Abstract
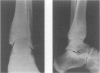
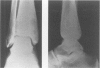
Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis is often confused with symmetrical Brodie's abscess as it has a similar pathogenesis. We report an otherwise healthy 17-year-old boy presenting with a true symmetrical Brodie's abscess. We conclude that a symmetrical Brodie's abscess presenting in an otherwise healthy patient is a separate clinical condition with a different management protocol.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brailsford J. F. Brodie's Abscess and its Differential Diagnosis. Br Med J. 1938 Jul 16;2(4045):119–138.1. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4045.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodie B. C. An Account of some Cases of Chronic Abscess of the Tibia. Med Chir Trans. 1832;17:239–249. doi: 10.1177/095952873201700111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day D. L., Griffiths H. Bilateral Brodie's abscess. Orthopedics. 1989 Jun;12(6):885–888. doi: 10.3928/0147-7447-19890601-15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS N. H., KIRKALDY-WILLIS W. H. PRIMARY SUBACUTE PYOGENIC OSTEOMYELITIS. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1965 Aug;47:526–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens M. M., MacAuley P. Brodie's abscess. A long-term review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988 Sep;(234):211–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]