Abstract
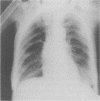
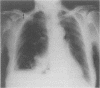
Boerhaave's syndrome or spontaneous oesophageal perforation, is a potentially lethal and frequently elusive medical condition which presents not only a diagnostic but also a therapeutic challenge. It is insufficiently considered in diagnostic hypotheses, yet may be confirmed or excluded by simple methods such as an erect chest film and a contrast study of the oesophagus. Errors in diagnosis are usually caused by unawareness of its varied and atypical presentations or failure to consider its possibility in acute cardiothoracic and upper gastrointestinal conditions. Early aggressive surgical intervention in the form of open and wide mediastinal and chest drainage, with or without oesophageal repair, resection or exclusion, offers the patient the best chance of survival against this otherwise invariably fatal event. Nonoperative therapy consisting of antibiotics, nil oral regimen, nasogastric tube suction, pleural drainage, H2 receptor blockers and either a feeding enterostomy or total parenteral nutrition, may also be appropriate in selected patients. It is probable that the condition is more common than is generally supposed. All clinicians need to be aware of this lethal disease, its frequently unusual presentations and the importance of early diagnosis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott O. A., Mansour K. A., Logan W. D., Jr, Hatcher C. R., Jr, Symbas P. N. Atraumatic so-called "spontaneous" rupture of the esophagus. A review of 47 personal cases with comments on a new method of surgical therapy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1970 Jan;59(1):67–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRETT N. R. Perforations of the oesophagus and of the pharynx. Proc R Soc Med. 1956 Aug;49(8):529–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRETT N. R. Spontaneous perforation of the oesophagus; review of the literature and report of three new cases. Thorax. 1946 Mar;1:48–70. doi: 10.1136/thx.1.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUNO M. S., GRIER W. R., OBER W. B. SPONTANEOUS LACERATION AND RUPTURE OF ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH. MALLORY-WEISS SYNDROME, BOERHAAVE SYNDROME, AND THEIR VARIANTS. Arch Intern Med. 1963 Oct;112:574–583. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1963.03860040170016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer C. L., LoCicero J., 3rd, Hartz R. S., Donaldson J. S., Shields T. Computed tomography in patients with esophageal perforation. Chest. 1990 Nov;98(5):1078–1080. doi: 10.1378/chest.98.5.1078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barringer M., Meredith J. Distal esophageal perforation: esophageal exclusion using a modified Sengstaken-Blakemore tube. Am Surg. 1982 Oct;48(10):518–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. J., Deveridge R. J., Wright J. S. Spontaneous rupture of the esophagus: a review with reports of six cases. Surgery. 1970 Nov;68(5):766–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bladergroen M. R., Lowe J. E., Postlethwait R. W. Diagnosis and recommended management of esophageal perforation and rupture. Ann Thorac Surg. 1986 Sep;42(3):235–239. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)62725-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blichert-Toft M. Spontaneous oesophageal rupture. An evaluation of the results of treatment 1944-1969. Scand J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1971;5(2):111–115. doi: 10.3109/14017437109135541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer L. A., 3rd, Carter R., Mulder G. A., Stiles Q. R. Options in the management of perforations of the esophagus. Am J Surg. 1986 Jul;152(1):62–69. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(86)90144-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Complications of vomiting. The Boerhaave and the Mallory-Weiss syndromes. West J Med. 1974 Jul;121(1):50–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curci J. J., Horman M. J. Boerhaave's syndrome: The importance of early diagnosis and treatment. Ann Surg. 1976 Apr;183(4):401–408. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197604000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DERRICK J. R., HARRISON W. H., HOWARD J. M. Factors predisposing to spontaneous perforation of the esophagus; the mechanical strength of the ulcerated esophagus. Surgery. 1958 Mar;43(3):486–489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dooling J. A., Zick H. R. Closure of an esophagopleural fistula using onlay intercostal pedicle graft. Ann Thorac Surg. 1967 Jun;3(6):553–557. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)66464-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drury M., Anderson W., Heffner J. E. Diagnostic value of pleural fluid cytology in occult Boerhaave's syndrome. Chest. 1992 Sep;102(3):976–978. doi: 10.1378/chest.102.3.976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endicott J. N., Molony T. B., Campbell G., Bartels L. J. Esophageal perforations: the role of computerized tomography in diagnosis and management decisions. Laryngoscope. 1986 Jul;96(7):751–757. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198607000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghahremani G. G. Radiologic evaluation of suspected gastrointestinal perforations. Radiol Clin North Am. 1993 Nov;31(6):1219–1234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grillo H. C., Wilkins E. W., Jr Esophageal repair following late diagnosis of intrathoracic perforation. Ann Thorac Surg. 1975 Oct;20(4):387–399. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)64235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han S. Y., McElvein R. B., Aldrete J. S., Tishler J. M. Perforation of the esophagus: correlation of site and cause with plain film findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985 Sep;145(3):537–540. doi: 10.2214/ajr.145.3.537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson J. A., Péloquin A. J. Boerhaave revisited: spontaneous esophageal perforation as a diagnostic masquerader. Am J Med. 1989 May;86(5):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(89)90385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry W. S., Munro A., Logie J. R. Spontaneous rupture of the oesophagus: principles of management. J R Coll Surg Edinb. 1986 Oct;31(5):274–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinder R. A., Baskind A. F., Le Grange F. A tube system for the management of ruptured oesophagus. Br J Surg. 1981 Mar;68(3):182–184. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800680314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jara F. M. Diaphragmatic pedicle flap for treatment of Boerhaave's syndrome. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1979 Dec;78(6):931–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. G., 2nd, Ginsberg R. J. Esophageal perforation: a continuing challenge. Ann Thorac Surg. 1992 Mar;53(3):534–543. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(92)90294-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keighley M. R., Girdwood R. W., Ionescu M. I., Wooler G. H. Spontaneous rupture of the oesophagus. Avoidance of postoperative morbidity. Br J Surg. 1972 Aug;59(8):649–652. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800590818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kossick P. R. Spontaneous rupture of the oesophagus. S Afr Med J. 1973 Oct 6;47(39):1807–1809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyons W. S., Seremetis M. G., deGuzman V. C., Peabody J. W., Jr Ruptures and perforations of the esophagus: the case for conservative supportive management. Ann Thorac Surg. 1978 Apr;25(4):346–350. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)63554-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKLER S. A. Spontaneous rupture of the esophagus; an experimental and clinical study. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1952 Sep;95(3):345–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARSTON E. L., VALK H. L. Spontaneous perforation of the esophagus: review of the literature and report of a case. Ann Intern Med. 1959 Sep;51:590–607. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-51-3-590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour K. A., Teaford H. Atraumatic rupture of the esophagus into the pericardium simulating acute myocardial infarction. A case report. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1973 Mar;65(3):458–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews H. R., Mitchell I. M., McGuigan J. A. Emergency subtotal oesophagectomy. Br J Surg. 1989 Sep;76(9):918–920. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800760915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalik R., Hatcher C. R., Jr, Miller J. I. Myocardial infarction complicated by Boerhaave's syndrome. South Med J. 1984 Apr;77(4):504–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel L., Grillo H. C., Malt R. A. Operative and nonoperative management of esophageal perforations. Ann Surg. 1981 Jul;194(1):57–63. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198107000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard A. H. 'Spontaneous' perforation of the oesophagus treated by utilization of a pericardial flap. Br J Surg. 1971 Jan;58(1):70–72. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800580115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NACLERIO E. A. The V sign in the diagnosis of spontaneous rupture of the esophagus (an early roentgen clue). Am J Surg. 1957 Feb;93(2):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(57)90781-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen R. Bridging of Esophageal Defect by Pedicled Flap of Lung Tissue. Ann Surg. 1949 Jan;129(1):142–147. doi: 10.1097/00000658-194901000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIVITERI C. A., GAY B. B., Jr Spontaneous rupture of the esophagus, with report of five cases. Radiology. 1951 Jul;57(1):48–57. doi: 10.1148/57.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips L. G., Jr, Cunningham J. Esophageal perforation. Radiol Clin North Am. 1984 Sep;22(3):607–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillay S. P., Ward M., Cowen A., Pollard E. Oesophageal ruptures and perforations--a review. Med J Aust. 1989 Mar 6;150(5):246–252. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1989.tb136456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeder L. B., DeFilippi V. J., Ferguson M. K. Current results of therapy for esophageal perforation. Am J Surg. 1995 Jun;169(6):615–617. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(99)80232-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUCH G. O., LYNCH R. E. SUBPHRENIC EXTRATHORACIC RUPTURE OF THE ESOPHAGUS: FIRST REPORTED CASE. Ann Surg. 1965 Feb;161:213–217. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196502000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner D. B., Little A. G., DeMeester T. R. Management of esophageal perforation. Am J Surg. 1980 Jun;139(6):760–764. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(80)90379-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilanus H. W., Bossuyt P., Schattenkerk M. E., Obertop H. Treatment of oesophageal perforation: a multivariate analysis. Br J Surg. 1991 May;78(5):582–585. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urschel H. C., Jr, Razzuk M. A., Wood R. E., Galbraith N., Pockey M., Paulson D. L. Improved management of esophageal perforation: exclusion and diversion in continuity. Ann Surg. 1974 May;179(5):587–591. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197405000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. S., Cameron E. W., Walbaum P. R. Diagnosis and management of spontaneous transmural rupture of the oesophagus (Boerhaave's syndrome). Br J Surg. 1985 Mar;72(3):204–207. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800720320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler R. J. CT of esophageal-pleural fistulae. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1986 Nov;147(5):907–909. doi: 10.2214/ajr.147.5.907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise W. S., Rivarola C. H., Williams G. D., Fink W. J., Read R. C. Experience with the Thal gastroesophagoplasty. Ann Thorac Surg. 1970 Sep;10(3):213–222. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)65590-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heerden J. A., Toxopeus M., Troxel G. Boerhaave's syndrome. A case report. Va Med Mon (1918) 1974 Jun;101(6):452–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]