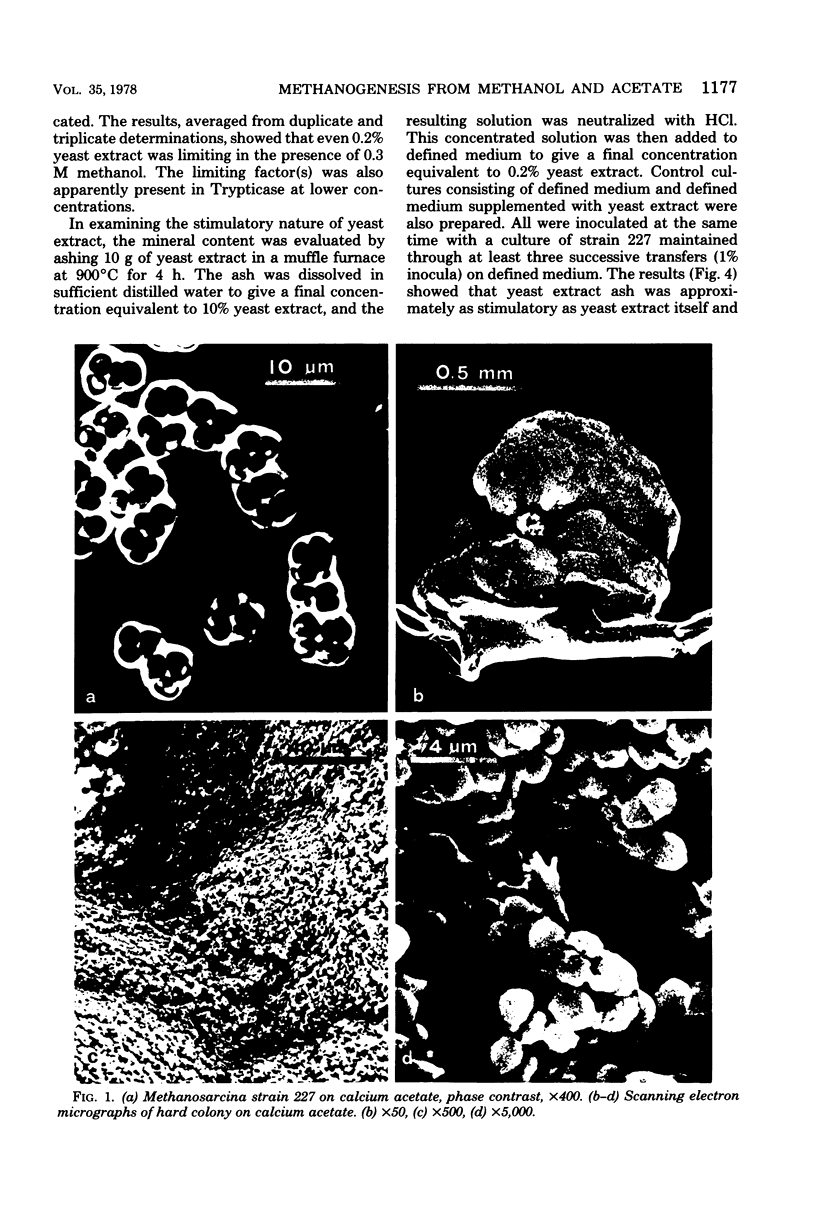
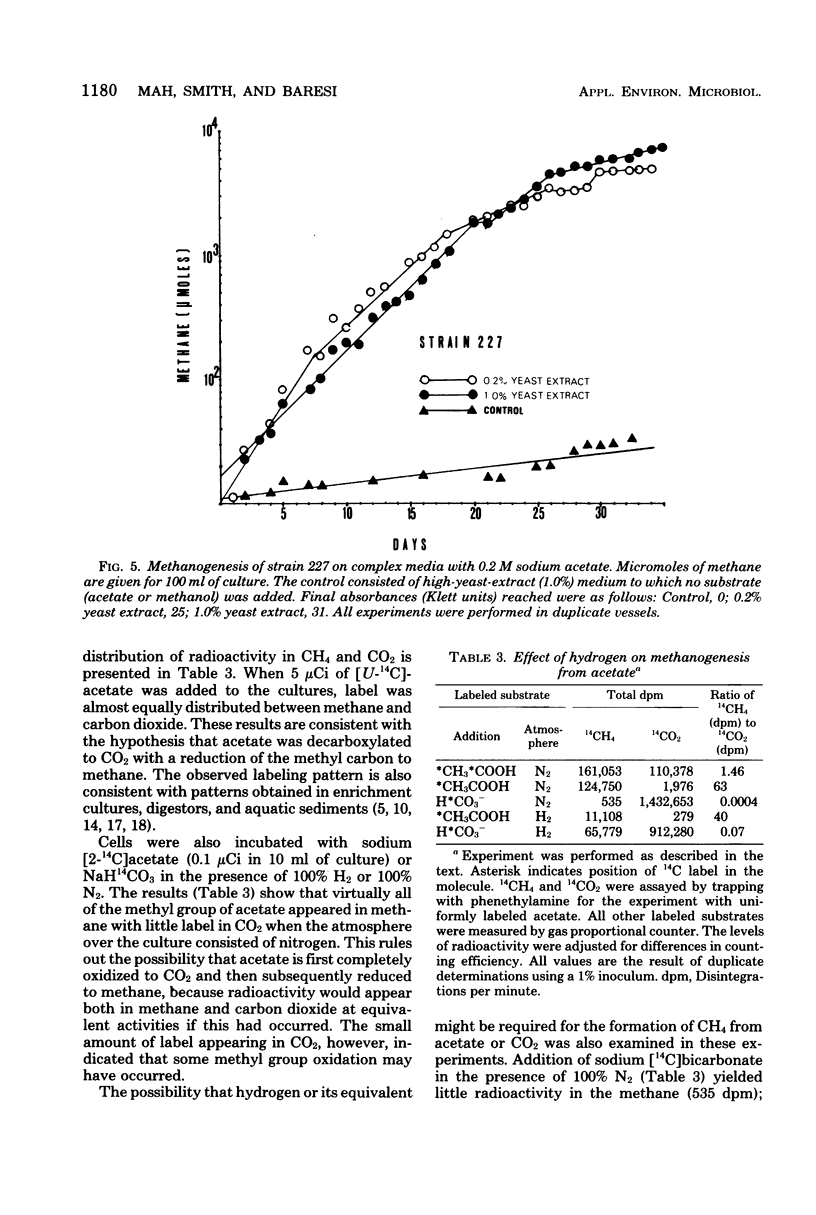
Abstract
An acetate-fermenting strain of Methanosarcina was isolated from an acetate enrichment culture inoculated with anaerobic sludge from a waste treatment digestor. In pure culture, this organism fermented acetate in the absence of added hydrogen at rates comparable in magnitude to those found in digestor systems. This rate was significantly higher than previously obtained for pure cultures of this genus. Mineral components of yeast extract were highly stimulatory for cultures growing on methanol. Comparable stimulation was not observed for cultures growing on acetate. Labeling studies indicated that acetate was converted to methane and CO2 as predicted by previous studies on mixed cultures. Total oxidation or reduction of acetate was not the mechanism of conversion of acetate to methane by the pure culture. The ability of this strain to form colonies or to produce methane from acetate was apparently influenced by the choice of substrate and conditions used for growing the inoculum.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Decker K., Jungermann K., Thauer R. K. Energy production in anaerobic organisms. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1970 Feb;9(2):138–158. doi: 10.1002/anie.197001381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry J. G., Wolfe R. S. Anaerobic degradation of benzoate to methane by a microbial consortium. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Feb;107(1):33–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00427864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. B., Stadtman T. C. Methanococcus vannielii: culture and effects of selenium and tungsten on growth. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1404–1406. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1404-1406.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINE M. J., VISHNIAC W. The methane fermentations of acetate and methanol. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jun;73(6):736–742. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.6.736-742.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfennig N., Biebl H. Desulfuromonas acetoxidans gen. nov. and sp. nov., a new anaerobic, sulfur-reducing, acetate-oxidizing bacterium. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Oct 11;110(1):3–12. doi: 10.1007/BF00416962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STADTMAN T. C., BARKER H. A. Studies on the methane fermentation. IX. The origin of methane in the acetate and methanol fermentations by methanosarcina. J Bacteriol. 1951 Jan;61(1):81–86. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.1.81-86.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. H., Mah R. A. Kinetics of acetate metabolism during sludge digestion. Appl Microbiol. 1966 May;14(3):368–371. doi: 10.1128/am.14.3.368-371.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman T. C. Methane fermentation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1967;21:121–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.21.100167.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G. T., Pirt S. J. Nutrition and factors limiting the growth of a methanogenic bacterium (Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum). Arch Microbiol. 1977 May 13;113(1-2):17–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00428574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Jungermann K., Decker K. Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):100–180. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.100-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. M., Mah R. A., Kaplan I. R. Methanogenesis from acetate: a nonmethanogenic bacterium from an anaerobic acetate enrichment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1185–1192. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1185-1192.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Nelson D. R., Klevickis S. C., Zeikus J. G. Association of hydrogen metabolism with methanogenesis in Lake Mendota sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):312–318. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.312-318.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe R. S. Microbial formation of methane. Adv Microb Physiol. 1971;6:107–146. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60068-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G. The biology of methanogenic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):514–541. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.514-541.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg L., Patel G. B., Clark D. S., Lentz C. P. Factors affecting rate of methane formation from acetic acid by enriched methanogenic cultures. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Sep;22(9):1312–1319. doi: 10.1139/m76-194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]