Abstract
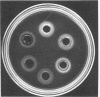
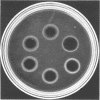
A rapid method for the detection of heat-stable staphylococcal nuclease in foods is described. The procedure consists of an acid precipitation, boiling, and centrifugation followed by enzyme detection in an agar plate containing deoxyribonucleic acid. To test the efficacy of the procedure, purified Staphylococcus aureus nuclease was added to various foods and recovery experiments were performed. Additionally, foods were inoculated and incubated with S. aureus, and the staphylococcal counts were compared with nuclease activity. The results indicate that the procedure possesses merit for a rapid method that can be incorporated into quality control programs. The procedure requires approximately 2.5 h, and it will detect nuclease levels as low as 10 ng/g of food.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber L. E., Deibel R. H. Effect of pH and oxygen tension on staphylococcal growth and enterotoxin formation in fermented sausage. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Dec;24(6):891–898. doi: 10.1128/am.24.6.891-898.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry A. L., Lachica R. V., Atchison F. W. Identification of Staphylococcus aureus by simultaneous use of tube coagulase and thermonuclease tests. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Mar;25(3):496–497. doi: 10.1128/am.25.3.496-497.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASMAN E. P., BENNETT R. W. DETECTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL ENTEROTOXIN IN FOOD. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:181–189. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.181-189.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter D. F., Silverman G. J. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B and nuclease production under controlled dissolved oxygen conditions. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):628–637. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.628-637.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter D. F., Silverman G. J. Synthesis of staphylococcal enterotoxin A and nuclease under controlled fermentor conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):243–248. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.243-248.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesbro W. R., Auborn K. Enzymatic detection of the growth of Staphylococcus aureus in foods. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Sep;15(5):1150–1159. doi: 10.1128/am.15.5.1150-1159.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cords B. R., Tatini S. R. Applicability of heat-stable deoxyribonuclease assay for assessment of staphylococcal growth and the likely presence of enterotoxin in cheese. J Dairy Sci. 1973 Dec;56(12):1512–1519. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(73)85400-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEIBEL R. H., WILSON G. D., NIVEN C. F., Jr Microbiology of meat curing. IV. A lyophilized Pediococcus cerevisiae starter culture for fermented sausage. Appl Microbiol. 1961 May;9:239–243. doi: 10.1128/am.9.3.239-243.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A., Deibel R. H. Production and heat stability of staphylococcal nuclease. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Mar;25(3):332–336. doi: 10.1128/am.25.3.332-336.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Hoeprich P. D., Genigeorgis C. Metachromatic agar-diffusion microslide technique for detecting staphylococcal nuclease in foods. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Jan;23(1):168–169. doi: 10.1128/am.23.1.168-169.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niskanen A., Nurmi E. Effect of starter culture on staphylococcal enterotoxin and thermonuclease production in dry sausage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jan;31(1):11–20. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.1.11-20.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor R., Lachica F., Weiss K. F., Deibel R. H. Relationships among coagulase, enterotoxin, and heat-stable deoxyribonuclease production by Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Jul;18(1):126–127. doi: 10.1128/am.18.1.126-127.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WECKMAN B. G., CATLIN B. W. Deoxyribonuclease activity of micrococci from clinical sources. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jun;73(6):747–753. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.6.747-753.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]