Abstract
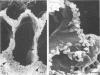
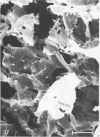
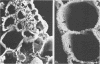
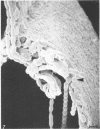
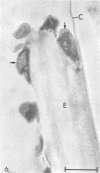
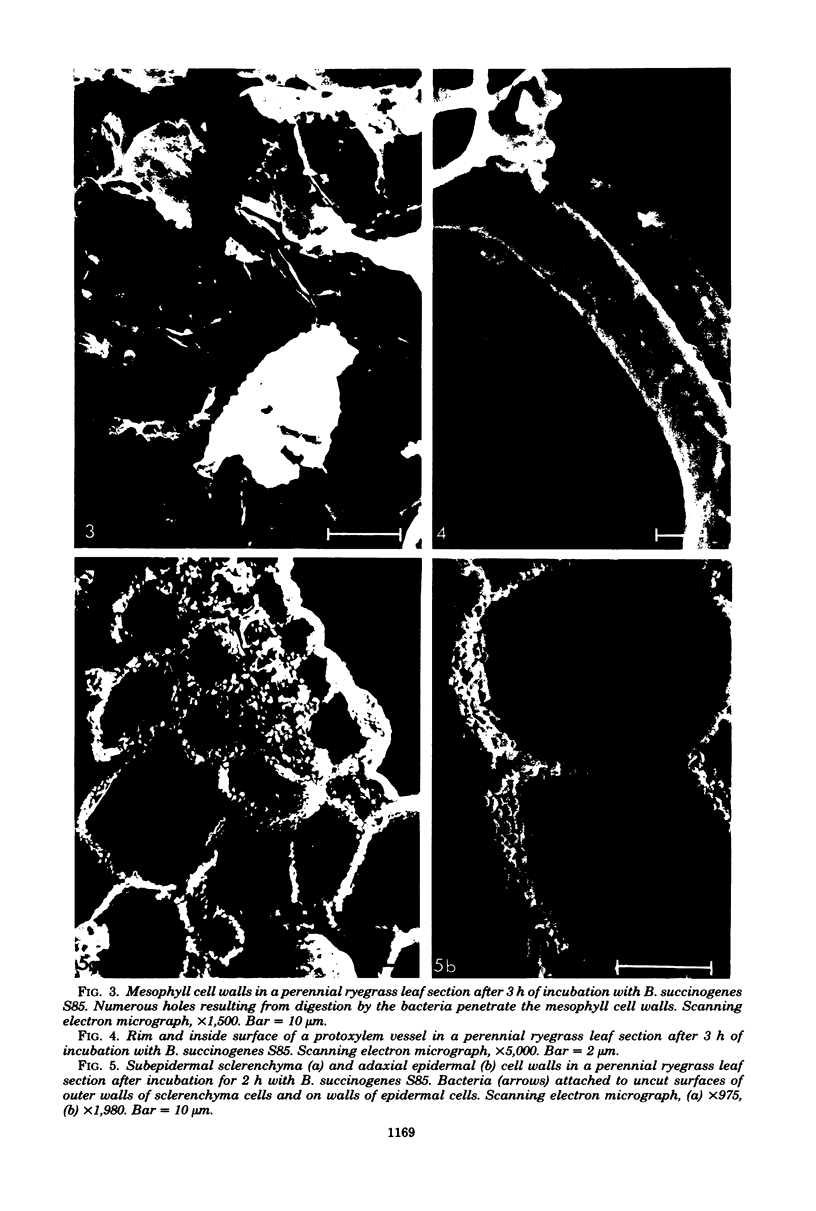
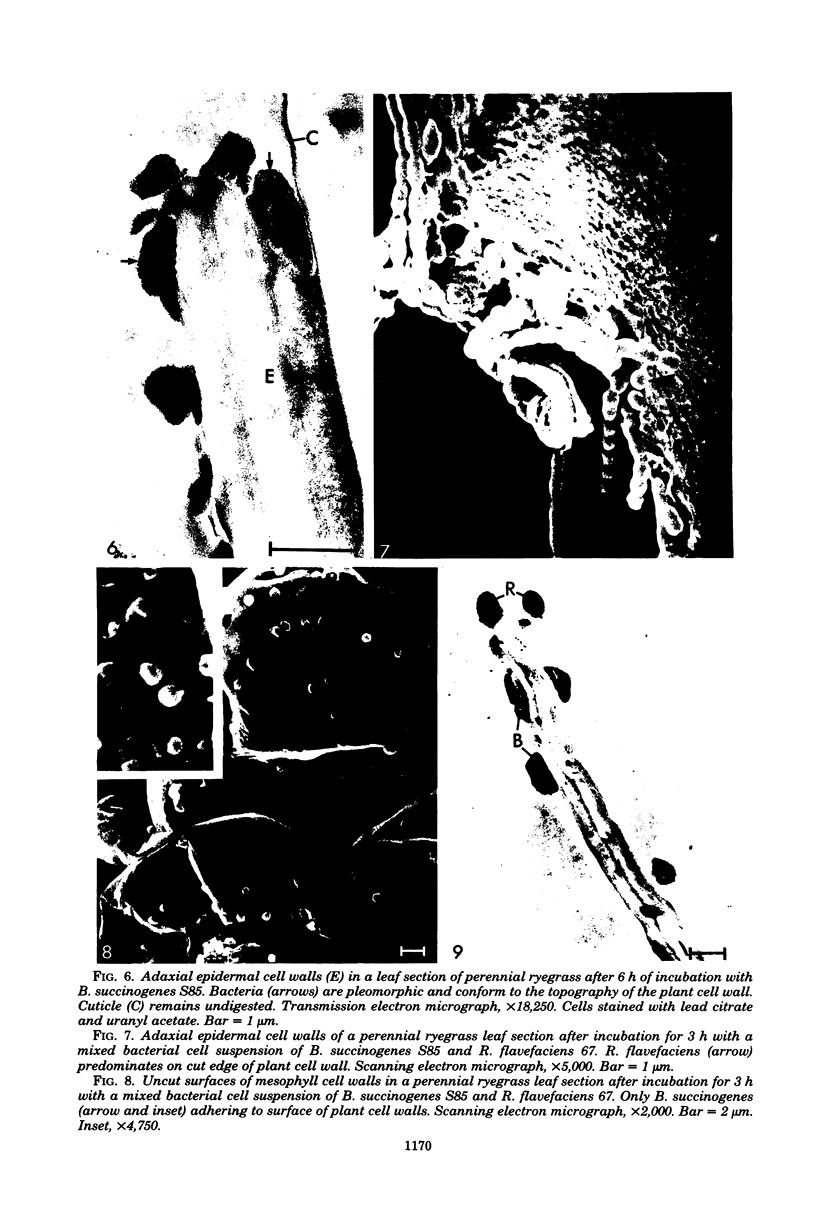
Bacteroides succinogenes and Ruminococcus flavefaciens are two of the most important cellulolytic bacteria in the rumen. Adhesion of B. succinogenes in pure culture, and in mixed culture with R. flavefaciens, to the various types of cell walls in sections of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L. cultivar S24) leaves was examined by transmission and scanning electron microscopy. B. succinogenes adhered to the cut edges of most plant cell walls except those of the meta- and protoxylem. It also adhered, though in much smaller numbers, to the uncut surfaces of mesophyll, epidermal, and phloem cell walls. In mixed culture, both species adhered in significant numbers to the cut edges of most types of plant cell wall, but R. flavefaciens predominated on the epidermis, phloem, and sclerenchyma cell walls. B. succinogenes predominated on the cut edges and on the uncut surfaces of the mesophyll cell walls, and its ability to adhere to uncut surfaces of other cell walls was not affected by the presence of the ruminococcus. Both organisms rapidly digested the epidermal, mesophyll, and phloem cell walls. Zones of digestion were observed around bacteria of both species when attached to the lignified cell walls of the sclerenchyma, but not when attached to the lignified xylem vessels.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akin D. E., Amos H. E. Rumen bacterial degradation of forage cell walls investigated by electron microscopy. Appl Microbiol. 1975 May;29(5):692–701. doi: 10.1128/am.29.5.692-701.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akin D. E., Burdick D., Michaels G. E. Rumen bacterial interrelationships with plant tissue during degradation revealed by transmission electron microscopy. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jun;27(6):1149–1156. doi: 10.1128/am.27.6.1149-1156.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akin D. E. Ultrastructure of rumen bacterial attachment to forage cell walls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Apr;31(4):562–568. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.4.562-568.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P. Commentary on the Hungate technique for culture of anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1324–1328. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Akin D. E., Costerton J. W. Rumen bacteria: interaction with particulate dietary components and response to dietary variation. Fed Proc. 1977 Feb;36(2):193–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Damgaard H. N., Cheng K. J. Cell envelope morphology of rumen bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):1132–1143. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.1132-1143.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Ingram J. M., Cheng K. J. Structure and function of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Mar;38(1):87–110. doi: 10.1128/br.38.1.87-110.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALLIWELL G., BRYANT M. P. THE CELLULOLYTIC ACTIVITY OF PURE STRAINS OF BACTERIA FROM THE RUMEN OF CATTLE. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Sep;32:441–448. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungate R. E. Studies on Cellulose Fermentation: III. The Culture and Isolation for Cellulose-decomposing Bacteria from the Rumen of Cattle. J Bacteriol. 1947 May;53(5):631–645. doi: 10.1128/jb.53.5.631-645.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham M. J., Brooker B. E., Pettipher G. L., Harris P. J. Ruminococcus flavefaciens Cell Coat and Adhesion to Cotton Cellulose and to Cell Walls in Leaves of Perennial Ryegrass (Lolium perenne). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jan;35(1):156–165. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.1.156-165.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott B. B., Whatley M. H., Lippincott J. A. Tumor induction by agrobacterium involves attachment of the bacterium to a site on the host plant cell wall. Plant Physiol. 1977 Mar;59(3):388–390. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.3.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]