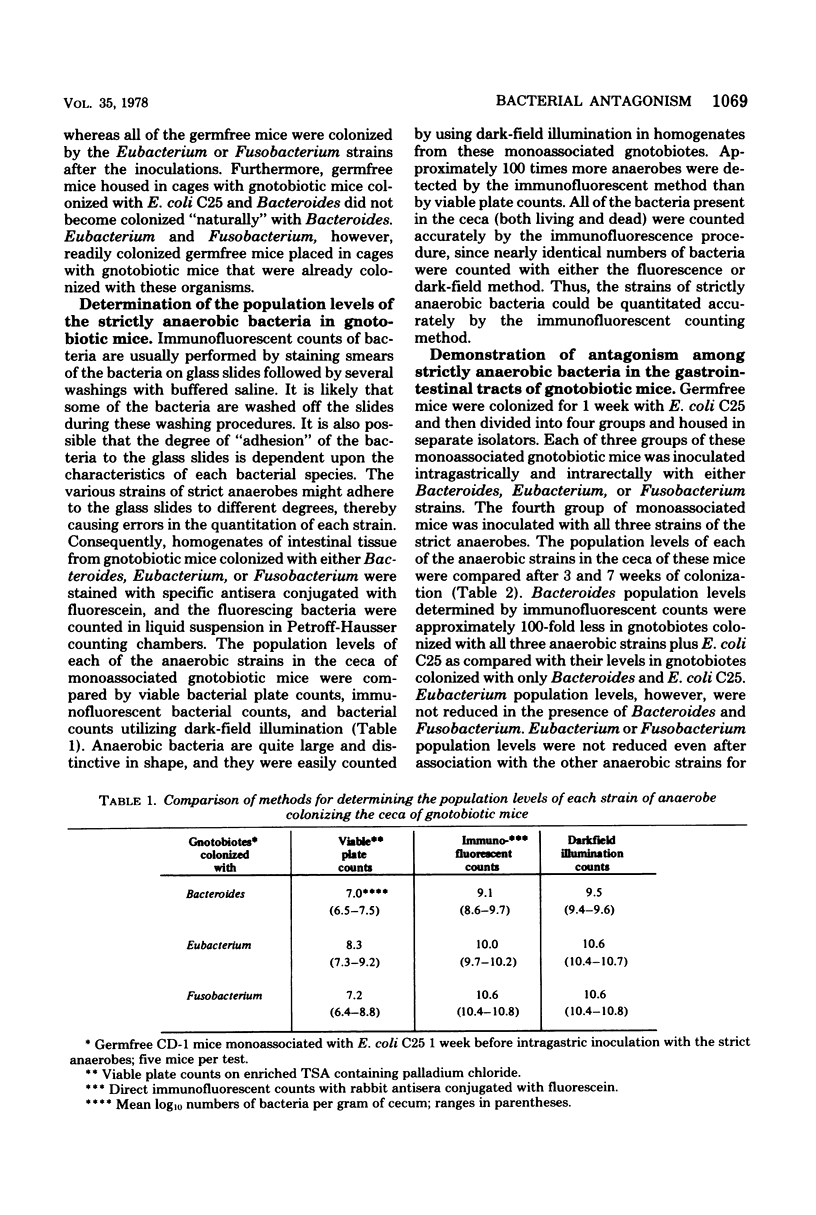
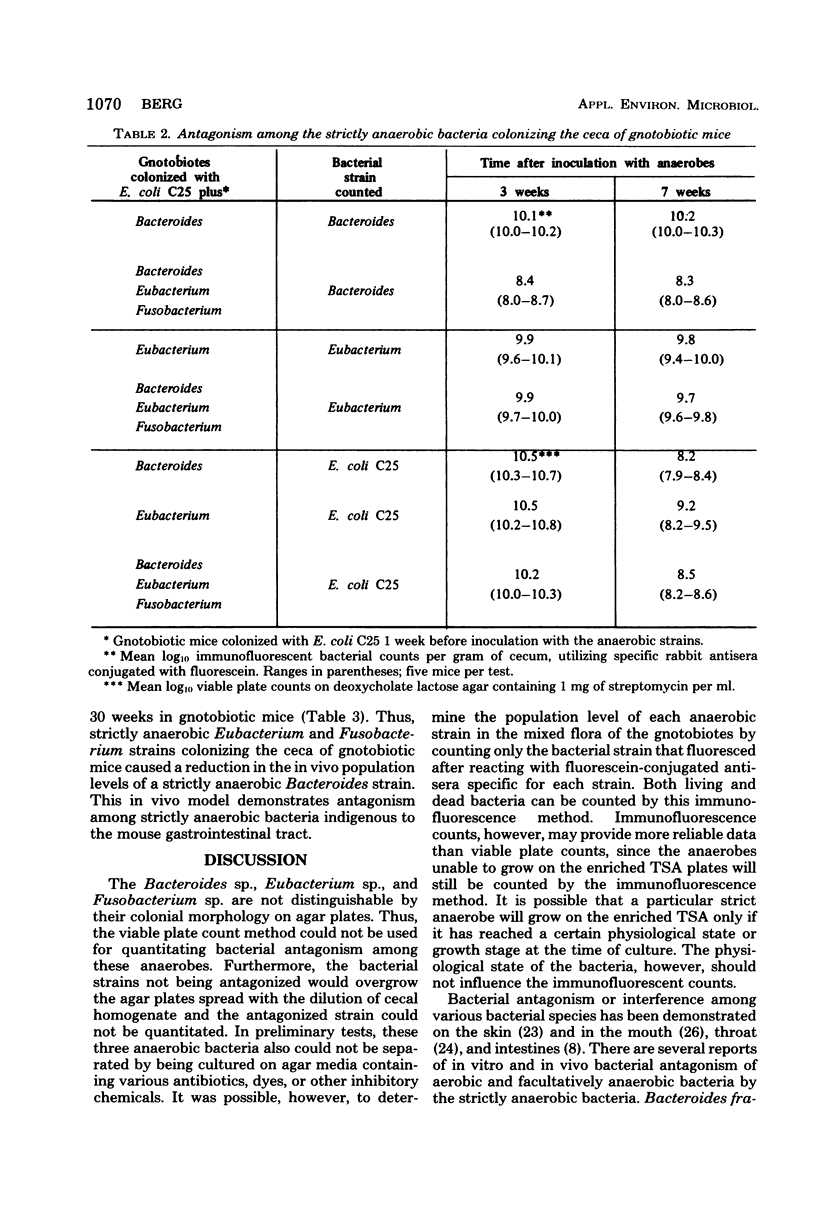
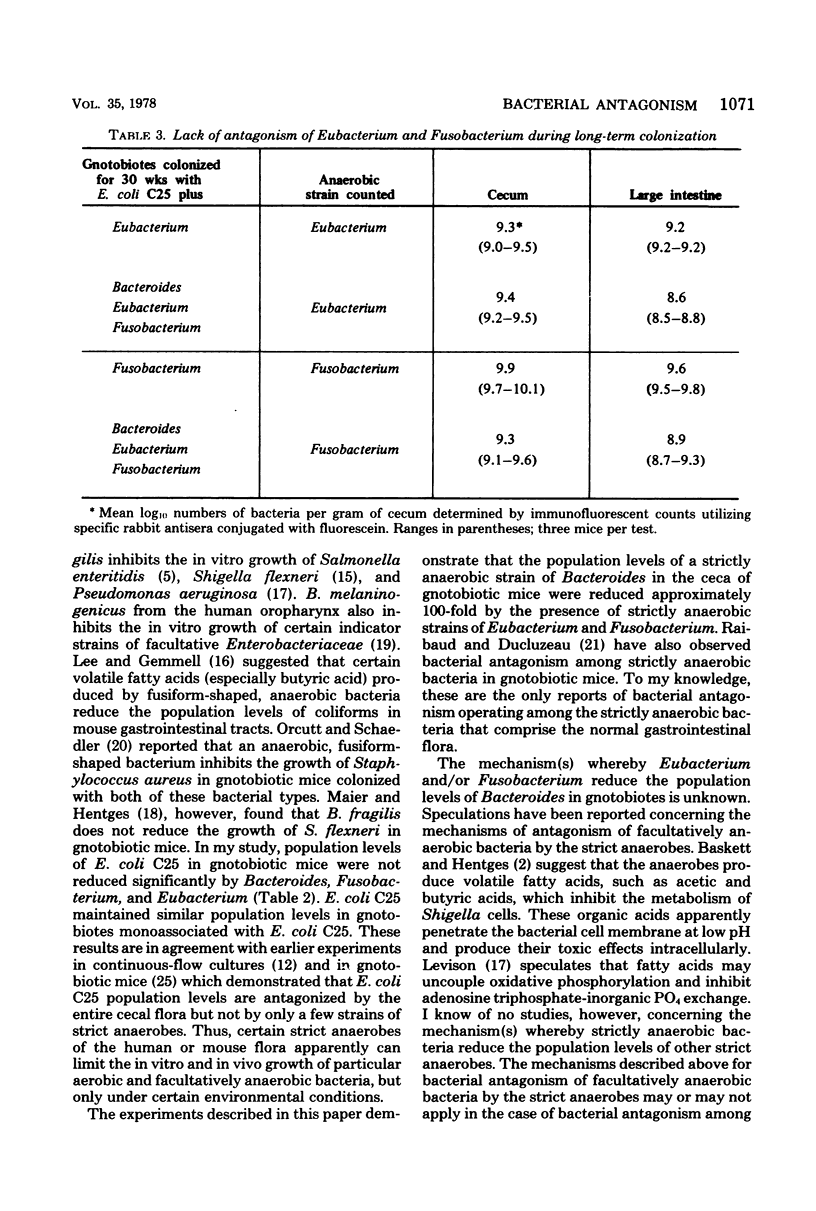
Strictly anaerobic Bacteroides sp., Eubacterium sp., and Fusobacterium sp. were isolated from the cecum of a conventional mouse. An immunofluorescent method utilizing rabbit antisera specific for each of these three strains was developed to determine their population levels in the gastrointestinal tracts of gnotobiotic mice. Population levels of these anaerobes in groups of gnotobiotic mice colonized with either Bacteroides, Eubacterium, or Fusobacterium were compared with those of gnotobiotes colonized with all three strains. Bacteroides population levels in gnotobiotes colonized with all three strains were 100-fold less than the Bacteroides population level in gnotobiotes colonized with only the Bacteroides strain. Eubacterium or Fusobacterium population levels were not reduced by the presence of the other anaerobic strains. Thus, strictly anaerobic Eubacterium sp. and Fusobacterium sp. that colonized gnotobiotic mice caused a reduction in the in vivo population levels of a strictly anaerobic Bacteroides sp.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aranki A., Freter R. Use of anaerobic glove boxes for the cultivation of strictly anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1329–1334. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOHNHOFF M., MILLER C. P., MARTIN W. R. RESISTANCE OF THE MOUSE'S INTESTINAL TRACT TO EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLA INFECTION. I. FACTORS WHICH INTERFERE WITH THE INITIATION OF INFECTION BY ORAL INOCULATION. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:805–816. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskett R. C., Hentges D. J. Shigella flexneri inhibition by acetic acid. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):91–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.91-97.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D., Savage D. C. Immune responses of specific pathogen-free and gnotobiotic mice to antigens of indigenous and nonindigenous microorganisms. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):320–329. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.320-329.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg R. D., Savage D. C. Immunological responses and microorganisms indigenous to the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1364–1371. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOS R., SCHAEDLER R. W., COSTELLO R., HOET P. INDIGENOUS, NORMAL, AND AUTOCHTHONOUS FLORA OF THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:67–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRETER R. Experimental enteric Shigella and Vibrio infections in mice and guinea pigs. J Exp Med. 1956 Sep 1;104(3):411–418. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.3.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRETER R. In vivo and in vitro antagonism of intestinal bacteria against Shigellaflexneri. II. The inhibitory mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1962 Jan-Feb;110:38–46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/110.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., Abrams G. D. Function of various intestinal bacteria in converting germfree mice to the normal state. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):119–126. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.119-126.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R. Interactions between mechanisms controlling the intestinal microflora. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Dec;27(12):1409–1416. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.12.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon H. A., Pesti L. The gnotobiotic animal as a tool in the study of host microbial relationships. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Dec;35(4):390–429. doi: 10.1128/br.35.4.390-429.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert G. A., Pelham P. L., Pittman B. Determination of the optimal ammonium sulfate concentration for the fractionation of rabbit, sheep, horse, and goat antisera. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jan;25(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/am.25.1.26-36.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentges D. J., Maier B. R. Inhibition of Shigella flexneri by the Normal Intestinal Flora III. Interactions with Bacteroides fragilis Strains in Vitro. Infect Immun. 1970 Oct;2(4):364–370. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.4.364-370.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A., Gemmell E. Changes in the mouse intestinal microflora during weaning: role of volatile fatty acids. Infect Immun. 1972 Jan;5(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.1.1-7.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levison M. E. Effect of colon flora and short-chain fatty acids on growth in vitro of Pseudomonas aeruginsoa and Enterobacteriaceae. Infect Immun. 1973 Jul;8(1):30–35. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.1.30-35.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier B. R., Hentges D. J. Experimental Shigella infections in laboratory animals. I. Antagonism by human normal flora components in gnotobiotic mice. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):168–173. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.168-173.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray P. R., Rosenblatt J. E. Bacterial interference by oropharynegeal and clinical isolates of anaerobic bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1976 Sep;134(3):281–285. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.3.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shedlofsky S., Freter R. Synergism between ecologic and immunologic control mechanisms of intestinal flora. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):296–303. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprunt K., Leidy G. A., Redman W. Prevention of bacterial overgrowth. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jan;123(1):1–10. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syed S. A., Abrams G. D., Freter R. Efficiency of various intestinal bacteria in assuming normal functions of enteric flora after association with germ-free mice. Infect Immun. 1970 Oct;2(4):376–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.4.376-386.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houte J., Gibbons R. J., Banghart S. B. Adherence as a determinant of the presence of Streptococcus salivarius and Streptococcus sanguis on the human tooth surface. Arch Oral Biol. 1970 Nov;15(11):1025–1034. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(70)90115-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WADDELL W. J. A simple ultraviolet spectrophotometric method for the determination of protein. J Lab Clin Med. 1956 Aug;48(2):311–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



