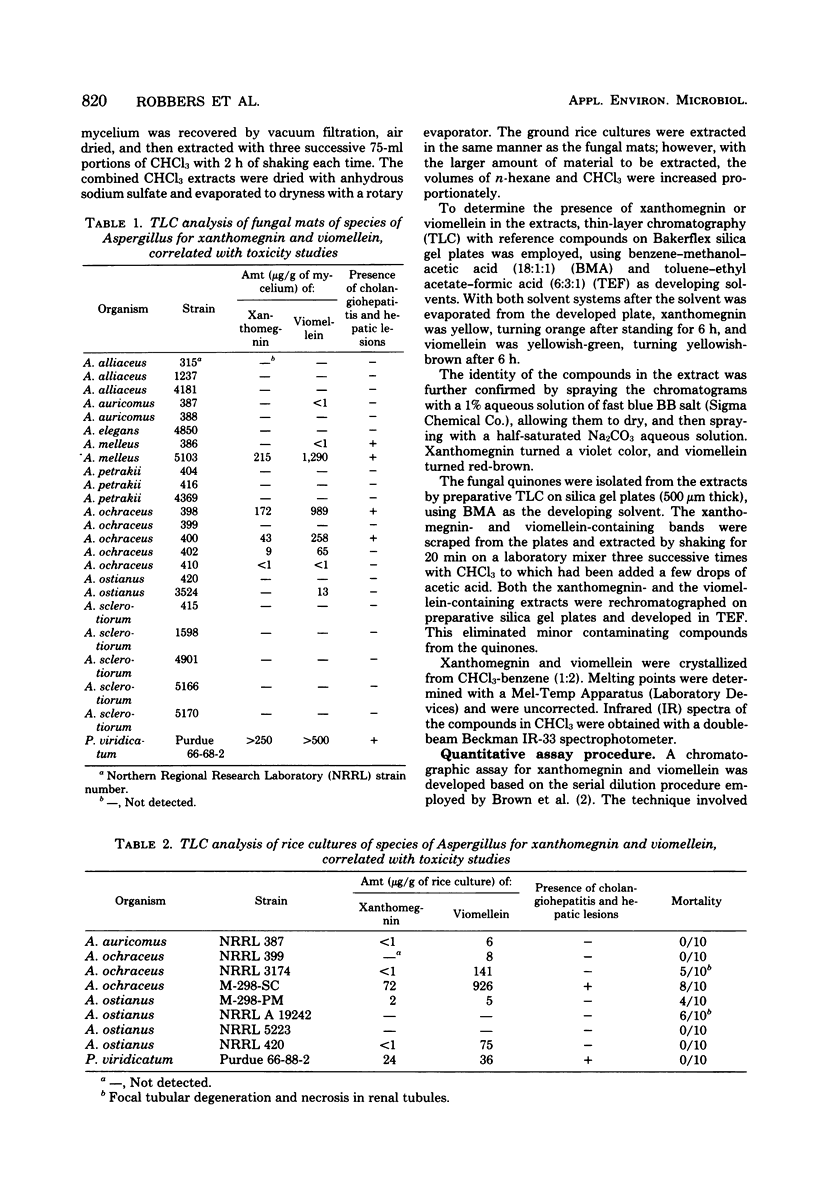
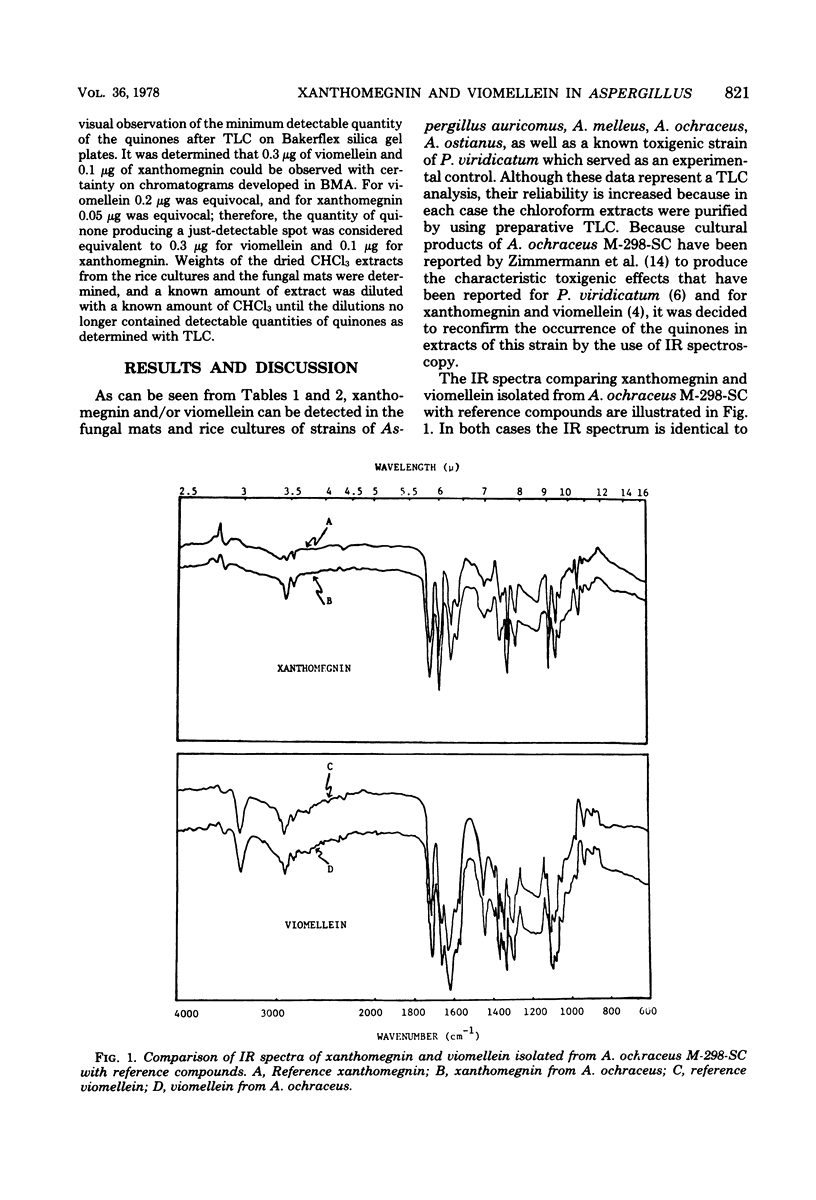
Abstract
By using thin-layer chromatography and infrared spectroscopy, xanthomegnin and viomellein have been isolated and identified from species of the Aspergillus ochraceus group. A correlation was established between the occurrence of these fungal quinones in the fungal cultural products and the ability of these products to induce mycotoxicosis in mice. In addition, a method was employed to estimate the amount of xanthomegnin and viomellein produced by the fungi.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLANK F., DAY W. C., JUST G. Metabolites of pathogenic fungi. II. The isolation of xanthomegnin from Trichophyton megnini Blanchard 1896. J Invest Dermatol. 1963 Mar;40:133–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN J. K., MALONE M. H., STUNTZ D. E., TYLER V. E., Jr Paper chromatographic determination of muscarine in Inocybe species. J Pharm Sci. 1962 Sep;51:853–856. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600510908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budiarso I. T., Carlton W. W., Tuite J. Investigations of dose, age, and duration of administration on the hepatorenal damage induced in mice by cultural products of Penicillium viridicatum. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1971 Nov;20(3):357–379. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(71)90279-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlton W. W., Stack M. E., Eppley R. M. Hepatic alterations produced in mice by xanthomegnin and viomellein, metabolites of Penicillium viridicatum. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;38(2):455–459. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(76)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlton W. W., Tuite J., Mislivec P. Investigations of the toxic effects in mice of certain species of Penicillium. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1968 Nov;13(3):372–387. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(68)90113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlton W. W., Tuite J. Mycotoxicosis induced in guinea pigs and rats by corn cultures of Penicillium viridicatum. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1970 Mar;16(2):345–361. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(70)90006-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durley R. C., MacMillan J., Simpson T. J., Glen A. T., Turner W. B. Fungal products. Part XIII. Xanthomegnin, viomellin, rubrosulphin, and viopurpurin, pigments from Aspergillus sulphureus and Aspergillus melleus. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1975;(2):163–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesseltine C. W., Vandegraft E. E., Fennell D. I., Smith M. L., Shotwell O. L. Aspergilli as ochratoxin producers. Mycologia. 1972 May-Jun;64(3):539–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stack M. E., Eppley R. M., Dreifuss P. A., Pohland A. E. Isolation and identification of xanthomegnin, viomellein, rubrosulphin, and viopurpurin as metabolites of penicillium viridicatum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):351–355. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.351-355.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann J. L., Carlton W. W., Tuite J., Fennell D. I. Mycotoxic diseases produced in mice by species of the Aspergillus ochraceus group. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1977 Oct;15(5):411–418. doi: 10.1016/s0015-6264(77)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann J. L., Carlton W. W., Tuite J. Mycotoxicosis produced in mice by cultural products of an isolate of Aspergillus ochraceus. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1976 Dec;14(6):571–575. doi: 10.1016/s0015-6264(76)80011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



