Abstract
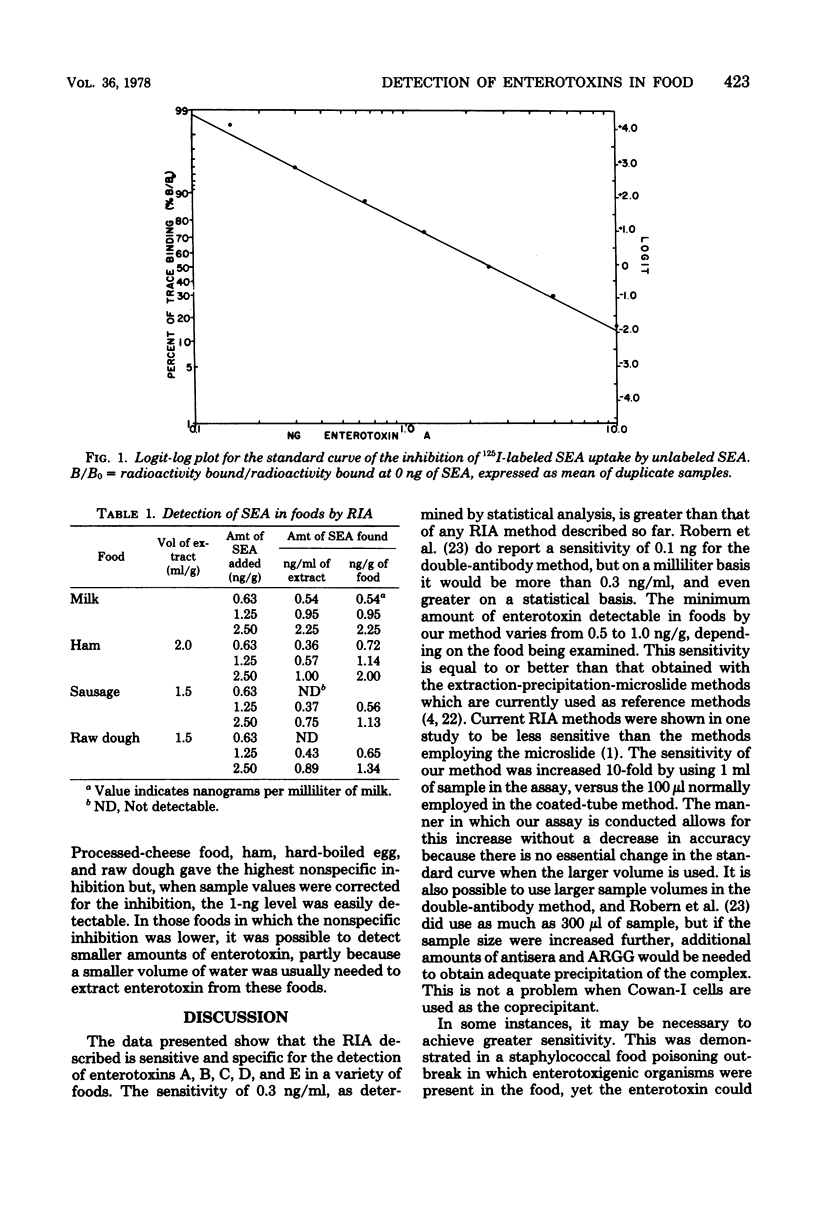
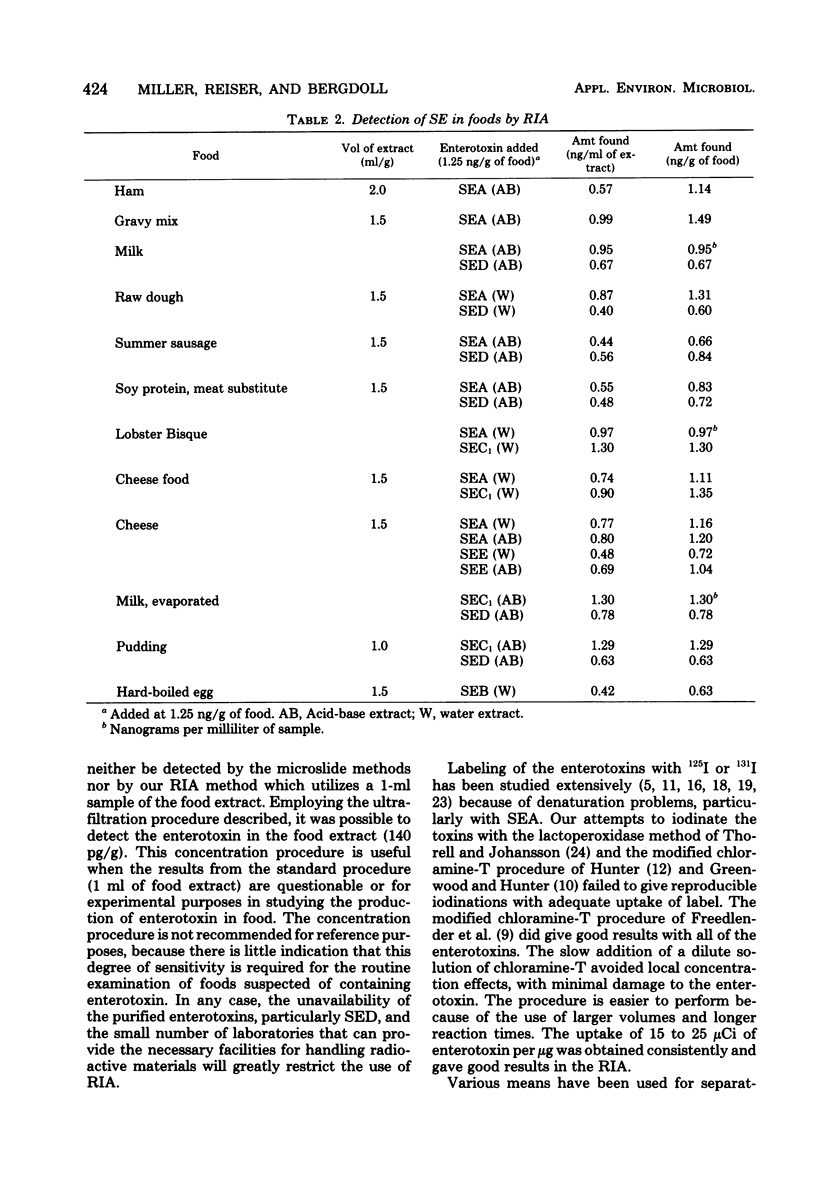
A sensitive radioimmunoassay utilizing Staphylococcus aureus cells containing protein A as a coprecipitant was developed for the detection and quantitation of staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, C, D, and E in a variety of foods. The enterotoxins were extracted from the foods by a simple and rapid procedure. The sensitivity of the assay is 1.0 ng or less of enterotoxin per g of food.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S., BAUMAN A., ROTHSCHILD M. A., NEWERLY K. Insulin-I131 metabolism in human subjects: demonstration of insulin binding globulin in the circulation of insulin treated subjects. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):170–190. doi: 10.1172/JCI103262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukovic J. A., Johnson H. M. Staphylococcal enterotoxin C: solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):700–701. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.700-701.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASMAN E. P., BENNETT R. W. DETECTION OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL ENTEROTOXIN IN FOOD. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Mar;13:181–189. doi: 10.1128/am.13.2.181-189.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins W. S., 2nd, Metzger J. F., Johnson A. D. A rapid solid phase radioimmunoassay for staphylococcal B enterotoxin. J Immunol. 1972 Mar;108(3):852–856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins W. S., Johnson A. D., Metzger J. F., Bennett R. W. Rapid solid-phase radioimmunoassay for staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Appl Microbiol. 1973 May;25(5):774–777. doi: 10.1128/am.25.5.774-777.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber J., Wright G. G. Ammonium sulfate coprecipitation antibody determination with purified staphylococcal enterotoxins. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):18–24. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.18-24.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter R. Standardization of the chloramine-T method of protein iodination. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Mar;133(3):989–992. doi: 10.3181/00379727-133-34611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Bukovic J. A., Kauffman P. E., Peeler J. T. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B: solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):837–841. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.837-841.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Bukovic J. A., Kauffmann P. E. Staphylococcal enterotoxins A and B: solid-phase radioimmunoassay in food. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):309–313. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.309-313.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman P. E., Johnson H. M. Stability of 125I-labeled staphylococcal enterotoxins in solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):776–779. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.776-779.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niskanen A., Lindroth S. Preparation of labeled staphylococcal enterotoxin A with high specific activity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Dec;32(6):735–740. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.6.735-740.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orth D. S. Iodination of staphylococcal enterotoxin B by use of chloramine-T. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):824–828. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.824-828.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orth D. S. Statistical analysis and quality control in radioimmunoassays for staphylococcal enterotoxins A, B, and C. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Dec;34(6):710–714. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.6.710-714.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober Z., Silverman G. J. Modified radioimmunoassay determination for staphylococcal enterotoxin B in foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Mar;33(3):620–625. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.3.620-625.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser R., Conaway D., Bergdoll M. S. Detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin in foods. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jan;27(1):83–85. doi: 10.1128/am.27.1.83-85.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robern H., Dighton M., Yano Y., Dickie N. Double-antibody radioimmunoassay for staphylococcal enterotoxin C2. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):525–529. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.525-529.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorell J. I., Johansson B. G. Enzymatic iodination of polypeptides with 125I to high specific activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


