Abstract
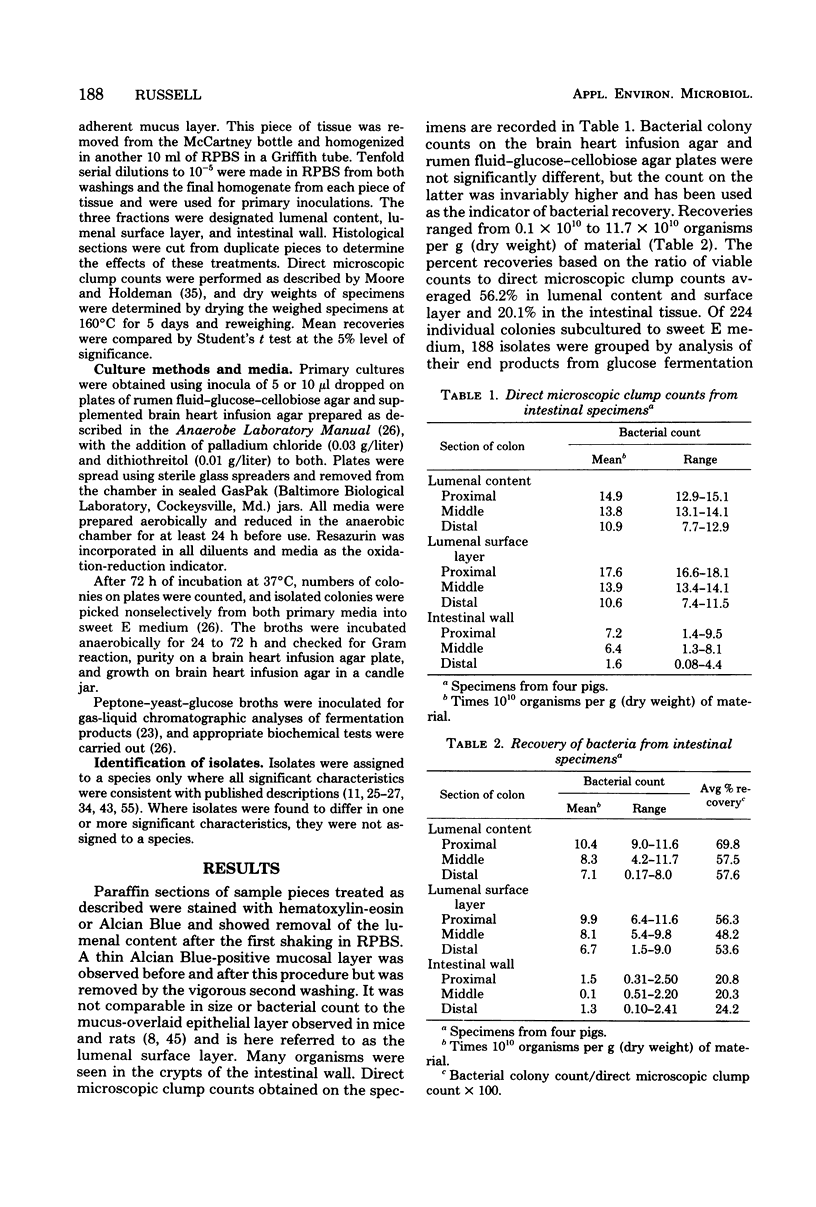
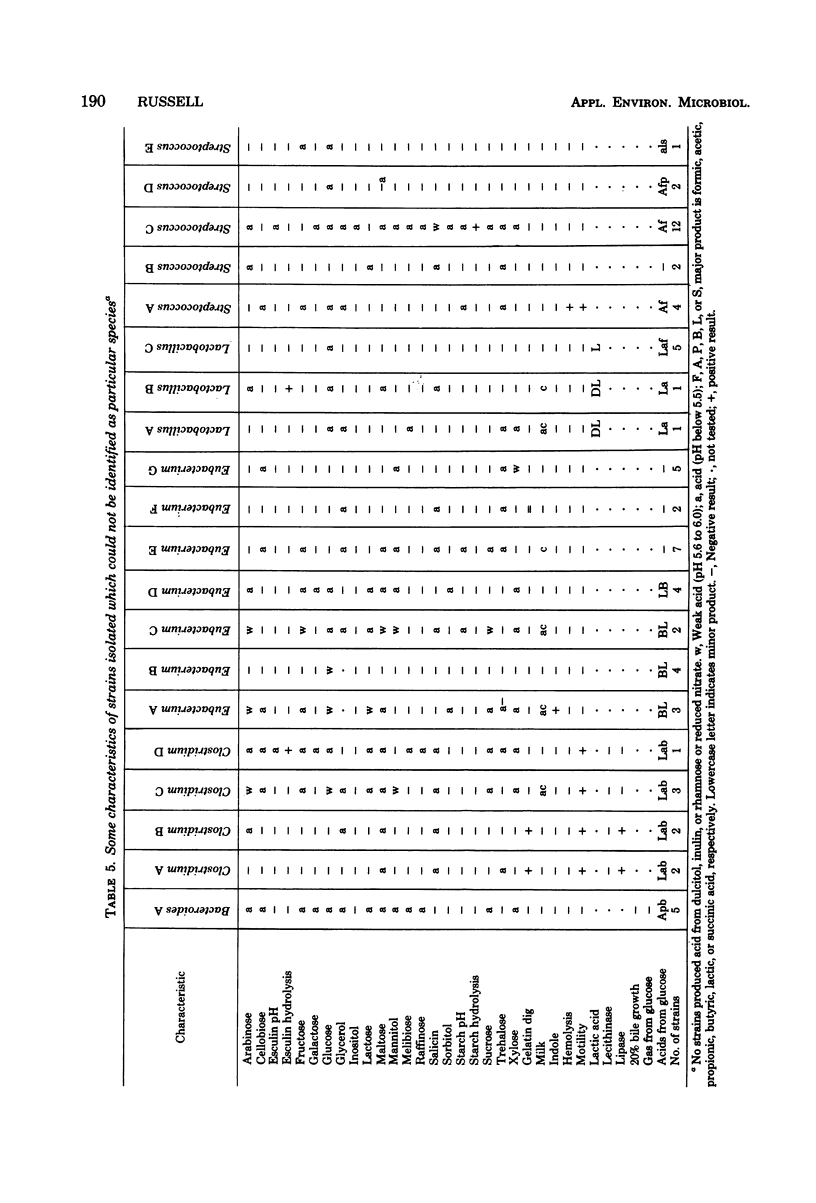
An examination was made of various sites along the length of the swine large intestine, using strictly anaerobic culture methods. Sites were separated by differential washing into fractions described as lumenal content, lumenal surface layer, and intestinal wall tissue. Direct microscopic clump counts averaged 13.3 × 1010 organisms per g (dry weight) of material in the lumenal content, 14.0 × 1010 in the surface layer, and 5.1 × 1010 in the intestinal wall tissue. Both direct microscopic counts and viable culture counts were higher from the lumenal content and surface layer than from the intestinal tissue at all sites sampled in the intestine. Cultural counts averaged 56.2% of the direct microscopic counts in lumenal content and surface layer and 20.2% in intestinal tissue. Over 90% of the bacteria isolated were gram positive and consisted mainly of gram-positive cocci, lactobacilli, eubacteria, and clostridia. Of 192 isolates recovered, only 124 could be assigned to recognized species.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aalbaek B. Gram-negative anaerobes in the intestinal flora of pigs. Acta Vet Scand. 1972;13(2):228–237. doi: 10.1186/BF03548576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arank A., Syed S. A., Kenney E. B., Freter R. Isolation of anaerobic bacteria from human gingiva and mouse cecum by means of a simplified glove box procedure. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Apr;17(4):568–576. doi: 10.1128/am.17.4.568-576.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attebery H. R., Sutter V. L., Finegold S. M. Effect of a partially chemically defined diet on normal human fecal flora. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1391–1398. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CATO E. P., MOORE W. E. A ROUTINE DETERMINATION OF THE OPTICALLY ACTIVE ISOMERS OF LACTIC ACID FOR BACTERIAL CLASSIFICATION. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Apr;11:319–324. doi: 10.1139/m65-039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranwell P. D. Microbial fermentation in the alimentary tract of the pig. Nutr Abstr Rev. 1968 Jul;38(3):721–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOS R., SCHAEDLER R. W., COSTELLO R., HOET P. INDIGENOUS, NORMAL, AND AUTOCHTHONOUS FLORA OF THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:67–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P., McAllister J. S., Savage D. C. Microbial colonization of the intestinal epithelium in suckling mice. Infect Immun. 1973 Apr;7(4):666–672. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.4.666-672.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. P. Preservation of gastrointestinal bacteria and their microenvironmental associations in rats by freezing. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):304–312. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.304-312.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decuypere J., Henderickx H. K., Vervaeke I. Influence of nutritional doses of virginiamycin and spiramycin on the quantitative and topographical composition of the gastro-intestinal flora of artificially reared piglets. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1973 Mar;223(2):348–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drasar B. S., Shiner M., McLeod G. M. Studies on the intestinal flora. I. The bacterial flora of the gastrointestinal tract in healthy and achlorhydric persons. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jan;56(1):71–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulghum R. S. Improved dispenser for use in preparing prereduced, anaerobically sterilized medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Aug;6(2):179–180. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.2.179-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giesecke D., Wiesmayr S., Ledinek M. Peptostreptococcus elsdenii from the caecum of pigs. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Nov;64(1):123–126. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-1-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilliland S. E., Speck M. L., Morgan C. G. Detection of Lactobacillus acidophilus in feces of humans, pigs, and chickens. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Oct;30(4):541–545. doi: 10.1128/am.30.4.541-545.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. H., Dubos R. The anaerobic bacterial flora of the mouse cecum. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):251–260. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb J. A., Dehority B. A. Variation in colony counts of total viable anaerobic rumen bacteria as influenced by media and cultural methods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Feb;31(2):262–267. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.2.262-267.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Glock R. D., Christensen C. R., Kinyon J. M. Inoculation of pigs with Treponema hyodysenteriae (new species) and reproduction f the disease. Vet Med Small Anim Clin. 1972 Jan;67(1):61–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser K. J., Zabransky R. J. Modification of the gas-liquid chromatography procedure and evaluation of a new column packing material for the identification of anaerobic bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jul;2(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jcm.2.1.1-7.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill I. R., Kenworthy R. Microbiology of pigs and their environment in relation to weaning. J Appl Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;33(2):299–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1970.tb02201.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdeman L. V., Good I. J., Moore W. E. Human fecal flora: variation in bacterial composition within individuals and a possible effect of emotional stress. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Mar;31(3):359–375. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.3.359-375.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A., Gordon J., Dubos R. Enumeration of the oxygen sensitive bacteria usually present in the intestine of healthy mice. Nature. 1968 Dec 14;220(5172):1137–1139. doi: 10.1038/2201137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. C., Simon J., Byerly C. S. The etiology of swine dysentery. III. The role of selected gram-negative obligate anaerobes. Vet Pathol. 1975;12(1):46–54. doi: 10.1177/030098587501200107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V. Human fecal flora: the normal flora of 20 Japanese-Hawaiians. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):961–979. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.961-979.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. P., Mata L. J. Bacterial flora associated with the human gastrointestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1970 Jan;58(1):56–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuru S., Osbaldiston G. W., Stowe E. C., Walker D. Fecal microflora of healthy cattle and pigs. Cornell Vet. 1972 Apr;62(2):242–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut A. G., Gorbach S. L., Nahas L., Weinstein L., Spanknebel G., Levitan R. Studies of intestinal microflora. 3. The microbial flora of human small intestinal mucosa and fluids. Gastroenterology. 1967 Dec;53(6):868–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall G. D., Wood A. J., Wescott R. B., Dommert A. R. Distribution of bacteria in feces of swine. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Nov;20(5):789–792. doi: 10.1128/am.20.5.789-792.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H. W., JONES J. E. OBSERVATIONS ON THE ALIMENTARY TRACT AND ITS BACTERIAL FLORA IN HEALTHY AND DISEASED PIGS. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1963 Oct;86:387–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salanitro J. P., Blake I. G., Muirhead P. A. Isolation and identification of fecal bacteria from adult swine. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Jan;33(1):79–84. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.1.79-84.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C., Dubos R., Schaedler R. W. The gastrointestinal epithelium and its autochthonous bacterial flora. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):67–76. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze F., Bathke W. Zur quantitativen Zusammensetzung der Magen-Darm-Flora beim Läuferschwein. Arch Exp Veterinarmed. 1977;31(2):161–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinkovics G. Therapeutic experiments and intestinal flora studies in swine dysentery. Zentralbl Veterinarmed B. 1974 Sep;21(9):706–714. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.1974.tb00546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada A., Uchida K., Mitsuoka T. Die Bacteroidaceenflora in den Faeces von Schweinen. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1976 Apr;234(3):362–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vervaeke I. J., Van Assche P. F. Occurrence of megasphaera elsdenii in faecal samples of young pigs. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig A. 1975;231(1-3):145–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vervaeke I. J., Van Nevel C. J. Comparison of three techniques for the total count of anaerobes from intestinal contents of pigs. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Sep;24(3):513–515. doi: 10.1128/am.24.3.513-515.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wren M. W., Eldon C. P., Dakin G. H. Novobiocin and the differentiation of peptococci and peptostreptococci. J Clin Pathol. 1977 Jul;30(7):620–622. doi: 10.1136/jcp.30.7.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



